
Objectives of the service
The objective of the feasibility study is to determine the technical feasibility and economic viability of a space aided ERTMS railway signalling system including positioning solutions using GNSS (in combination with other on board sensors) and wireless communications (satellite in combination with terrestrial communications).
Users and their needs
Potential users of Space Based Services for Railway Signalling are Infrastructure Managers and Railway Undertakings in Europe and worldwide. The study has identified the Community of European Railway and Infrastructure Companies (CER) and the ERTMS Users Group as reference users.
ERTMS solutions have been exported to several markets around the world (e.g. China, Australia and Brazil) thanks to the considerable benefits ERTMS can bring including: increased capacity, higher speeds, higher reliability rates, lower production costs, reduced maintenance costs, open supply market, reduced contract lead time, simplified approval process, and improved safety for passengers.
The typically high investment required for the implementation of the ERTMS standard constitutes an obstacle for the deployment of such a high safety standard in Regional Lines and Local Lines.
The drivers of main cost are:
- Equipment installation and maintenance costs of the trackside;
- Train signalling on-board equipment costs; and
- Costs related to standardized communication between the trackside and on-board.
Service/ system concept
The SBS-RailS Study investigated how and Satellite technologies (Satcom, SatNav) can be used within the ERTMS and its foreseen evolution.
In this context, the study has taken as input the Virtual Balise concept as conceived by the Next Generation Train Control (NGTC) project and the Future Railway Mobile Communications System as defined by the UIC (International Railway Union).
The concept of virtual balise detection using GNSS has been defined in order to minimize impacts on the existing ETCS.
The study additionally investigated Satcom solutions suitable for the introduction of future carrier independent telecommunication solutions as a replacement for GSM-R.
The introduction of satellite technology shall minimize the modification to the existing standard ERTMS/ETCS, shall guarantee interoperability with the existing specification and shall reduce the complexity of the commissioning and of the operational scenarios.
In the figure below, a general architecture of SBS-RailS ERTMS with GNSS architecture is illustrated. Blue boxes represent the existing ERTMS system, Orange boxes are the new elements introduced: The key elements are:
- TALS (Track-Area LDS Server), which represents the “Wayside and Augmentation Signalling Center” and whose main function is to provide GNSS augmentation information to the on-board.
- SBAS Augmentation and Local Augmentation represents the augmentation Sources (EGNOS in Europe, or a railway-adapted GBAS where no SBAS is available).
- The on-board receives information from the TALS using the existing safe communication channel between the trackside (RBC) and the on-board.
The Satcom solutions analysed has been assessed against the Future Railway Mobile Communication System User Requirements Specification.
All the solutions taken into account will be used in a multi-bearer environment taking into account the guidelines given by EUAR for the evolution of the railways radio communication system for operation and signalling.
In the figure below, a general architecture of SBS-RailS ERTMS with Satcom is illustrated.
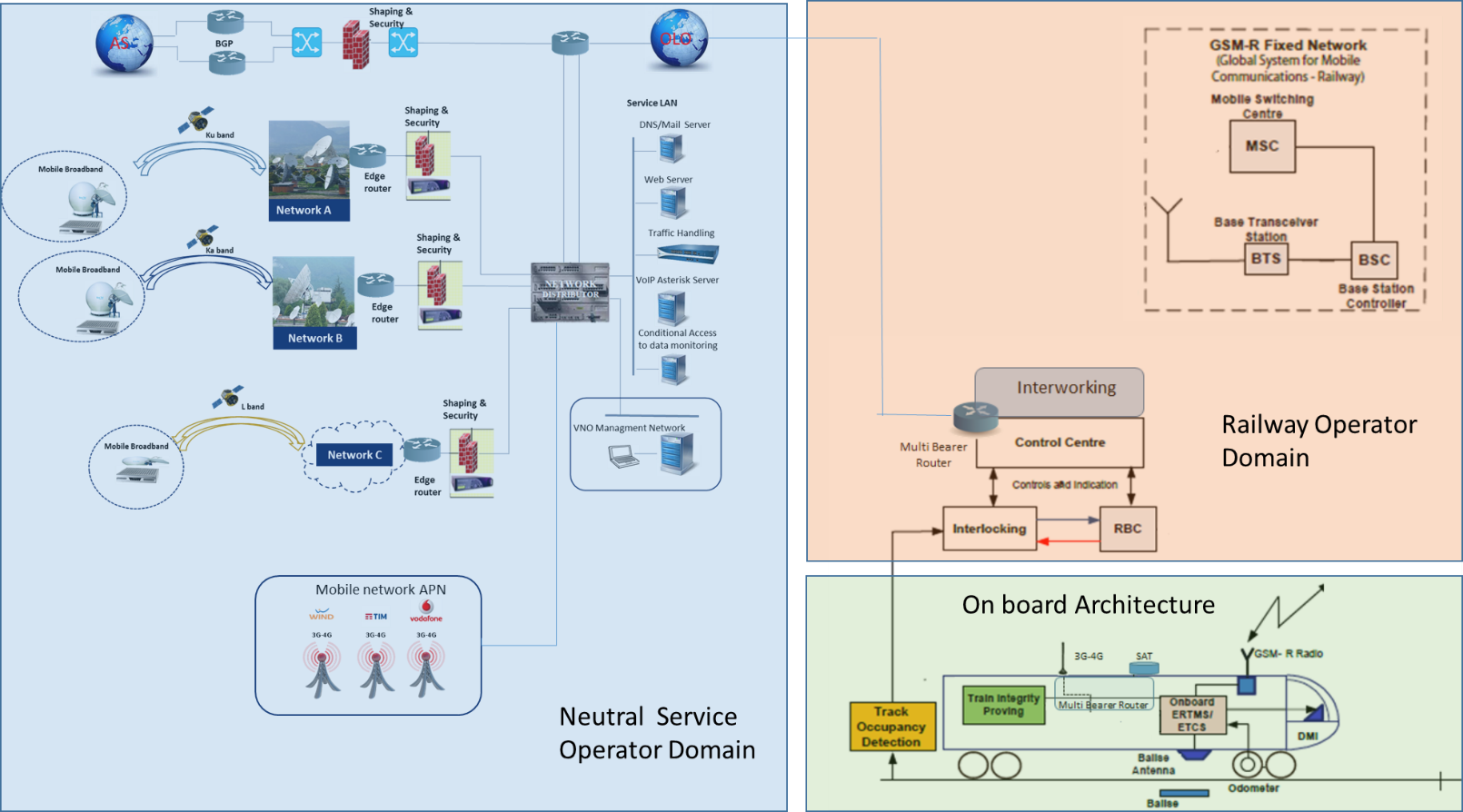
An important part of the SBS-RailS study has been the Proof-of-Concept, whose main objective aimed to further investigate critical issues through simulations and analysis before launching dedicated test campaigns, adopting the enhanced ERTMS solution based the Virtual Balise Reader.
In particular, the following elements have been studied:
- Characterization and modelling of multipath and RF interference effects on the on-board GNSS receiver;
- High level investigation of a EGNOS dedicated integrity concept for railway, assuming minimal/no change to EGNOS infrastructure; and
- Safety analysis to determine the magnitude of risk reduction that can be achieved using EGNOS with respect to hazards originating from the system.
The main outcomes of the PoC activities, performed using the high demanding GNSS test scenarios implemented:
- The injected RFI events did not reduce the performance of the enhanced ERTMS, not impacting on safety.
- The injected Multipath and RFI events perturbs the GNSS PVT performance. However, the combination of the virtual balise detection algorithm with odometry and on-board RAIM transforms these effects into PVT availability issues only, not having impact on safety.
The CBA investigated the economic convenience of the project solution from a public point of view in the long term.
The general methodological framework of the Cost-Benefit Analysis aimed to compare costs and benefits of alternative scenarios year by year with a discounted sum approach.
The baseline scenario implies the traditional ERTMS (with physical balises and GSM-R), while the project scenarios are multiple, all including virtual balises, but differentiated in terms of augmentation and TLC solution.
The alternative four solutions (project 1 …project 4) have been applied to the set of case studies (Local line and Regional line), represented by reference railway lines defined in the first part of the project and characterized by different trackside parameters and operating conditions. For each case study the best scenario is the Project scenario 3, that is the one envisaging the use of virtual balises for the localization of the train, EGNOS for GNSS augmentation and a multi-bearer solution for the telecommunication. The analysis highlighted that the EGNOS augmentation solution is more cost effective with respect to the railway dedicated solution and that the multi-bearer solution is more cost effective with respect to the GSM-R solution.
The additional “impact analyses” that have been carried out aimed to investigate the economic convenience from the point of view of specific stakeholders: Railways Infrastructure Managers and Railway Undertakings.
With some differences among scenarios and case studies, such analyses have shown that more relevant benefits (and a definite convenience) are accrued by IMs, whereas the RUs have a thinner business case. The best strategy would therefore be to set up benefit-sharing mechanisms (e.g. via the access charges) between the two types of operators, since the overall system has a long term convenience to implement the satellite based project solution.
The feasibility study:
- confirmed the preliminary ERTMS Enhanced functional architecture based on Virtual Balise as a good starting reference functional architecture;
- the enhancement of the ERTMS Radio Communication Network towards a multi-bearer solution has been confirmed as a valid solution;
- the preliminary performance analysis on EGNOS (carried out with RINEX field data recorded in Sardinia Trial Site) outlined the need of on-board RAIM complemented with hybridization (e.g. IMU) and other on-board defensive techniques to cope with on-board and local environment feared events;
- confirmed the need of a modelling & simulation environment to predict the railway system performances;
- highlighted that the EGNOS augmentation solution is more cost effective with respect to the railway dedicated solution and that the multi-bearer solution is more cost effective with respect to the GSM-R solution.
Space Added Value
The SBS Study targeted the scenario of local and regional lines in Europe. Approximately 50% of these railways are currently operated with different legacy solutions and lack in many cases the high safety standard achievable with the ERTMS.
The aim is to reduce cost (CAPEX and OPEX) of ETCS trackside by reducing the number of real balises installed along the track (reducing also exposure to theft and vandalism), and to find alternatives to terrestrial solutions for communications when terrestrial antenna deployment is not economically viable.
Current Status
The project has reached its completion and the project results and recommendations have been presented, on April 6th 2017 in ESTEC, to ERTMS Users Group, European Union Agency for Railways, Community of European Railway and Infrastructure Companies (CER), national Infrastructure Managers representatives (Italian RFI and Swedish Trafikverket).
Prime Contractor(s)
Subcontractor(s)







