
Objectives of the service
Together with the EU-Africa Infrastructure Trust Fund (ITF - the instrument of the wider European and African Union’s Partnership on Infrastructure) and the Luxembourg Agency for Development Cooperation (LuxDev), the European Space Agency (ESA) started the Satellite-enhanced Telemedicine and eHealth for sub-Saharan Africa Programme (eHSA).
The goal of the eHSA programme is to “enable the development of a satellite-enhanced eHealth and telemedicine infrastructure for the benefit of the sub-Saharan African region”. The programme is a key recommendation of the Telemedicine Task Force, a group which was set up to develop a detailed understanding of telemedicine opportunities in sub-Saharan Africa and formulate recommendations for its implementation.
The study on Sustainability, Liability and Business Aspects is the last of the four studies executed in parallel within the eHSA programme.
The study objectives were:
- To develop a generic model by which eHealth projects may become sustainable over the medium-term and develop into self-sustaining eHealth services.
- To assess the background of Sub-Saharan countries and provide a ranking of the countries which offer the best environment to foster sustainable eHealth projects.
- To identify, describe and assess approximately 30 opportunities for eHealth projects in Sub-Saharan Africa.
Users and their needs
Achieving long-term sustainability of eHealth and telemedicine services in sub-Saharan Africa has been difficult historically for a variety of reasons. Frequently, projects or services that have been established in the region, providing hope to communities, flourish for a while before failing, leaving a dependent population without services along with abandoned infrastructure and equipment.
The study objective it to propose a transition strategy into sustainable operations of the infrastructure and services generated by means of the eHSA programme.
The users of the services proposed are the ones interacting with the healthcare system. It includes the patients, healthcare workers, healthcare service management, Government healthcare agencies, medical/health research institutions, etc.
The study targets 48 Sub-Sahara African countries: Angola, Benin, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroon, Cape Verde, Central African Republic, Chad, Comoros, Congo-Brazzaville, Democratic Rep. of Congo, Djibouti, Equatorial Guinea, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Gabon, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Kenya, Lesotho, Liberia, Madagascar, Malawi, Mali, Mauritania, Mauritius, Mozambique Namibia, Niger, Nigeria, Rwanda, Sao Tome & Principe, Senegal, Seychelles, Sierra Leone, Somalia, South Sudan, Sudan, Swaziland, Tanzania, Togo, Uganda, Zambia and Zimbabwe.
Service/ system concept
The study focuses on four categories of service for eHealth:
- eCare (Telemedicine) –comprising the use of ICT to support the core transaction pathway elements of: (i) Prevention, (ii) Consultation, (iii) Referral, (iv) Intervention and (v) Rehabilitation & Monitoring. The use of ICT, particularly telecommunications, enables the extension of geographical coverage of healthcare services where telemedicine techniques are appropriate.
- eAdministration – comprising the use of ICTs to improve the internal workings of healthcare sector organisations, introducing transparency and accountability, and leading to cost efficiencies in service provision.
- eLearning – the use of ICT for learning with the object of improving the quality of education, increasing accessibility for geographically-isolated (remote) students or those with poor local learning facilities, and making new and innovative forms of education and new information widely available.
- eSurveillance – which refers to the routine collection of data at all levels of the healthcare system (or data influencing the health of the population) to develop a robust surveillance capability in order to take preventive measures. The organised use those data systems can help health officials to decide where best to target interventions and attempt disease management and mitigation. A key value element is the execution of risk assessments.
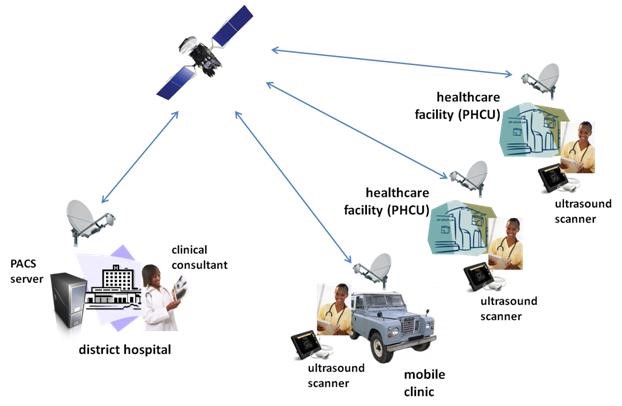
Space Added Value
The main services benefiting the most from satellite communications are eCare and eLearning. They both require the most bandwidth, the most service reliability and real-time capabilities. The added values of satellite from which eHealth would benefit the most are:
- Ubiquity of service coverage: satellite provides a way to install quickly and efficiently coverage anywhere and at anytime.
- Service reliability: satellite offers a service reliability that is essential for some eHealth services, particularly for eCare and eLearning but eAdministration needs also to be available at all times.
- Broadcast/multicast capabilities: Satellite provides broadcast capabilities that are valuable for eLearning services.
- Real time capabilities: Services such as remote diagnose need reliable and real time connection for critical cases.
Current Status
The study is finalised. The main achievements are the following:
- Description of a generic sustainability model with best practices, generic activities, generic risks and mitigation plans based on the analysis of sixteen (16) use cases and “in the field experience”.
- The specification of Key Performance Indicators (KPI) and Sustainability Assessment Criteria (SAC) which provide some key success factors for the implementation of eHealth services and their extension into service (mature) operations.
- The definition and implementation of an “eHealth Sustainability Index” (eHSI) index and the ranking of sub-Saharan countries with the implementation of the eHSI index-management platform (ED2) which enables users to access and visualise 91 indicators and indices based on any indicators stored in the database.
- The identification, description and assessment of 29 opportunities along with provision of a business process methodology for managing the evolution of such opportunities and the implementation of a software platform to enable that process (ED1).
- The identification and assessment of the business cases of the opportunities and an assessment of the business case from a satellite services point of view.







