Hot on the heels of the worst bushfires in Australia for a decade, ESA BIC Bavaria alumnus OroraTech has launched a new wildfire management tool using global satellite data, enabling fires to be identified remotely and fire management teams to react quickly.

The 2019 bushfire season in South Australia was the most devastating in the last decade. Not only were animal populations and their ecosystems destroyed in the fires, but the air quality and local weather conditions were greatly altered, including a sharp rise in CO2 levels. The Government scrambled to make decisions when it came to fire management and exhausted first responder resources, incurring millions of dollars of extra costs.
One potential aid for the future – in Australia and elsewhere – has been launched by Munich start-up OroraTech. Founded in 2018, the company specialises in early wildfire detection and monitoring from space using existing satellite data and advanced wildfire algorithms.
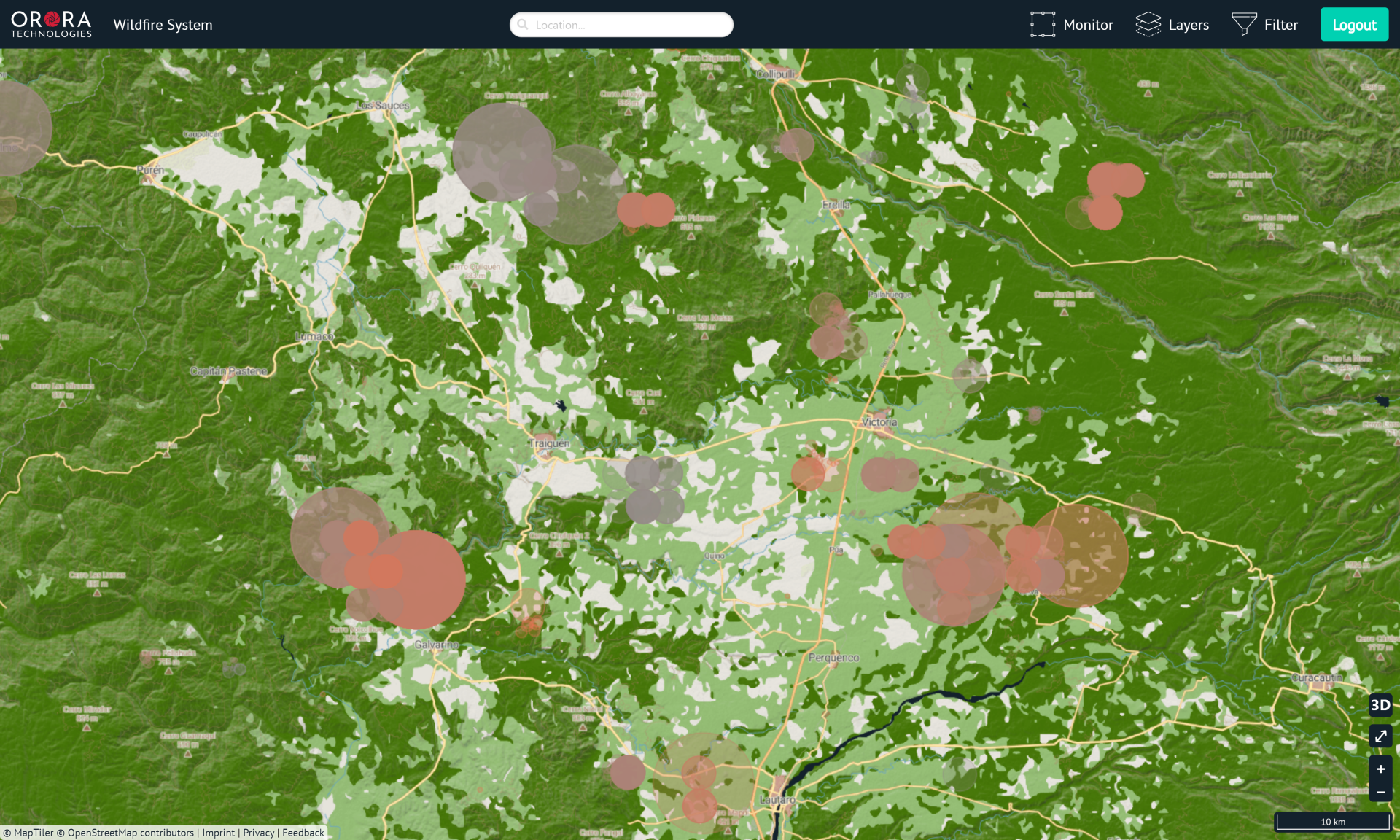
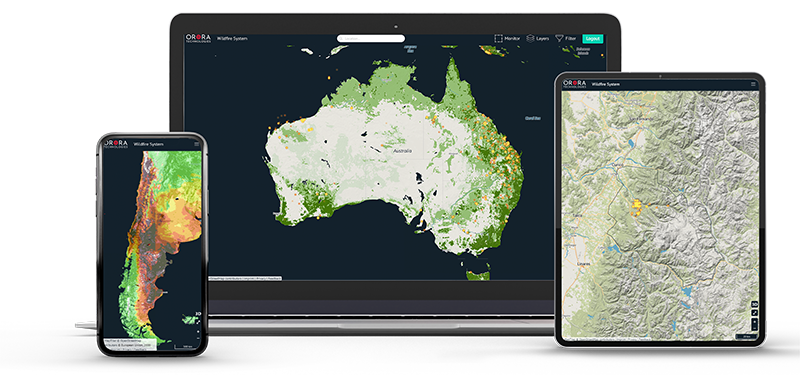
OroraTech recently released the first early access version of its wildfire monitoring system that provides notifications of potential wildfires in a user’s area. Features include visualisation of a fire's propagation, satellite overpass projections and tools for scientific hotspot analysis. The system also provides numerous map layers, such as fire danger and fuel maps that are updated daily to incorporate the latest weather forecast.
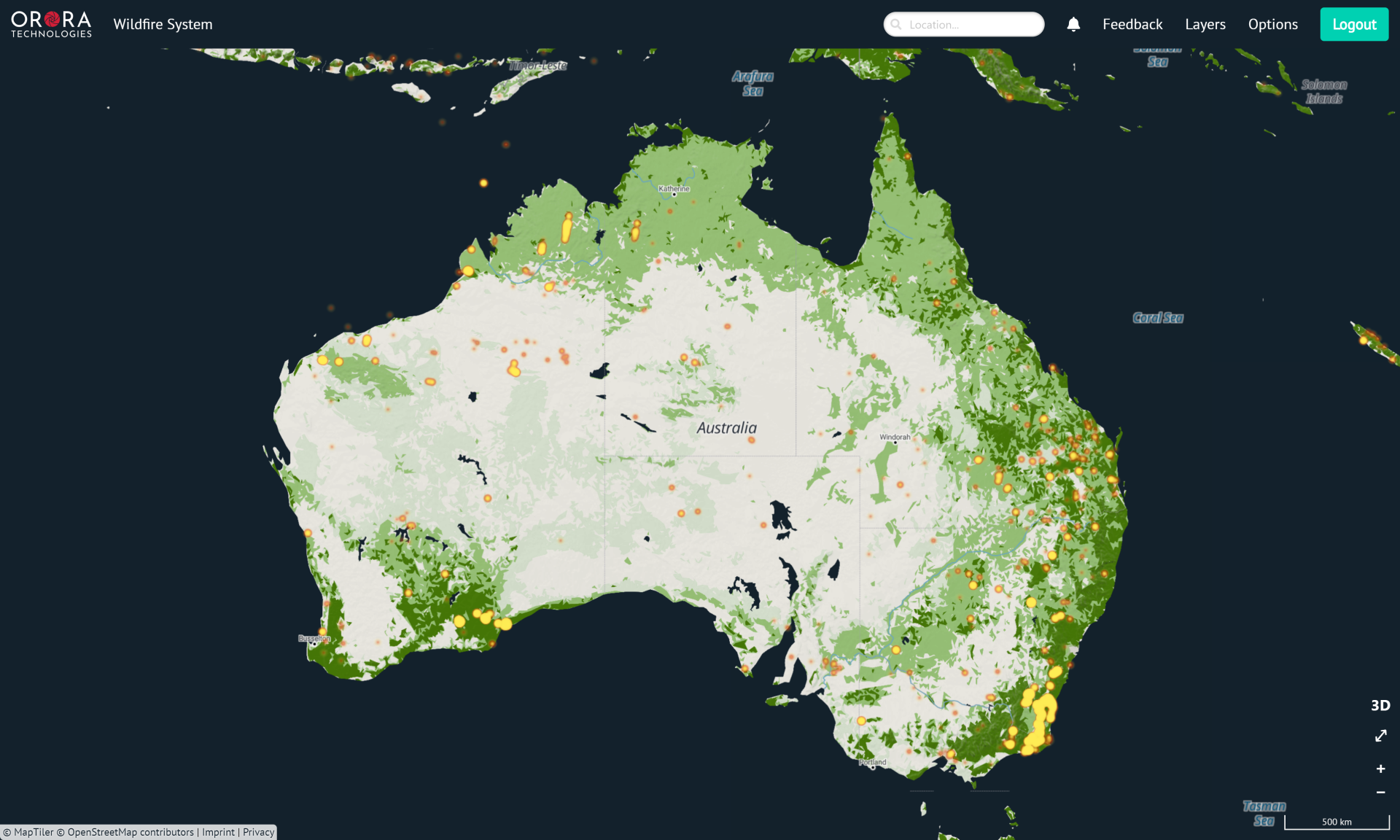
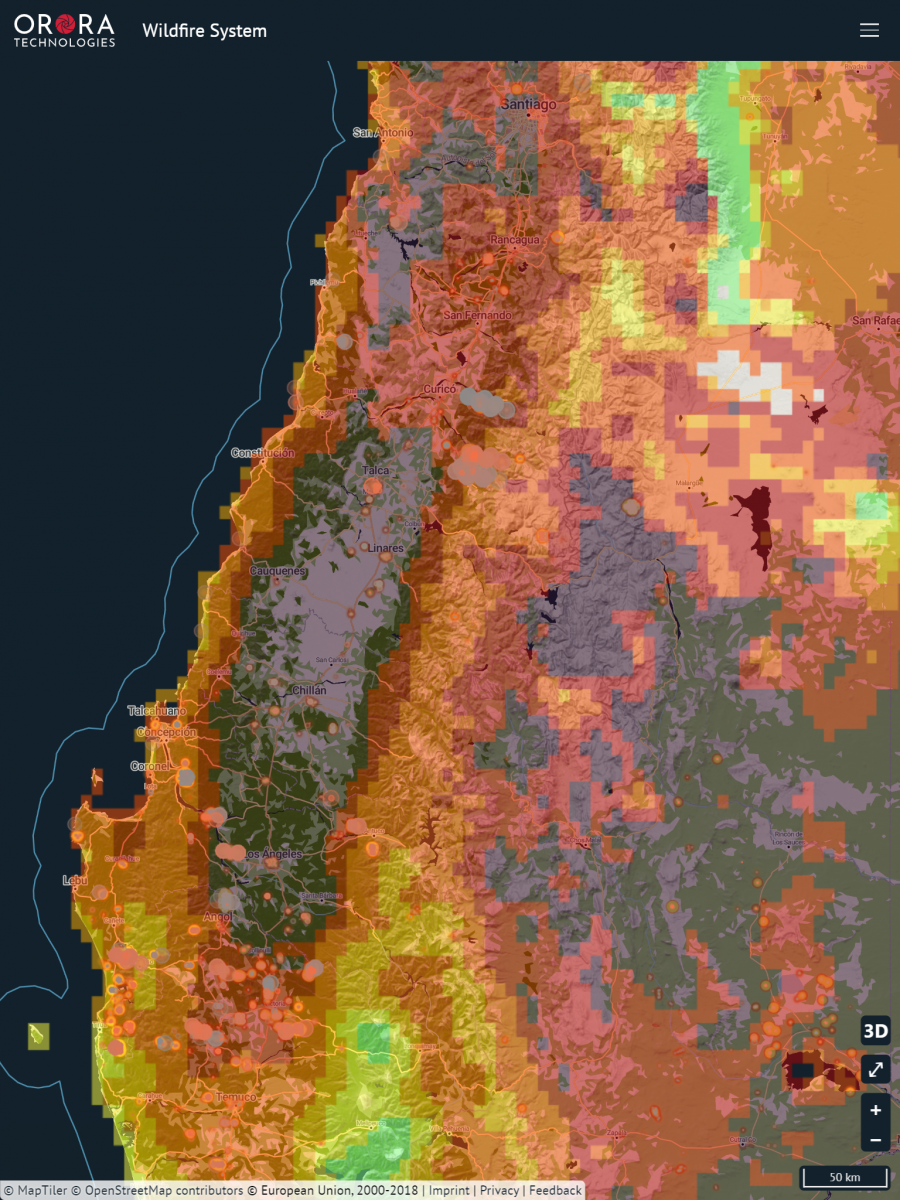
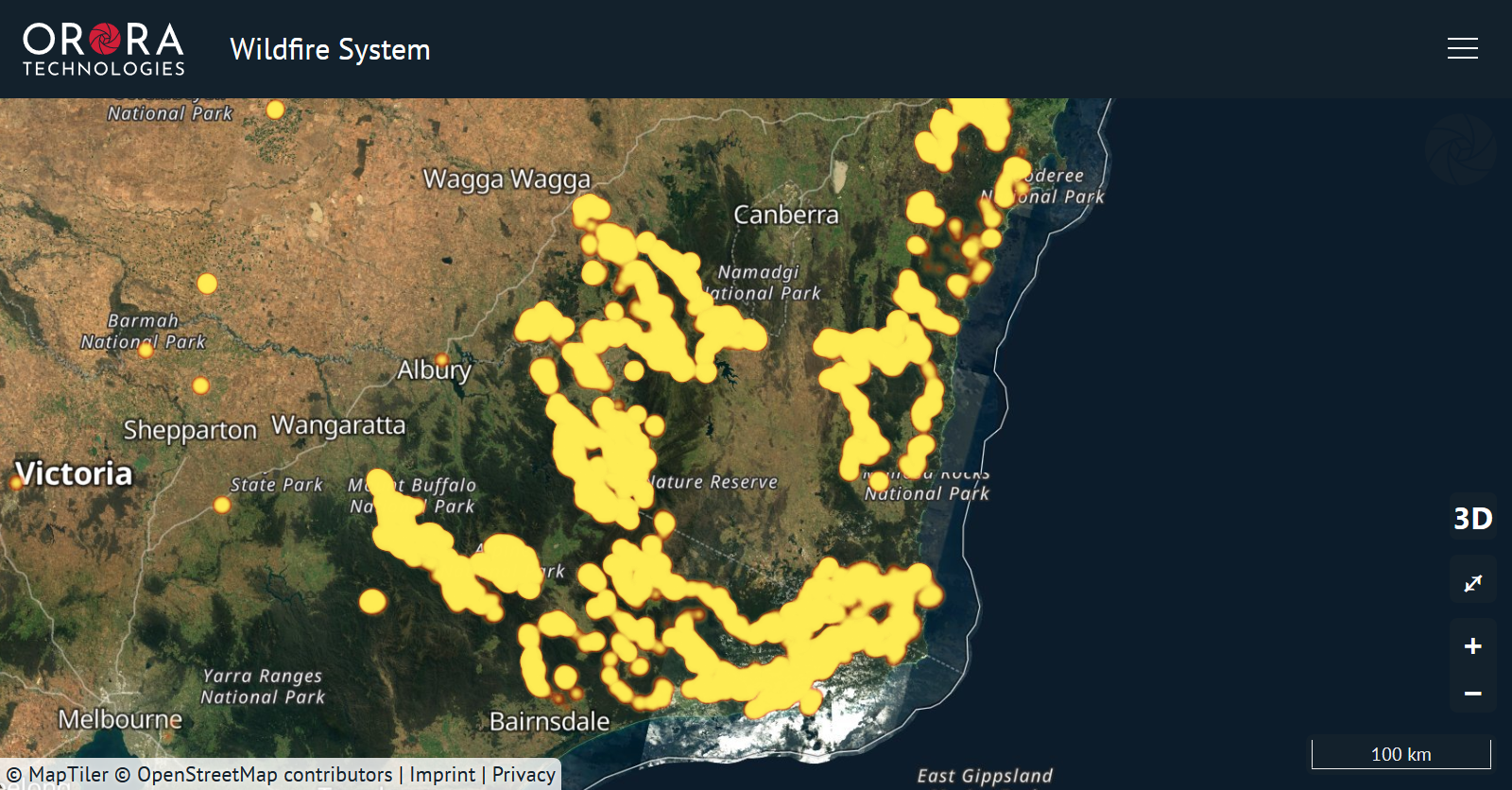
Global satellite data fuels all-in-one fire management tool
OroraTech's wildfire system stands out from its competitors by combining a large amount of data from several satellites, including ones from ESA, NASA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and EUMETCast, and through the subsequent analysis and presentation.
The vision behind the system's creation was to help reduce CO2 emissions, conserve nature, and protect lives and infrastructure.
OroraTech's customers in forest services and commercial forestry have confirmed the system offers a faster update rate that has helped them spot fires remotely.
“We are making a real difference in the rising global wildfire challenges with an all-in-one system that enables the fastest detection of wildfires on a global scale,” said OroraTech Lead Engineer and Co-founder Rupert Amann.
'Eyes in the sky' set to replace 'boots on the ground'
With the effects of rising temperatures and longer dry seasons, wildfires are likely to become larger and burn longer in areas that do not have the capacity to maintain an early fire management and execution plan. This means fire management developers are searching for alternative resources for early detection, rather than only relying on watchtowers and boots on the ground.
The satellite images in the OroraTech system, provided by the Copernicus Programme, enable users to monitor fires from a different perspective.
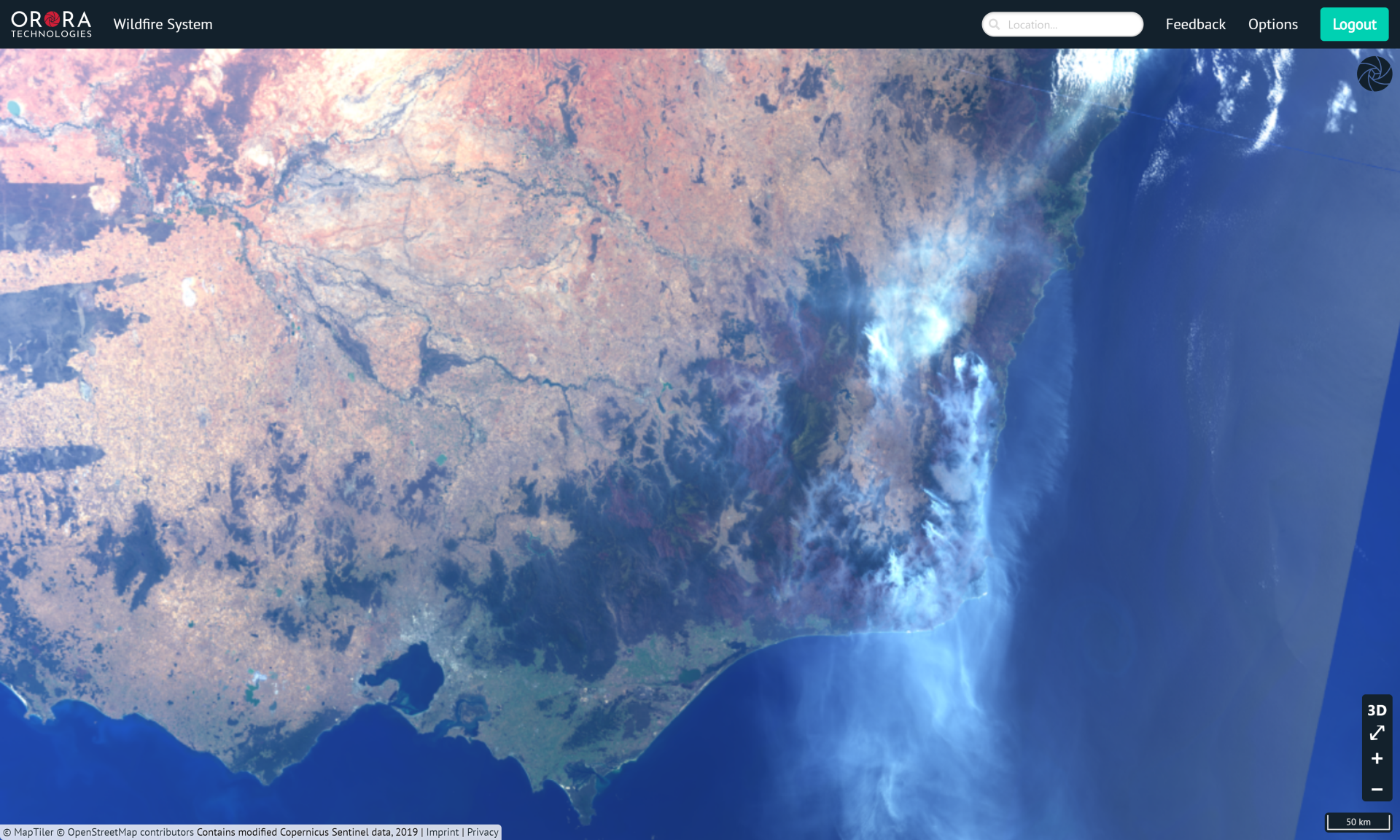
Multiple satellite sources provide the extensive data for the wildfire system, allowing customers to react before a fire becomes uncontrollable. The data is quickly processed through a cloud-based processing framework and is then accessible through a wildfire API and an innovative web-based interface. This combination results in a system that offers customers and researchers an advanced tool for fire analytics.
The OroraTech system with all premium features is currently available for a free trial period, accessible at OroraTech.
ESA BIC Bavaria
ESA Business Incubation Centre (BIC) in Bavaria promotes companies with disruptive products and digital businesses in areas like robotics, mobile, mobility, automotive, aviation and satellites. Since 2004, ESA BIC Bavaria, managed by Anwendungszentrum GmbH Oberpfaffenhofen (AZO), has supported more than 165 start-ups with an annual turnover of around €150 million (2018), creating more than 2,800 high-tech jobs in Bavaria and attracting over €50 million in venture capital (2018). For more information, see www.esa-bic.de.


