A pioneering climate insurance system, developed in association with ESA’s Business Applications and Space Solutions (BASS) programme, is transforming the livelihoods of farmers across the developing world. Created by Luxembourg insurtech company IBISA, the index-based solution uses satellite data to provide accurate and affordable insurance to cover farmers against climate-related risks.
The challenges presented by climate change are considerable, and no more so than for smallholder farmers in developing countries, where livelihoods are heavily dependent on the whims of the weather. Adverse weather events significantly impact farmers and associated businesses, leading to diminished or even lost harvests with consequential financial distress, and often require time-consuming and resource-heavy physical loss assessments. Insurance models have traditionally fallen short in providing precise, transparent and fair coverage for these vulnerable farming communities — until now.
Through the ESA BASS Demonstration Project, IBISA set out to develop an end-to-end index-based insurance platform using satellite data to monitor critical weather parameters such as rainfall, wind speed, and temperature, in-situ measurements and bespoke risk modelling software to create informed and realistic insurance policies. This cost-efficient and scalable approach eliminates the need for traditional physical assessments, offering farming communities unequivocal protection against climate risks and ensuring their financial stability. These benefits extend across the wider ecosystem, offering added security to input dealers, food companies and financial institutions.
IBISA firstly presented a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) to assess customer needs and demands, running a field-test with DHAN Foundation, a non-governmental organisation in India. A series of further successful programmes in India, the Philippines and Senegal validated the IBISA solution across diverse conditions, such as drought and excess rain, and affirmed the real-world utility of the service. IBISA continued to improve its offering, while converting pilot users into commercial clients.
“This project, made possible through our collaboration with the European Space Agency, has truly been a catalyst, bolstering our technological and commercial capabilities,” said Maria Mateo Ibora, Founder and CEO at IBISA. “As we look ahead, we see a landscape rich with opportunity, and IBISA is ready to rise to the challenge.”
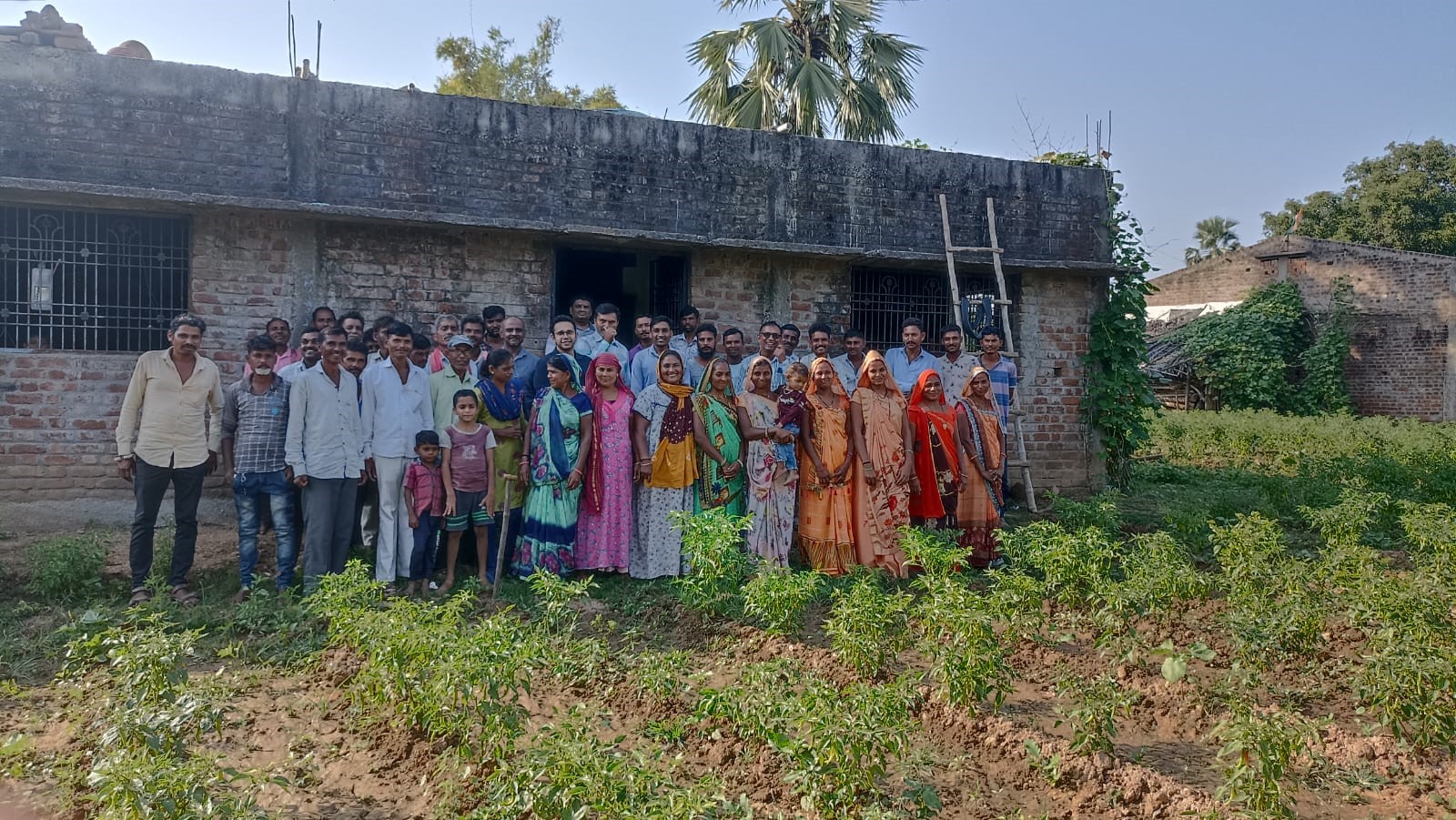

IBISA has now secured contracts with each of its pilot users, including the DHAN Foundation, CLIMBS Cooperative in the Philippines and CNAAS in Senegal. A pilot with dairy cooperative MILMA in Kerala, India, resulted in more than 14,000 farmer enrolments in a week, and a collaboration with Indian AgriTech firm Nurture Farm expanded IBISA’s reach into 77 new districts, home to millions of smallholder farmers. IBISA’s solution is already providing insurance services to more than 200,000 policy holders across these three countries, generating widespread tangible impact.
Gaelle Jimenez, National Delegate for ESA BASS at Luxembourg Space Agency (LSA), said “IBISA is a very good example of how space can help tackle the consequences of climate change and benefit Earth-based activities. LSA is proud to have supported this initiative in its first steps and eager to see IBISA thrive in its mission.”
Beatrice Barresi, Technical Officer at ESA, said “We are very pleased to have supported IBISA and to witness the progress made during its implementation. We are excited by the potential IBISA’s solution has demonstrated and we look forward to seeing it continue to support small communities around the world, combating the impacts of climate change.”
Facilitated by ESA’s expertise and space-based technology, IBISA’s offering and client base continue to expand and evolve, fostering a new era of agricultural resilience, protecting the livelihoods of farmers across the world, and paving the way for a more sustainable future.



