
Objectives of the service
For inland waters, bad water quality due to cyanobacterial blooms is an increasing problem. Especially when cyanobacteria form thick floating mats, called scums or floating layers, cyanobacteria are a threat. Problems arise in the fields of public health, the aesthetic value of the surface water and the ecological status of the water.
The current monitoring methods and techniques which are in use by water management organizations provide insufficient data and information required to prevent the occurrence of scums or to deal with emerging and already existing scums.
CyMonS provides water management organizations with datasets of several water quality parameters, at a large spatial and temporal scale. These data is used to initialize models for providing short term forecasts.
With CyMonS, the dynamics of surface water bodies are better understood, problems are identified and prevented at an early stage, together resulting in better surface water quality..
Users and their needs
CyMonS is available for:
- Water management organizations which are responsible for the operational management of surface waters, such as lakes, lagoons and rivers.
- Drinking water utilities relying on drinking water basins as intake for drinking water production
CyMonS make it possible to:
- Monitor water quality of entire surface water bodies, using high resolution Sentinel-2 imagery.
- Monitor water quality on selected locations at a high measuring frequency, in real-time
- Provide detailed forecasts on the presence of cyanobacteria
- Take effective mitigation measures based on (near) real-time datasets and forecasts
CyMonS has several applications:
- Operational management of recreational lakes and bathing water locations.
- The dynamics and functioning of an entire water system can be better understood, by making use of monitoring data and forecasts
- Increase the efficiency of active mitigation measures, such as water pumps, air pumps and vertical mixers.
CyMonS can be applied on many types of inland surface waters.
Service/ system concept
Sentinel-2 imagery can be used to monitor chlorophyll-a and cyanobacteria scums at a 10 meter resolution. Image acquisition is every five days.
The EcoSpot and the EcoWatch monitor the following water quality parameters: chlorophyll-a, phycocyanin (as indicator for cyanobacteria), cyanobacteria scums, total suspended matter and vertical attenuation coefficient.
The algae forecasting model simulates the expected distribution of cyanobacteria biomass and cyanobacteria scum layers. The simulation runs at detailed grid size and at an hourly time step.
These data products provide data on full spatial and temporal scales. Separately, but also when integrated they provide information from a unique perspective about the water quality.
The data is available via several ways, such as maps, time series, tables, animations and raw data. This gives the users the opportunity to make use of the data as required.
The data is delivered in common file types that are compatible with the most data management systems. This way the data can be stored in the user’s data management systems and allows efficient analysis.
The following figure illustrates how each data product is positioned on a spatial and temporal scale.
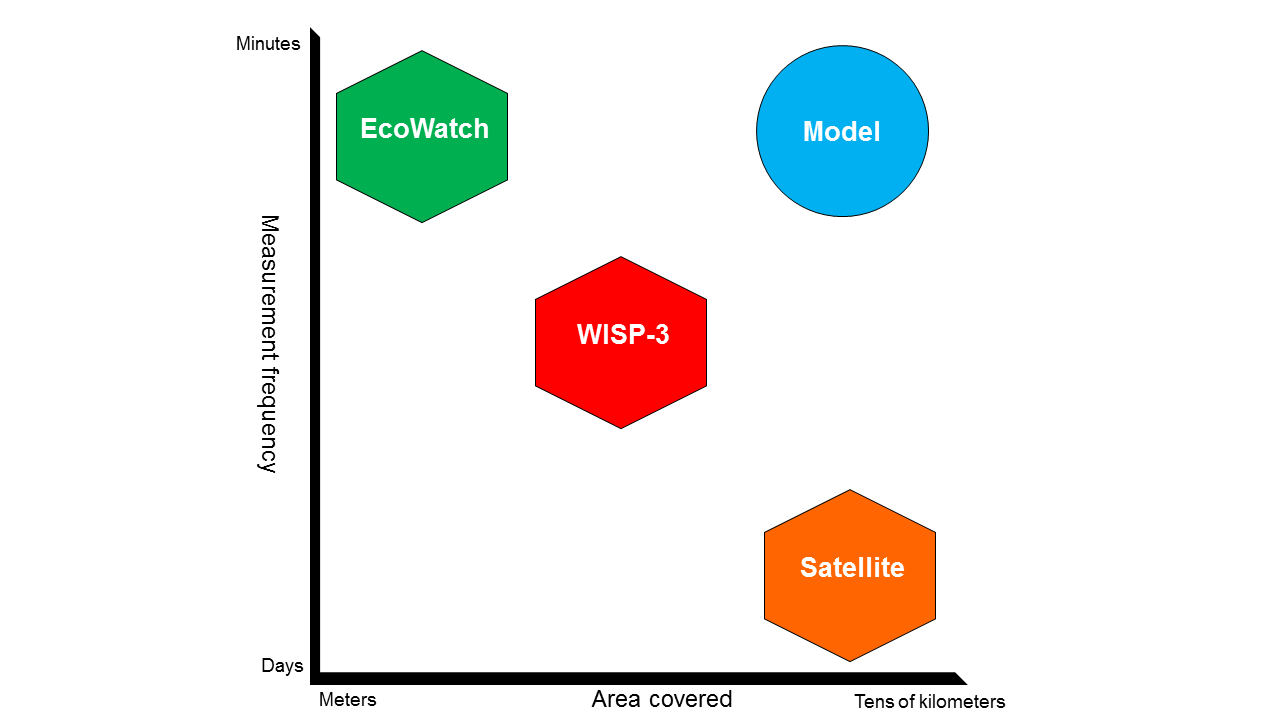
Space Added Value
It is recognized by water managers that water samples do not provide a representative image for an entire water body. They also know that water quality is highly variable over the horizontal and vertical surface area and over time. Current monitoring therefore does not give adequate information for the water managers. With satellite monitoring, the entire area of surface waters is covered. This enables better analysis of water systems.
Earth Observation based information is one of the main features and a unique element of the service. The provision of satellite imagery in the field of water management is an upcoming market, and especially for water quality there is a significant added value.
The spatial images are used in CyMonS as input for algae forecasting model EWACS. This model forecasts the occurrence of cyanobacteria scums. The advantage of using satellite imagery for this, is that it provides an accurate and detailed overview of the spatial distribution of cyanobacteria biomass.
Another space asset is the use of GNSS in the EcoSpot field instrument. The EcoSpot measures water quality in the field. GNSS is used for retrieving the coordinates at which a measurement is taken. Another unique feature of the EcoSpot is the direct transfer of the measurement to a database over the mobile data network.
The use of satellite imagery and field measurements is complementary. A field measurement can be taken any time of the day, but only covers a smaller area. A large area is covered by satellite imagery, with a lower acquisition frequency.
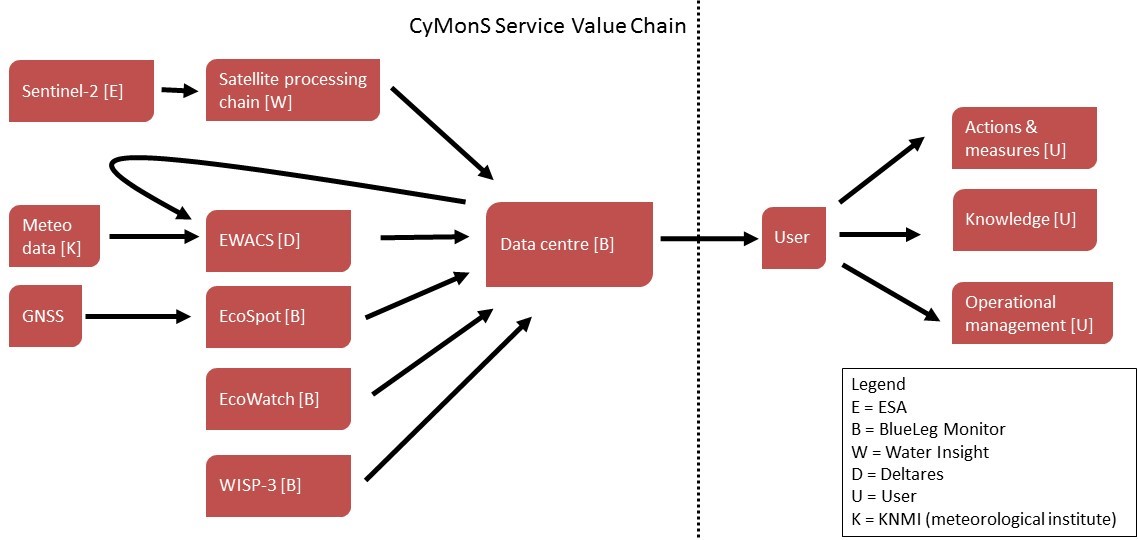
The figure depicts the value chain of the service. Each arrow represents the direction of the data flow and where value is added. The data centre is where data is transferred from the service providers to the Users.
Current Status
The project has been finalised May 2017, after a successful pilot period with three participating water authorities.
A selection of the project outcomes:
- Sentinel-2 imagery can be used to accurately retrieve chlorophyll-a concentrations and cyanobacteria scums in surface waters. Retrieval algorithm for Sentinel-2 have been applied and validated.
- The algae forecasting model is operational. Forecasting runs can be initiated on request.
- The satellite images, model results and field measurements have been integrated in a single software application
- The accuracy of the algae forecasting model has been determined. In pilots, 85% of the appearance and disappearance of cyanobacteria is forecasted correctly
- A large amount (thousands) of measurements have been stored in a central database available to the users.
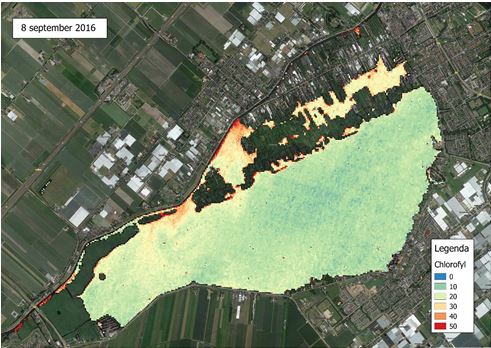
Chlorophyll a concentrations in Lake Westeinderplassen, retrieved by Sentinel-2 on 8 September 2016
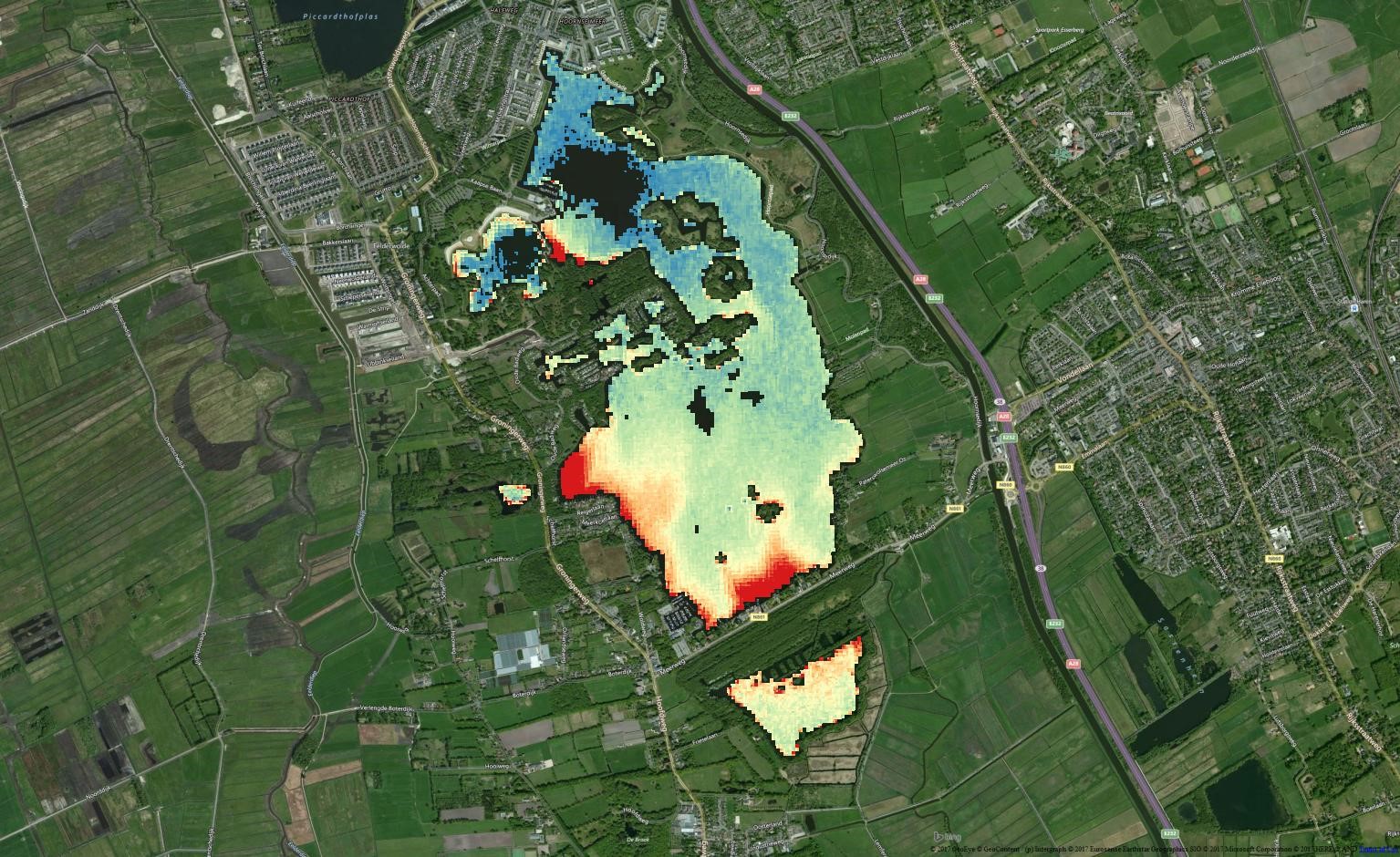
Chlorophyll a concentrations in Lake Paterswoldsemeer, retrieved by Sentinel-2 on 7 June 2016
Prime Contractor(s)
Subcontractor(s)





