
Objectives of the service
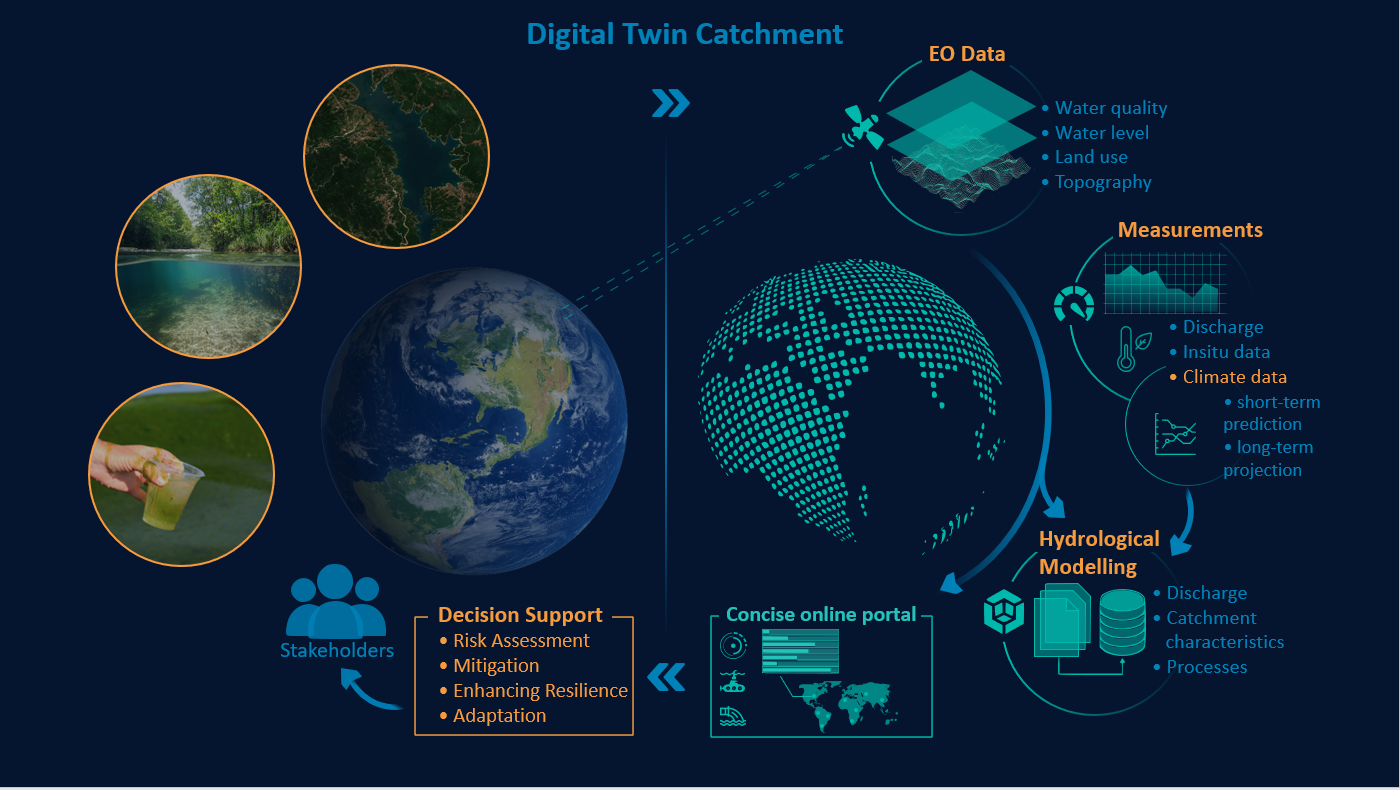
Better decisions in catchment-related water management require in the first instance: Better and sufficient data in terms of highest temporal and spatial resolution and accuracy – closing the usually huge data gaps in connected catchments. In second instance, it requires easy-to-use tools to visualize integrated information, enable risk assessment and the development of mitigation strategies.
With DITCH users’ key problems like:
-
Unrealistic understanding of the catchment status and behaviour
-
No early detection of environmental changes to provide protection of ecosystems and early warning of the population
-
Difficulties to identify drivers of disasters
-
Economic losses
-
No base for mitigation actions
-
Pressure from politics and publics, etc
are addressed and solved with a holistic view on the whole catchment, enabling for example:
-
Understanding combined dynamics of water volume and water constituents from land use, slope, climate, soil and management practices
-
Forecasting
-
Scenarios for impact analysis
-
NRT data for continuous, automatic monitoring
-
Alert functions
-
Early warning systems
-
Visualization for internal and public relations, etc.
The project thereby offers decision Support for integrated river management and monitoring, hotspot identification with alerts also of ungauged areas, visualization of projects using a combination of key hydrological, climatological and morphological parameters in a globally consistent way.
Users and their needs
Targeted user groups have been identified by their high exposure risk to water stress, including companies acting with water, like critical infrastructure providers (hydropower and drinking water supply) or water-bound industries like irrigated agriculture, fisheries, mining etc. As affiliated segment, insurance companies are interested in the level of water resilience of their customers acting directly with water. Focussed on risk management and long-term assessments, local, regional and state water authorities (WA) form another target stakeholder group. An additional customer segment identified are transboundary river commissions who require a central harmonized data platform. The geographical reach is in principle all countries with rivers and reservoirs under the influence of water induced stress for both humans and environments.
Service/ system concept
The proposed service aims to support the stakeholders in assessing and reducing their water footprint, improve resource efficiency and achieve net positive water impact targets.
Therefore, the following information is delivered to the user:
-
Baseline analysis of key parameters like sediment loads, water quality and catchment data
-
Tools to explore variable dependencies and correlations
-
Forecasting of key components like discharge and Harmful Algae Blooms (HAB)
-
Continuous NRT monitoring
-
Resilience and risk indicator tool
-
Alert functions
-
Visualization of data and analysis results in dashboards
Thereby the users are capable of:
-
Improve management practices in operation of infrastructure
-
Meet environmental reporting duties
-
Save costs for disaster handling
-
Identify connections between different parts of the catchment water system
-
Forecasting
-
Immediate information about critical developments
-
Possibility to coordinate mitigation measures
-
Easy preparation of public relations material
To provide the above to the users input data such as satellite data, in-situ data, and modelling data is processed into valuable information by the EO data processors and the hydrological model. The input data is stored and handled by the System Storage, while the backend server handles the user rights, accounting, and data access. It directly interacts with the user frontend inputs and outputs and interacts with the visualization block.
Space Added Value
SatEO is one of the primary components for the digital twin and therefore a necessary asset. Through combining Earth Observations with measurements from other sensor systems, a novel multi-sensor service for the digital representation of catchments was created, combining the strengths of all systems. EOMAP uses the Copernicus satellites (mainly Sentinel-1, -2 and -3) to get optical, radar and altimeter data, supported by missions from Landsat-5 to 9. Third-party mission satellites such as hyper-spectral (PRISMA, ENMAP) and VHR data (Planet Doves, WorldView 3) are used for hot spot analysis, bathymetry or vegetation/habitat mappings.
It is not possible to obtain the same coverage range for inland mapping and monitoring with any in-situ or land-based systems. Only EO allows to access, and map extended areas covering whole catchments globally, to perform studies on catchment properties such as sediment dynamics, discharge or land cover. Compared to multispectral aerial campaigns, satellite data is much more economic, carbon neutral and allows for mapping extended areas in very rapid turnaround time. Installed monitoring stations for the mapping of hydrological parameters such as discharge, sediment distributions or temperature in river catchments are currently limited to sampling at a few discrete points in space and time.
Current Status
The feasibility study was concluded successfully in October 2024. Main outcomes were a concept for the DITCH solution, a business plan, technical and commercial viability assessments, user engagements to understand user requirements, mock-ups and a prototype.
EOMAP is aiming for the continuation of the service to a commercial maturity within a subsequent demonstration study, partly funded by ESA. An outline proposal has been submitted.



