
Objectives of the service
Nature-based solutions projects are essential for sustainable development practices that monitor and reduce carbon emissions in line with global net-zero goals. Obtaining accurate data related to carbon emissions in nature-based solutions can be particularly challenging because it requires field visits, leading to issues of low reactivity, partial measurements, and low scalability.
To combat these problems, Kayrros Biomass Watch enables project developers to reduce financial and reputation risks with independent environmental metrics based on transparent and standardized remote sensing data. By using our platform, forestry carbon offset project developers can more accurately assess the effectiveness of their projects in reducing carbon emissions, demonstrating the quality of their work to final buyers.
This Feasibility Study proves the scalability of Kayrros methodology for biomass measurements at the global level, whatever the biome (from temperate to tropical forests and drylands).
Users and their needs
The key customers / customer segments targeted by this service are:
-
Carbon project developers: companies that identify areas suitable for reforestation and/or forest protection, carry out activities to sequester and/or reduce carbon emissions, and issue credits based on the success of those activities.
-
Carbon credit brokers: companies that invest in projects on behalf of their customers, by building and managing credit portfolios.
-
Governments: public institutions in charge of drafting and implementing targeted mitigation strategies.
-
International bodies and Agreements: multilateral organizations in charge of monitoring and enforcing global climate agreements.
-
Carbon credit final buyers: companies that purchase credits to offset their carbon footprint and burnish their corporate brand.
Service/ system concept
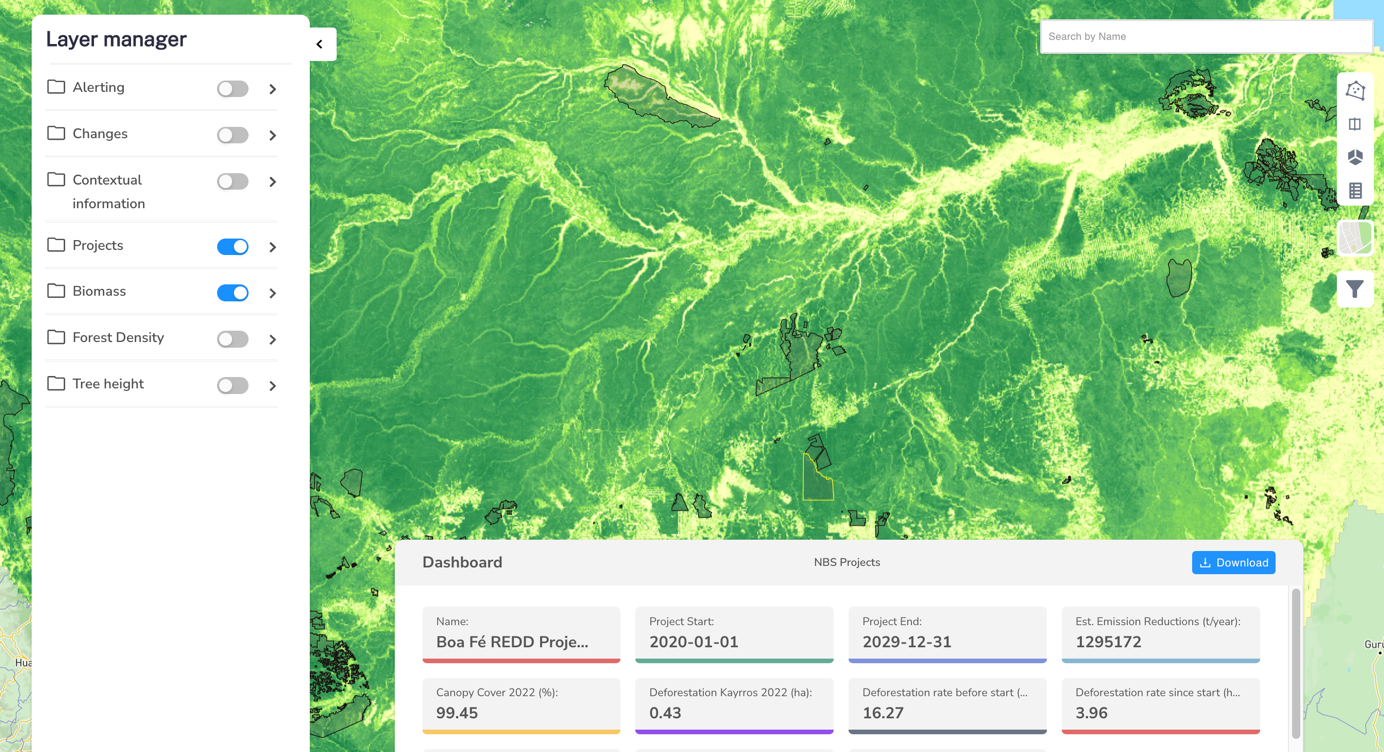
The product organizes around a map of 10-m resolution of forest biomass for the main biomes currently invested by the voluntary carbon market.
-
Carbon stock mapping: Get access to carbon stock maps with global coverage and high 10-m resolution.
-
Degradation monitoring: Kayrros tracks forest degradation beyond clear-cut deforestation.
-
Historical data analysis: Accelerate project origination with historical data on canopy cover and deforestation.
Space Added Value
The Space data used are Sentinel-2 (L2A) and Sentinel-1 (GRD) imagery.
Global coverage of the space data: it allows building the data product at the global scale.
-
High-frequency space data (3 days for Sentinel-2, 6 to 12 days for Sentinel-1): it allows to build the wall-to-wall data products with a yearly revisit even for regions with high cloud cover (tropical)
-
High-resolution space data (10m): it allows building data products at high resolution and with good accuracy.
-
The high resolution, global coverage and yearly revisit allow new analysis on forests for the business: fine-scale biomass loss and gain, attribution of changes, and consistent comparison of forests across the globe.
Biomass Watch is a step forward compared to traditional methods relying on field inventories, which are expensive and do not allow for a robust monitoring methodology at scale. It also positions as a unique combination of fine resolution (10m, the standard for project-level analysis) and scale, with regional maps allowing for jurisdictional analysis and standardized project benchmarking.
Current Status
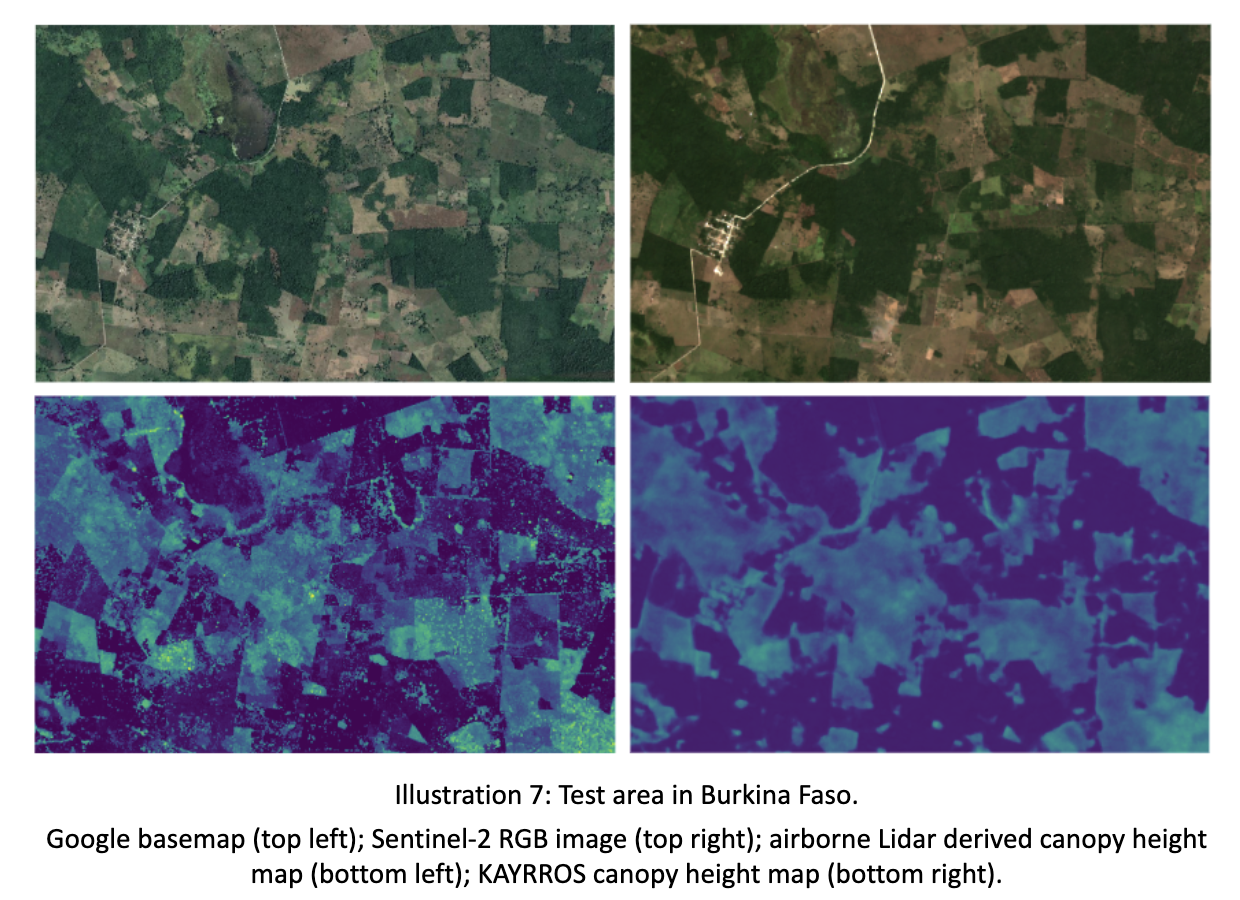

The results indicate a successful outcome with all main criteria met. The study validated customer desirability and commercial viability, including by confirming potential price points. However, most of the focus was put on the validation of technical capabilities, as the capacity of a canopy height model initially trained in a temperate forest to accurately scale to different and more complex biomes had to be demonstrated.
On the measurement accuracy front, our canopy height models demonstrate strong performance, with the best results in temperate forests (22% mean absolute percentage error) and reasonably acceptable errors in more challenging dry forest environments (up to 33% MAPE in the worst cases analyzed). For biomass mapping, results were very encouraging, with 15% MAPE in the Amazon and 24% in the worst-case scenario (Mexico) compared to ground truth plots. Critically, we have also validated our ability to successfully scale localized models to broader regional levels while maintaining fidelity.



