
Objectives of the service
Cardiac irregularities and precursors are often displayed in the early stages of forming cardiovascular health conditions. It is imperative to identify and intervene on these precursors as early as possible for the best patient outcomes.
Currently, the established healthcare pathway across services around the world are limited in their ability to monitor patients remotely for long periods of time and pick up on these precursors. This has produced a reactive healthcare approach that leads to patients getting treatment once a condition is in its later stages, significantly increasing costs and worsening patient outcomes.
Machine learning mechanisms are capable of picking up on these early indicators through patient electrocardiogram (ECG) data. KYMIRA’s ECG monitoring electronic(e)-textile system provides accurate ECG data of wearers. Integrated with these machine learning mechanisms, an envisioned service could help an associated medical professional diagnose a developing cardiac condition or be alerted to alarming cardiac behavior. This could notably improve patient outcomes and reduce associated healthcare costs.
Users and their needs
Existing ambulatory cardiac monitoring devices have limited monitoring periods which lowers diagnostic yield, are often bulky/inhibiting and have high associated costs. Moreover, device data requires further manual doctor hours to produce a diagnosis and devices don’t alert to arising emergencies.
Our main target user, Healthcare providers, would benefit from a device that:
- doesn’t inhibit wearers,
- has flexible monitoring periods,
- is cost-effective,
- reduces doctor time to diagnosis
- alerts to alarming cardiac behaviour
Gathering accurate ECG data from athletes is difficult due to their environments.
Elite sporting bodies would benefit from a device that can:
- provide real-time ECG data that helps analyse performance and optimize training,
- function through environmental factors e.g. high impacts, underwater (aquatic sports) without inhibiting performance.
Smart apparel companies gather ECG data using e-textiles for analysis of athletic recovery and more. These textiles are often uncomfortable and/or cannot produce accurate data during movement which limits analysis. These companies would benefit from a wearable that:
- is comfortable to wear,
- can capture accurate ECG data during movement
Another end user are university, charity and private research institutions. They have very similar needs to smart apparel companies and will benefit from the same features offered to this user group.
Service/ system concept
The diagnostic ECG garment is to be developed at different maturity levels over three iterative release stages.
The first design, targeting research institutions and smart apparel companies, is an ECG garment that:
- improves on comfort compared to existing solutions - a stretchy and non-inhibiting e-textile
- can produce accurate ECG data during movement
The second design, targeting elite sporting bodies is an ECG garment that can:
- withstand high impacts accustomed in Rugby, football etc. or
- function underwater
This design can be specialised for aquatic or non-aquatic sports.
Both designs will have accompanying software whereby end users can view their data in real-time or post-activity via a computer or tablet/smartphone application.
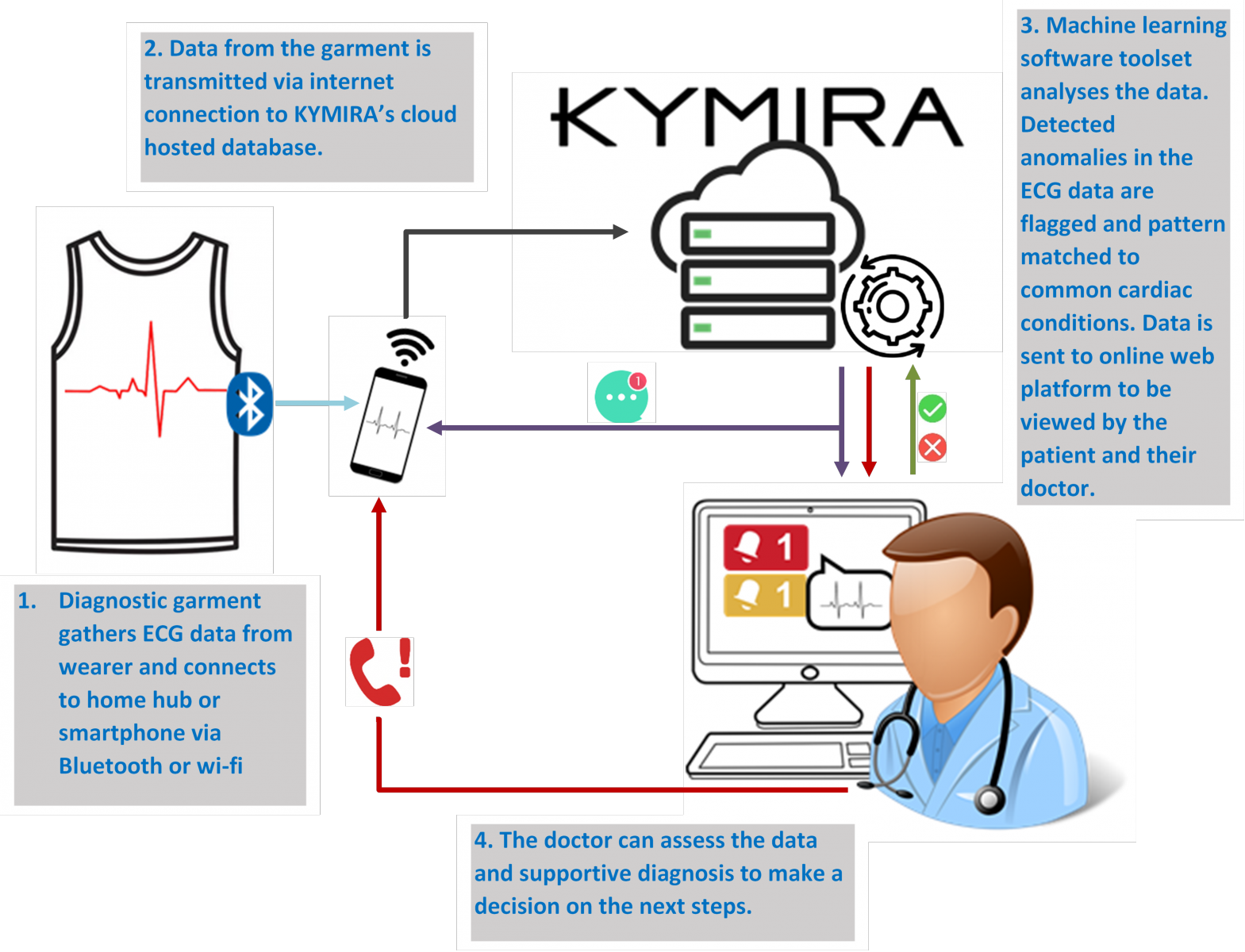
The final design targets healthcare providers: an ECG garment that provides supportive diagnosis and emergency alerts to doctors. Machine learning software delineates QRS complex in in a wearer’s ECG data and identifies anomalies i.e. irregular heartbeats.
The software can match the irregular heart rhythms to known medical conditions i.e. an arrhythmia for an initial diagnosis or an arising acute cardiac event i.e. a stroke. The associated doctor will be able to use this information to support their final diagnosis.
The diagram below illustrates the system architecture for healthcare providers.
Space Added Value
Satellite navigation
Through satellite navigation, the Diagnostic ECG garment could track patient activity and location, broadening the dataset. Location services also enable more freedom in end user activity as wearers can be located in the event of an emergency. This has been signified as a valuable additional feature to healthcare providers with patients who need constant supervision.
This technology was not assessed in this project but has been identified for future implementation.
Space operations
Novelty Detection and DrMUST are respective anomaly detection and pattern matching data mining software developed by ESA.
In this project, Novelty Detection was investigated in its ability to detect anomalous and irregular ECG data. It was found that alternative algorithms proved to be more effective than this technology.
DrMUST was not investigated but has the potential to be validated in future work as a tool for pattern matching anomalous cardiac data to known cardiac conditions, a key feature in the diagnostic ECG garment.
Current Status
We gained assurance of customer desirability and conformance with existing NHS procedures from our main customer segment, healthcare providers, through consultation with medical professionals at key partner organisations. Representatives of other target markets expressed their interest through letters of intent from a smart apparel company, a research institution and an elite sporting body.
The garment’s software was developed, and algorithms were identified for two key service features: QRS complex delineation and anomalous heartbeat detection. During this process, ESA’s Novelty Detection was determined to be less effective than non-space software.
Due to the non-reliance on space technology within the operational service the study cannot develop into a demonstration project at this stage.
Prime Contractor(s)
Subcontractor(s)




