***CLOSING DATE EXTENDED TO 26 JANUARY 2024***
This call is part of the umbrella of “Space for Infrastructure” thematic call for proposals.
The second thematic area, Energy infrastructure, refers to the physical structures and networks that are used to transport and store energy. This includes:
- Power plants
- Transmission lines
- Pipelines
- Energy storage facilities
- Other related infrastructure.
These structures are essential for the efficient and reliable delivery of energy to consumers. The interconnection of geographically-dispersed energy assets is a key requirement for sustaining the uptake of renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar energy. The infrastructure must be designed, installed and operated in a safe, dependable and efficient manner. It also must be able to:
- Manage the increasing and variable demand for energy
- Adapt to changing energy sources and technologies.
How can space technology help?
Satellite imagery can be used to monitor energy infrastructure, such as power lines, pipelines, and oil and gas wells. This can help to detect and prevent potential structural problems before they occur. Additionally, satellite-based sensors can be used to measure energy consumption in remote areas, allowing for more efficient energy management. Uncrewed solutions including robots and drones hold an enormous potential to improve efficiency and reduce human risks during installation and operation of (renewable) energy plants in remote areas, as well as during the decommissioning phase.
Safety and protection of critical energy infrastructure has gained significant momentum and requires a combination of in-situ sensors and large-scale observation tools to ensure continuous and reliable monitoring. Assets include:
- Generation (power plant)
- Transmission
- Distribution (e.g. energy networks, underwater offshore cables)
Finally, energy security is becoming increasingly important for nations looking to secure their energy futures. This can be achieved through the deployment of new energy generation infrastructure, whether this be through deploying new renewable energy infrastructure or scouting for new renewable energy, oil or gas sites.
Value of Space
Satellite technology and data have a significant part to play in the development of potential services:
Satellite Communications (SatCom) enables the provision of ubiquitous connectivity to enhance the communication links, connectivity of IoT devices and support for remote locations. In addition, satellite communications can provide real-time, long-range communications with infrastructure monitoring systems (i.e. UAVs/robots/remote assets). Example applications include and are not limited to:
- Ensuring a secure and constant communication service to monitor assets along with maintenance and emergency personnel during emergency situations
- Communication of infrastructure grid IoT devices in remote locations
- Communication to maintenance related UAVs
Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) can be used to enable geo-referencing of in-situ data, as well as navigation and tracking of vehicles, people and goods (PNT). GNSS-based technologies can be used for time-stamping reference system information, ensuring the traceability of the data. For example, GNSS allows the tracking and navigation of uncrewed vehicles and can facilitate the automation of infrastructure maintenance through robotics or UAVs. Example applications include and are not limited to:
- Navigation of autonomous infrastructure maintenance vehicles. E.g. Drones/robots
- Geo-fencing assets and vehicles
- Maintenance data validation
- Sensitive goods tracking e.g. air turbine blades
Satellite Earth Observation (satEO) (including next-generation nano satellite and CubeSat networks) can be used in multiple ways including:
- Monitoring of the status of the working sites
- Planning, construction and maintenance of the infrastructure
- Collecting information on geographical and environmental parameters for the sustainability analysis
- Integration of environmental data
- Identification of patterns and trends that may be linked to infrastructure safety risks, and insights into how to best address them.
Example applications include and are not limited to:
- Validation of digital twin models
- Scouting of new energy generation sites
- Monitoring of electricity grids over a large area
What We Are Looking For
We look for teams that have identified an attractive market opportunity with real potential to engage customers. Motivation, business experience and domain expertise are all important features. We want to hear about your ideas involving the utilisation of either space technology or space data.
In particular we are looking for those opportunities with the potential to become market disruptors to the energy infrastructure markets and with a high level of innovation.
About The Opportunity
ESA will support Feasibility Studies and Demonstration Projects under this ‘Announcement of Opportunities’:
- Feasibility Studies allow successful teams to analyse, design and plan their intended service
- Demonstration Projects allow successful teams to put their intended service into practice. Teams will test their service in the market by running a pilot with significant users and, by the end of the project, the service should be operational.
How To Apply
- Register your team on esa star Registration (https://esastar-emr.sso.esa.int) today. If your team is made up of more than one company or organisation, each entity will need to register.
- Scroll down to the ‘Downloads’ section of this webpage to download all the official documents. Official documents include a document explaining the scope of this opportunity and the past two webinars hosted by ESA.
- Download the Activity Pitch Questionnaire template and submit your pitch as instructed in the Activity Pitch Questionnaire guidelines, through the online form.
- ESA will evaluate your pitch. Teams whose pitches are positively evaluated will be invited to prepare an Outline Proposal and then a Full Proposal. Teams must obtain a Letter of Authorisation from their respective National Delegation before submitting a Full Proposal. Contact details of all National Delegates can be found here: National Delegation(s).
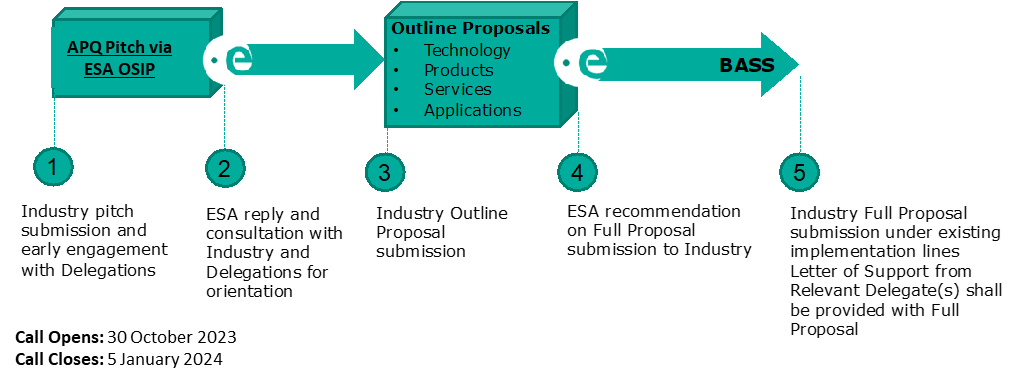
Authorisation Of Funding
For this call, companies residing in the following Member States will be eligible to apply: Austria, Belgium, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Lithuania, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovenia, Sweden, Switzerland and the United Kingdom.
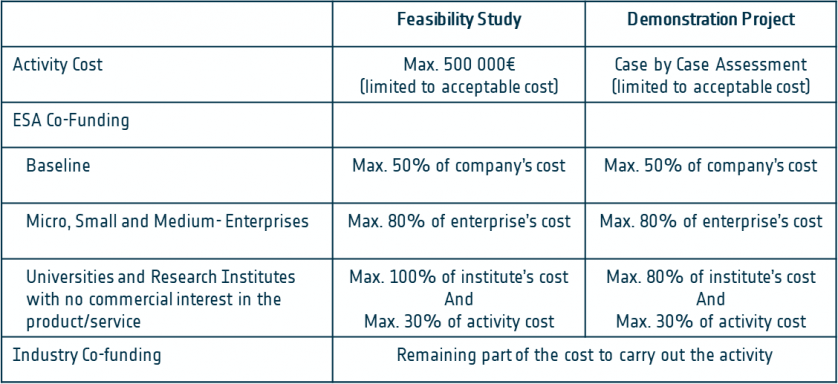
Funding Scheme
Funded participation is open to any company and/or organisation, be it as group of users, public body or non-governmental organisation, residing in any of the ESA Member States that are participating to the programme as specified in the Letter of Invitation in esa-star.
The applicable funding level of the individual prime- or subcontractors is subject to authorisation by the involved National Delegation(s). Therefore bidding teams are requested to obtain a Letter of Authorisation from all their national delegations before submitting a Full Proposal.
The funding level is summarised in the table below:
LinkedIn Contact Details For Key People
Jonathan Crabb: https://www.linkedin.com/in/dr-jonathan-crabb-8157a777/
Beatrice Barresi: https://www.linkedin.com/in/beatrice-barresi-920a8332/
Davide Coppola: https://www.linkedin.com/in/davide-coppola-75b99b23/
Webinar
A webinar is scheduled for 18 October 2023. Please use the register button at the top of this page to sign up for it.
- External speaker: Sebastian Schäfer from E.On Group Innovation GmbH
- External speaker: Mark McGranaghan from EPRI
- External speaker: Ricardo Almeida Henriques from E-REDES



