Objectives of the service
A growing population, land degradation, climate change, and food security are all interrelated challenges that must be addressed to ensure sustainable agriculture. These issues are particularly pressing in underdeveloped countries like those in Africa, which are more vulnerable to environmental risks.
Digital technologies and tools, by enabling proactive actions based on monitoring and risk predictions, could help the African population become more sustainable and resilient, establishing a stable and secure food provision system. This supports the achievement of Zero Hunger (SDG2, Sustainable Development Goal 2), aiming to improve food security.
The DT4CMI project, supported by ESA through its Kick-Start program under the thematic call "Connected Agriculture," focuses on enhancing sustainable and resilient agriculture by using emerging technologies and developing innovative digital services. DT4CMI utilizes several space assets, including Earth Observation (EO) and Satellite Communication (SatCom), to create a Digital Twin tool as a service. This tool provides farmers with comprehensive agricultural information and timely predictions related to critical factors such as diseases, plant pests, and irrigation needs. By supporting farmers with this data, the tool helps them improve agricultural practices and increase their yield, fostering more efficient and resilient farming methods.
Users and their needs
The targeted user communities for the DT4CMI project are smallholder farmers and agricultural cooperatives in particularly Africa, where cocoa farming is a key industry. These farmers face numerous challenges, including climate change, irregular rainfall, soil degradation, and limited access to technology.
User needs:
-
Real-time agricultural insights (e.g., soil moisture, crop health) to optimize farming practices.
-
Predictive capabilities to forecast weather patterns and detect diseases or pests early.
-
Cost-effective solutions for farm management with a focus on improving yield and reducing input costs (e.g., fertilizers, irrigation).
-
Access to easy-to-use technology, especially for farmers with limited digital literacy.
-
Support for sustainable practices to combat environmental challenges and ensure long-term productivity.
Service/ system concept
The DT4CMI project combines Earth Observation (EO), Satellite Communication (SatCOM), Internet of Things (IoT), and Artificial Intelligence (AI) to develop a Digital Twin (DT) tool for African farms, creating a reliable virtual representation of agricultural environments, processes, and products. This tool offers real-time insights for farmers, enabling them to optimize farming practices and improve yields.
A crucial component of the DT4CMI tool is in-situ data generated by IoT sensors, providing high-temporal resolution for real-time monitoring. This data addresses the limitations of EO data, such as satellite availability gaps (every 7–10 days), cloudy conditions, and nighttime data collection. By integrating both IoT and EO data, the tool ensures a comprehensive, accurate representation of farm environments.
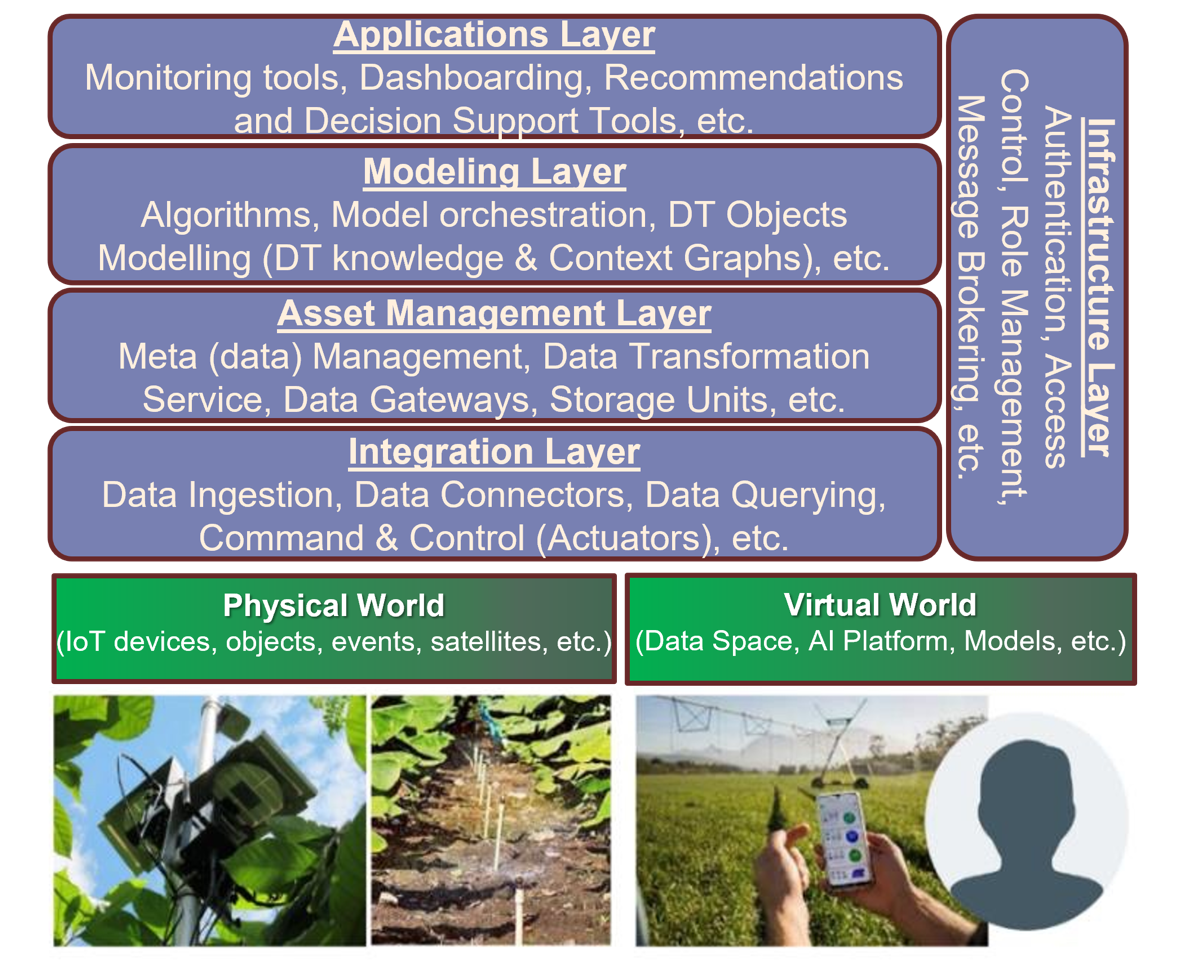
The system architecture consists of five key layers:
-
Physical World: Represents the farm, including IoT devices, satellite data, and environmental factors.
-
Integration Layer: Links the physical world to the virtual model, managing data input and optimization.
-
Asset Management Layer: Ensures data integrity and handles storage.
-
Modeling Layer: Houses data models and applies AI/ML for analysis and prediction.
-
Applications Layer: Provides decision support tools, dashboards, and recommendations for farmers.
The Digital Twin system is powered by the secure and scalable Max-ICS platform (link: http://www-max-ics.earthlab.lu) developed by EarthLab. This platform is crucial for integrating, storing, and transforming complex data into actionable insights, which are then translated into optimized farming practices, improving yields and minimizing risks due to climate changes. For real-time data collection and visualization, the Lumbara platform (link: https://frontierconnect.me) developed by Frontier-Connect will be used, reflecting the dynamics of the environment and crops. This IoT digital platform helps farmers monitor their fields, take proactive actions, and avoid crop losses.
Space Added Value
The DT4CMI project leverages key space assets including Earth Observation (EO) data and Satellite Communication (SatCOM) to enhance agricultural practices in Sub-Saharan Africa. EO data from satellites like Sentinel-2 provides high-resolution imagery, allowing for comprehensive monitoring of crop health, soil conditions, and environmental factors, even in remote areas where traditional methods may be limited. SatCOM ensures seamless connectivity, enabling real-time data transmission from rural farms, which often lack reliable cellular network coverage.
By combining these space assets with IoT sensors, the DT4CMI tool offers a holistic view of the farm, with predictive capabilities that improve decision-making, optimize resource usage, and mitigate risks like diseases and pests. Compared to current methods used by existing competitors, which may rely solely on ground-based monitoring or sparse data collection, the integration of EO data and SatCOM ensures continuous, wide-area coverage and real-time updates, overcoming the limitations of traditional agriculture solutions. This combination provides farmers with more accurate, timely, and actionable insights, ultimately increasing crop yields, reducing environmental impact, and enhancing sustainability.
Current Status
The Kick start project has successfully completed its feasibility study and user needs analysis, including several workshops held across Ivory Coast and Togo, where farmers, cooperatives, and agricultural stakeholders provided valuable input. These sessions helped refine the specific requirements for the Digital Twin tool and highlighted the importance of integrating Earth Observation (EO) data and IoT sensors.
Currently, the project is finalizing the system architecture and integrating the Max-ICS and Lumbara platforms for processing satellite and IoT data. IoT sensors have been deployed on selected pilot farms, and initial satellite data processing is underway.
Next, the project will enter the pilot phase in Togo, testing the Digital Twin service on a select group of farms. The team will also focus on refining the AI models for disease prediction and resource management, using feedback from the pilot phase to further optimize the solution.






