Objectives of the service
Rain has a significant influence on the global economy. It has impacts on different disciplines such as energy supply, transportation and critical infrastructure, management of food and water resources. Rain is highly variable spatially and temporally, making it very difficult to measure satisfactorily. Therefore, dense measurement networks are required in order to capture this variability.
CERASAT is an innovative solution for this purpose that can complement existing approaches. The main idea of CERASAT is to extract rainfall information from the signalling data generated in Satellite Communication Network by employing advanced machine learning and signal processing techniques. There are more than 300,000 satellite ground terminals across Europe and 2 million worldwide; these terminals can be transformed into reliable and real time rainfall measurement sensors. The signalling data is already aggregated into a central database, eliminating the need to create an elaborate network to feedback such sensor data. Further, a single GEO satellite can provide coverage to regions as large as whole Europe. Thus, the proposed solution is an efficient complement to existing rainfall measurement methods in terms of accuracy and CAPEX/ OPEX. CERASAT may also be used in order to enhance accuracy of current solutions such as rain radar.
Users and their needs
Heavy rainfall influences the insurance business in multiple ways: river and flash floods, damage to buildings and infrastructure. The success of this business heavily relies on the accurate evaluation and estimation of the risks for premium calculation. Without accurate data, the risk evaluation might be wrong and premiums might be low to cover potential damages. For instance, an extreme rainfall caused deadly flood events in Germany and France in summer of 2016. Insurance claims linked to these events in Germany were estimated to reach about €1.2 billion.
Today insurance industry uses flood risk maps for the estimation of flood impact. These risk maps are focussing on rivers or water-bodies only. Insurance companies would be able to reduce the losses caused due to wrong risk calculation by developing dedicated evaluation measures for flash flood, as they are different from river flood. Flash floods are result of extreme rainfall events and can occur at any time and place. Therefore, accurate and timely determination of rainfall data is necessary and helpful when examining flood related damage claims.
In this activity, we collaborated with RSS-Hydro company with expertise in flood hydrology. We investigated possibility of providing real–time flash flood risk map for Luxembourg using rainfall data from CERASAT.
Luxembourg
Service/ system concept
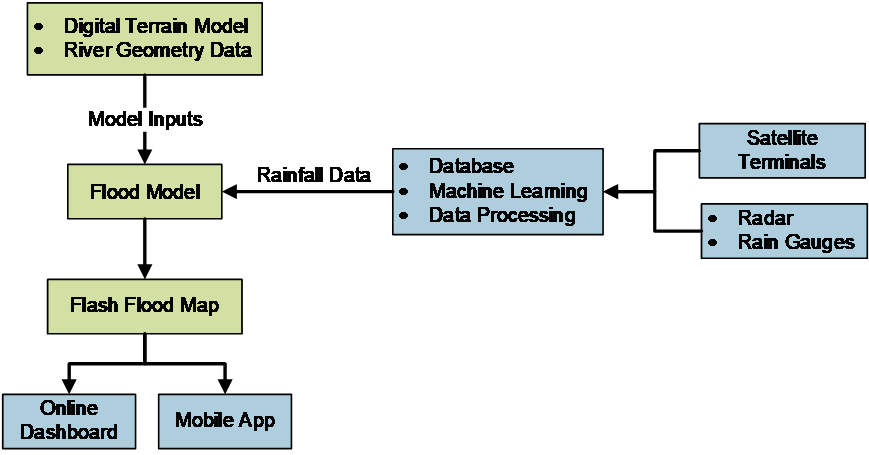
Below figure shows system architecture of flash flood map and its main building blocks. First rainfall data is augmented with other rainfall data such as radar and rain gauge data. Then, data is fed into flood model in order to generate flash flood map. An online dashboard and a mobile app are used to display the flash flood map to the end users.
Space Added Value
The space asset used for this service is signalling data from satellite communication networks. In typical SatCom networks, in order to maintain a certain level of quality of service for users, gateway stations continuously monitor the links between satellite and satellite ground terminals (enabled by the bidirectional link). The signal quality is mainly affected by the rain attenuation at the operational Ka/band frequencies. By using appropriate signal processing and machine learning techniques, we are able to estimate the rainfall from signalling measurements to a high accuracy.
A unique aspect of using data from SatCom networks is providing coverage for very large region. With a single GEO satellite, it is possible to provide coverage to whole continent Europe and middle east. Moreover, all signalling data is already available at a central database (gateway) and doesn’t require new investment for infrastructure. Therefore, rainfall information could be extracted from signalling data for very large area cost efficiently. CERASAT creates added-value to the signalling data generated in the satellite communication networks which otherwise will not be exploited.
Current Status
The CERASAT project ended on 28th of March 2019. Technical and commercial feasibility of flash flood map service for Luxembourg was assessed. Potential customers were identified and their need and requirements were discussed. System architecture was designed in order to satisfy those requirements. In addition, business model for the service was studied. Currently, we are planning for the next phase of the project in order to implement the flash flood map service. In this phase, we will collaborate with an insurance company in Luxembourg as a potential customer.


