Objectives of the service
ABSeaD targets the sustainable management of Posidonia Oceanica seagrass beds, crucial for marine biodiversity and carbon sequestration. This service aids local fisheries and marine research institutions in making informed, eco-friendly decisions. It provides plugins and APIs for data analysis, crucial for conserving marine ecosystems and promoting sustainable fishing. Additionally, it supports participation in the Voluntary Blue Carbon Market by offering precise carbon sequestration data. The project's main goal is to blend technological innovation with marine conservation, thereby enhancing biodiversity protection, sustainable aquaculture, and global carbon reduction efforts.
Users and their needs
The ABSeaD service is designed for three primary user communities:
-
Local Fisheries:
-
Need for sustainable fishing methods to preserve marine life and ensure long-term industry health.
-
Challenges include integrating eco-friendly practices while maintaining economic sustainability.
-
-
Marine Research Institutions:
-
Require detailed, reliable data on marine ecosystems, particularly Posidonia Oceanica seagrass beds.
-
Challenge in accessing up-to-date, accurate environmental data for effective conservation and research.
-
-
Participants in the Voluntary Blue Carbon Market:
-
Need for verified data on carbon sequestration in marine environments to participate in carbon credit trading.
-
Challenges include obtaining credible and quantifiable data to support carbon offset initiatives.
-
Service/ system concept
The ABSeaD service offers a diverse range of information to its users:
-
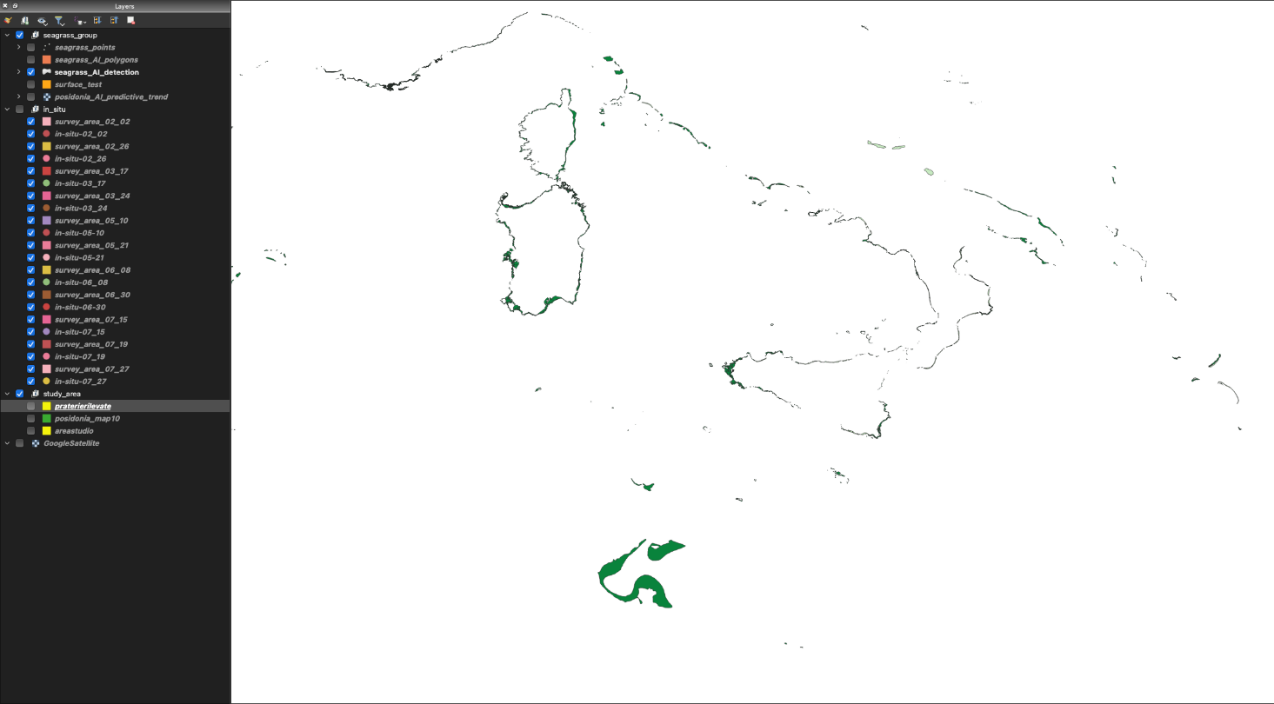
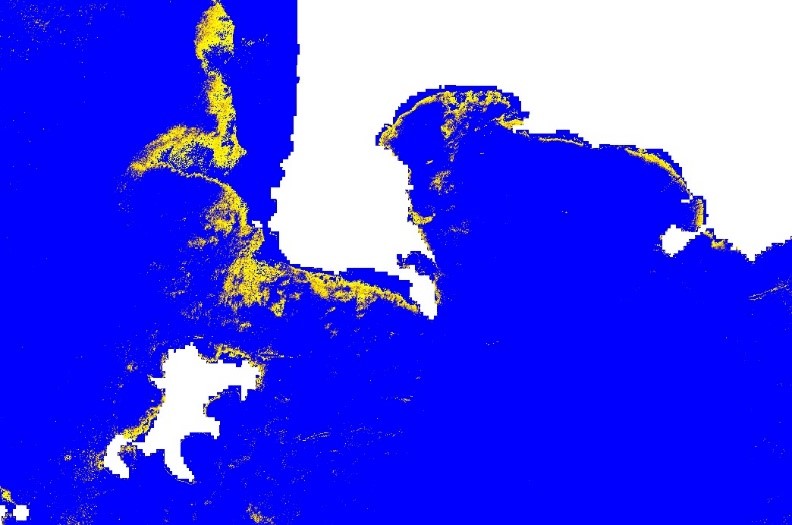
Environmental Data Analysis: Users are provided with comprehensive insights into the condition and well-being of Posidonia Oceanica seagrass beds, which are crucial for marine biodiversity. This encompasses data regarding seagrass coverage, health, and carbon sequestration capacity.
-
Seafood Traceability: Users have the capability to trace the seafood supply chain for locally sourced fisheries that embrace our software.
ABSeaD operates by combining satellite imagery and ground data to analyse marine habitats. This data is processed through machine learning algorithms, making it accessible and actionable. Users interact with this information via a user-friendly interface, e-commerce plugins, or APIs.
The system architecture comprises three layers to support a web platform in terms of user interaction, data preprocessing and analysis, data storage. This structure ensures ABSeaD is both effective in analysis and accessible to users.
Space Added Value
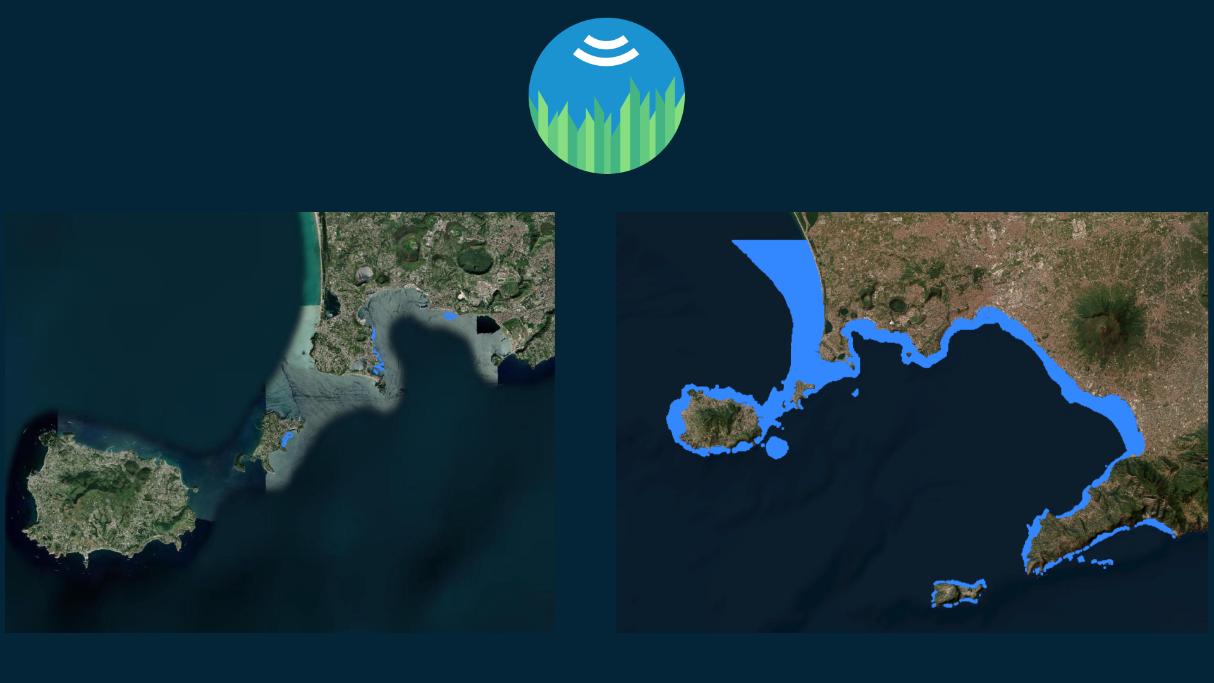
The ABSeaD system leverages space assets, primarily utilizing Earth Observation data, to monitor marine ecosystems. Multispectral and hyperspectral imagery, crucial for the detailed analysis of marine environments, have been particularly used for detection of Posidonia Oceanica seagrass beds.
The use of Earth Observation satellite data offers a key added value compared to traditional methods. These space assets enable extensive area coverage and consistent data collection over time, allowing for comprehensive and ongoing monitoring of marine habitats. This is a considerable improvement over ground-based methods, which are often limited in scope and frequency.
Current Status
The activity is being successfully concluded. Requirements were captured from the potential customer groups and were implemented in the design of the system architecture.
The prototype of the system has successfully integrated satellite data into its machine learning models. This integration has enabled the preliminary monitoring of Posidonia Oceanica seagrass beds in targeted Mediterranean regions.
Currently, the project team is refining the data processing algorithms to enhance the accuracy of biomass monitoring. This involves extensive testing and calibration using the acquired satellite data. Additionally, efforts are underway to improve the system's user interface for better accessibility and ease of use. However, the system has encountered limitations, particularly in correlating satellite data with Blue Carbon estimates. This limitation affects the accuracy of carbon sequestration estimates in seagrass meadows, thus impacting the overall effectiveness of the system in this specific area of analysis.
Also, a business analysis was successfully conducted to demonstrate how the proposed solution is commercially viable.
In the upcoming phase, ABSeaD will expand its geographical scope, aiming to include additional marine areas for monitoring. The team is also preparing to conduct a series of field validations to compare satellite data insights with in-situ observations, ensuring the reliability and accuracy of the system's outputs.