
Objectives of the service
Agriculture can make a considerable contribution to reducing the CO2 content in the atmosphere by binding CO2 via crop production methods and storage in the soil through the targeted creation of humus / soil organic carbon. For carbon farming, it is important to know how much carbon is stored in the soil in the form of organic material or humus. Soil Organic Carbon (SOC) is defined as the carbon component of the organic compounds in soil and is therefore measurable.
In this kickstart activity, a service that derives soil organic carbon content maps from Earth Observation (EO) data was developed. Deriving Soil Organic Carbon content from optical EO data offers the unique opportunity to track the carbon storage in the soil for wide areas in a spatially continuous way and with regular updates. This allows a regular monitoring to see whether carbon conservation efforts led to an increase in stored organic material, or whether depletion of organic materials took place. The provisioned information can be used by farmers directly to keep their soil fertility at optimum or increase carbon storage in the soils with specific measures if there is still the possibility of improvement.
Users and their needs
The soil organic carbon mapping service developed within the kickstart activity EO4CarbonFaming is of relevance for several different user and customer segments, the most important of which are:
- Carbon certifiers, regional carbon partnerships, governmental agencies and NGOs who have a need to get proof for carbon sequestration into soils for carbon certification.
- Agricultural machinery manufacturers and farmers who need to know soil differences for every point in a field for site-specific farming measures.
- Soil probing service providers who would like an addition to their service portfolio in offering continuous humus maps.
- The food industry for which sustainable production becomes ever more important both for business and marketing.
During the kickstart activity, VISTA engaged primarily with users from Germany and Austria, however many of these users do have an international presence.
One of the important conclusions of this kickstart was that there is wide European and global interest in carbon farming.
Service/ system concept
The service delivers soil organic carbon content maps. These maps can be updated every few years to see whether carbon conservation efforts led to preservation or an increase in stored organic material, or whether on the other hand, depletion of organic materials took place.
For this, dense time series of Sentinel-2 data are analysed. The images are atmospherically corrected, bare soil pixels are filtered out and then soil organic carbon content is calculated on these pixels using a specifically developed algorithm. Finally, the derived carbon values are combined to a soil map.
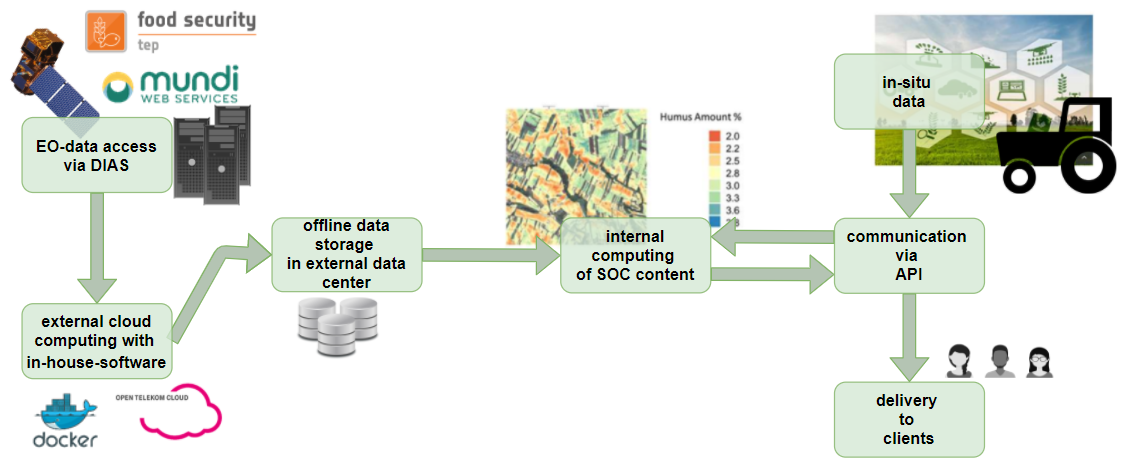
Space Added Value
High-resolution multi-spectral EO time series from Sentinel-2 are used for the service. Current approaches that calculate carbon content in the soil for carbon certification use soil samples and chemical laboratory analyses as input. Several soil samples are collected on each field and then the analyses values are averaged to give a field-wise value. Using Sentinel-2 data with 10m spatial resolution as input, a new degree of detail can be reached by showing also the variability of the humus content within the fields, allowing to target specific measures like e.g. taking steps to build up humus in specific parts of the field.
The use of high-resolution data such as Sentinel-2 makes it possible to provide information at the field level, while the big data approach makes it possible to give recommendations for larger areas as well, making the service attractive for additional stakeholders from NGOs to the food industry.
Current Status
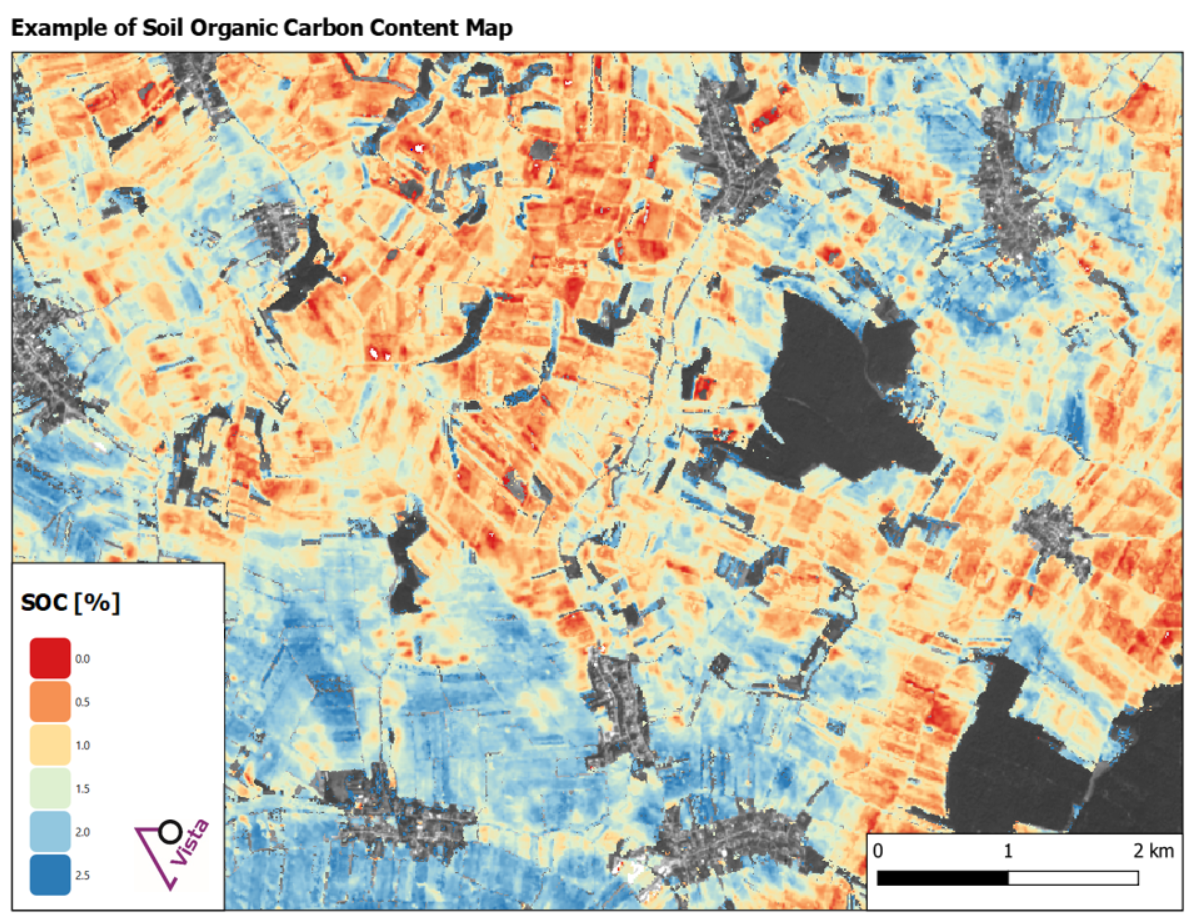
The EO4CarbonFarming kickstart activity has been successfully concluded. During the activity, first soil organic carbon content maps were calculated and validated, user requirements were gathered from several different user groups (e.g. carbon sponsorships, food producers, soil probing service providers), and a roadmap to the future was generated.



