Objectives of the service
The automotive industry has made very stringent requirements on the accuracy, availability and integrity of the position information for autonomous cars. Obviously, there is a need for a highly redundant positioning system and a powerful sensor fusion. The ANavS Integrated Sensor Platform (ISP) is the ideal solution for the automotive industry and related R&D.
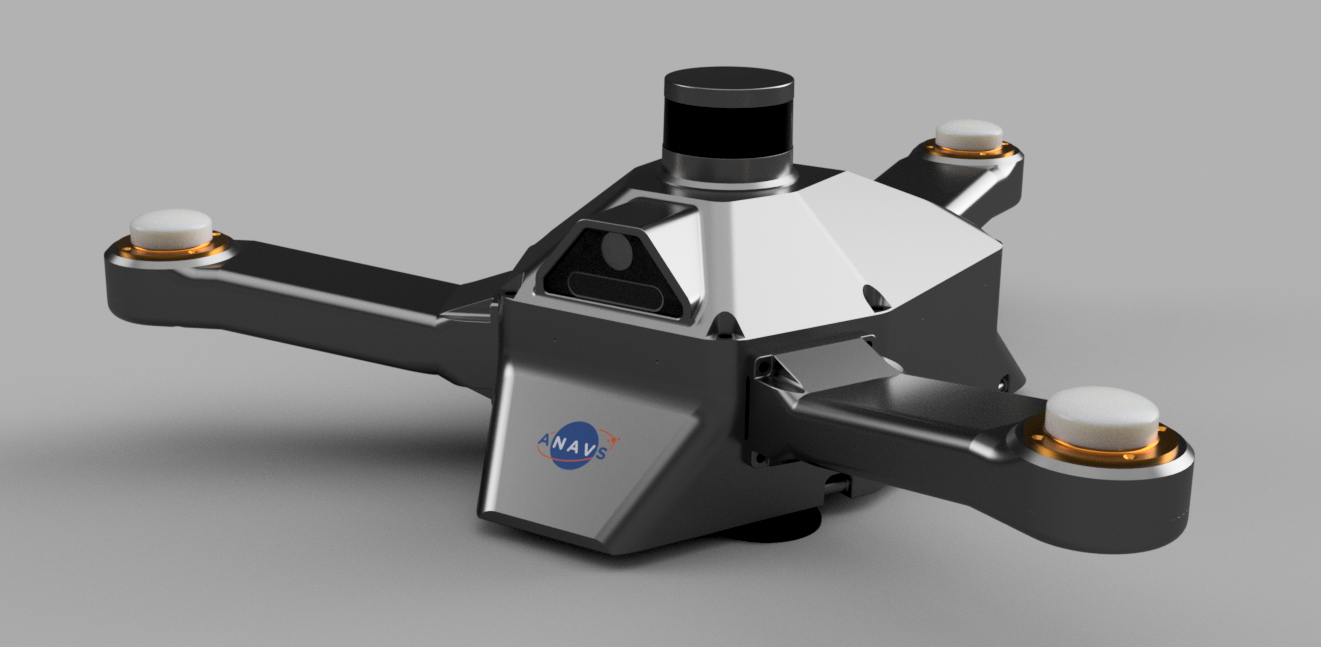

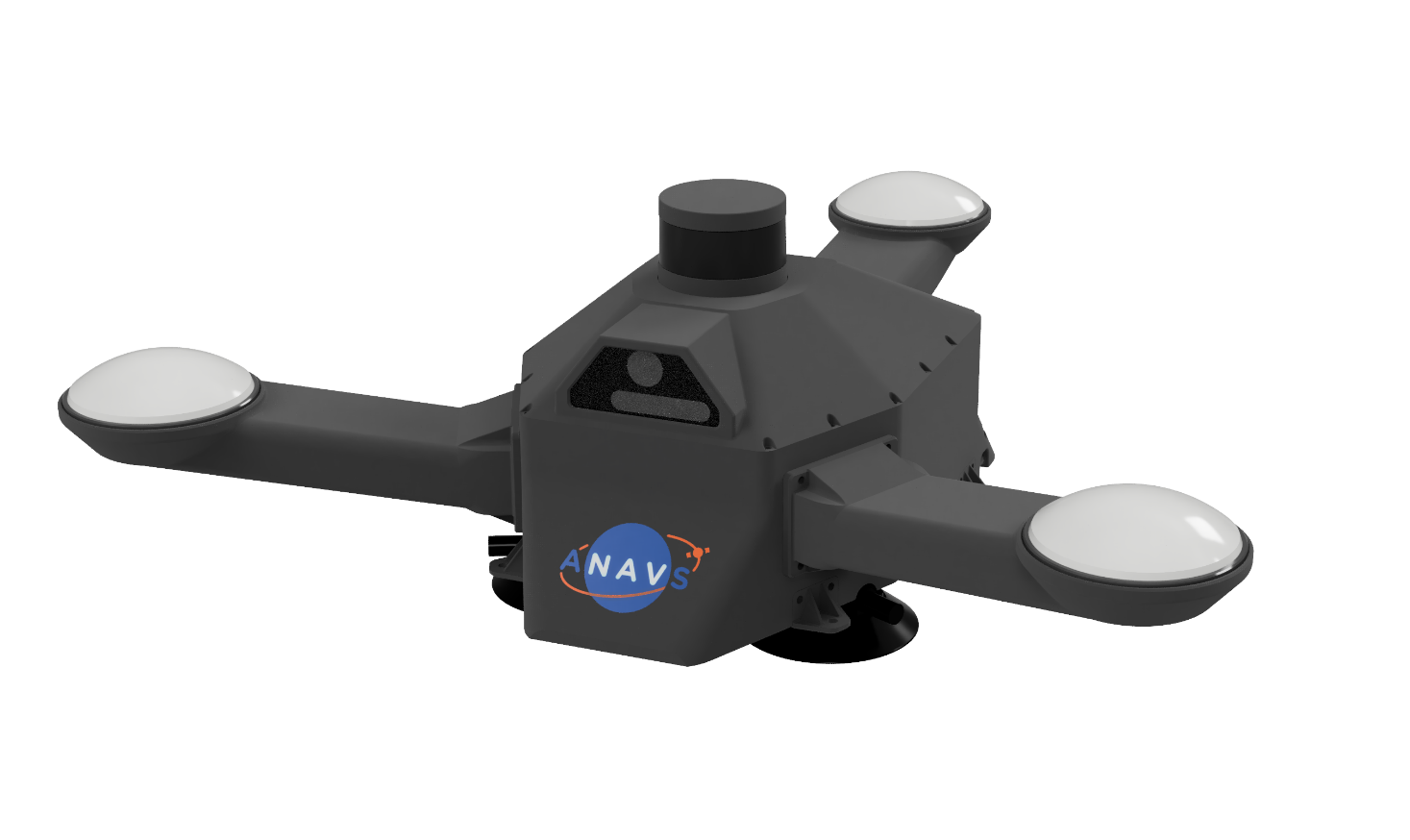
Fig. 1: The Integrated Sensor Platform of ANavS
Image credit: ANavS GmbH, Project: MUSE/ ISP
The Integrated Sensor Platform (ISP) is a hardware basis for easy integration of a large variety of sensors without any effort for mouniting and calibration (fixed lever arms to each sensor).
The ISP includes 3 Multi-frequency, Multi-GNSS (GPS + Galileo + Glonass + Beidou) receivers, high-grade MEMS IMU, a barometer, a CAN interface for reception of vehicle data (wheel odometry and steering angle), an LTE module for reception of RTK/ PPP corrections (e.g. from ANavS® RTCM reference station), and the powerful ANavS® Sensor Fusion on a single board. The latter one performs a tight coupling of all sensor data with an Extended Kalman Filter (EKF).
On top of the standard sensors a fully integrated computer vision module is equipped, that can be flexibly configured with two cameras and/or a 3D-LiDAR.
The ANavS ISP, the ANavS RTK positioning and the ANavS sensor fusion are protected by various patents including EP 20000278, DE 10 2019 000 804.9 and EP 2479588 B1 and EP 2624013 B1.

Users and their needs
The ISP addresses multiple user needs:
First, operators and users of development car fleets request an easy and fast installation and removal of the sensors from vehicles. It is important to protect the sensors while still being fully operational. The ISP fully addresses these user needs. There is no need to measure lever arms manually, which is a time-consuming and often error-prone process.
Second, users require a very accurate position, velocity and attitude information for autonomous driving, precise mapping and object detection. The ISP fulfils these needs with its Multi-Sensor, Multi-Frequency and Multi-GNSS RTK positioning.
Third, the automotive industry requires a very demanding level of availability and integrity for autonomous driving. The ISP of ANavS addresses these needs by a large sensor redundancy (3 GNSS, INS, wheel odometry, 2 cameras and Lidar) and a powerful sensor fusion.
ANavS targets manufacturers, operators and users of research and development cars in any country.
Service/ system concept
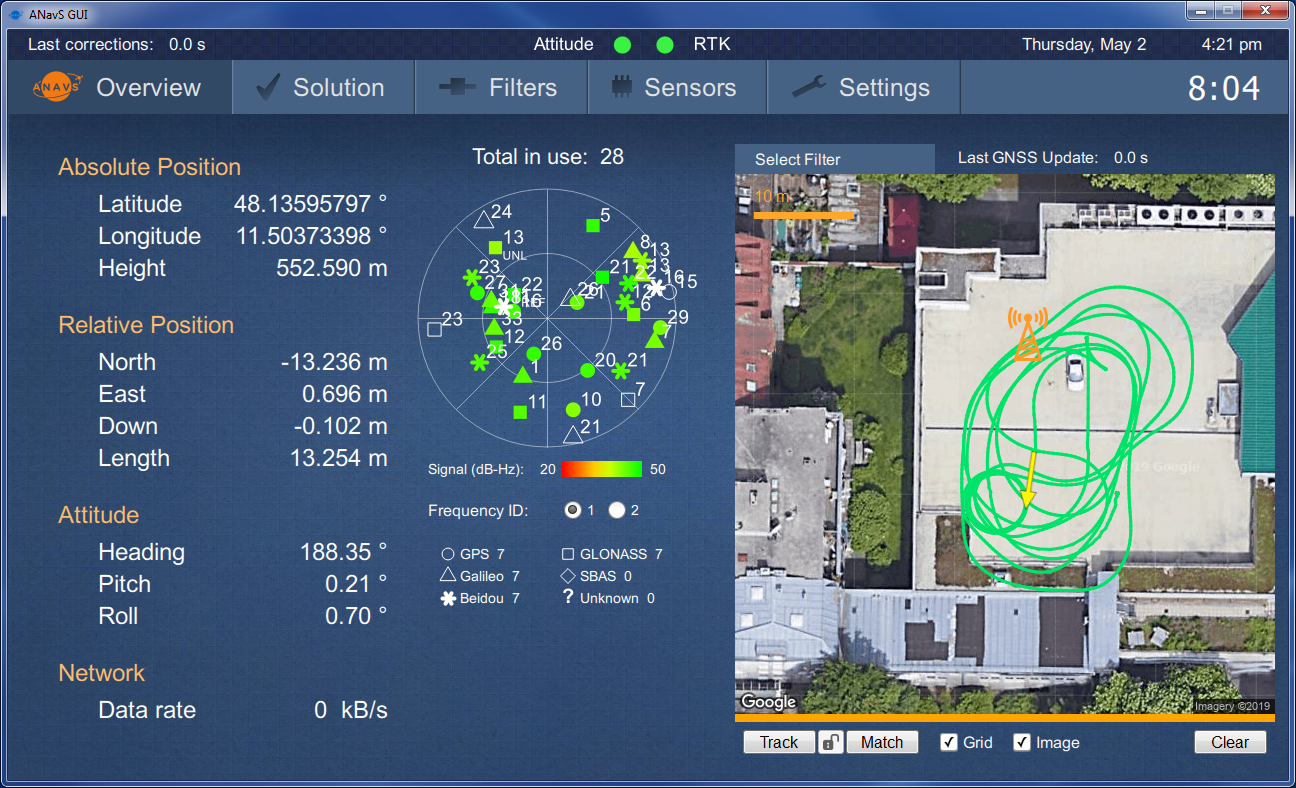
The Integrated Sensor Platform (ISP) of ANavS provides precise position, velocity and attitude information as well as the accuracy of these parameters. The system architecture of the ISP is shown in Fig. 3: The three main components of the ISP are the ANavS Multi-Sensor RTK module (Fig. 4), the ANavS computer vision board, and the ANavS ISP interface board. Further integrated components are two cameras, a 3D Lidar, three Multi-frequency GNSS antennas, a WiFi patch antenna, and an LTE antenna. The ISP also includes waterproof power, CAN, Ethernet and USB connectors.
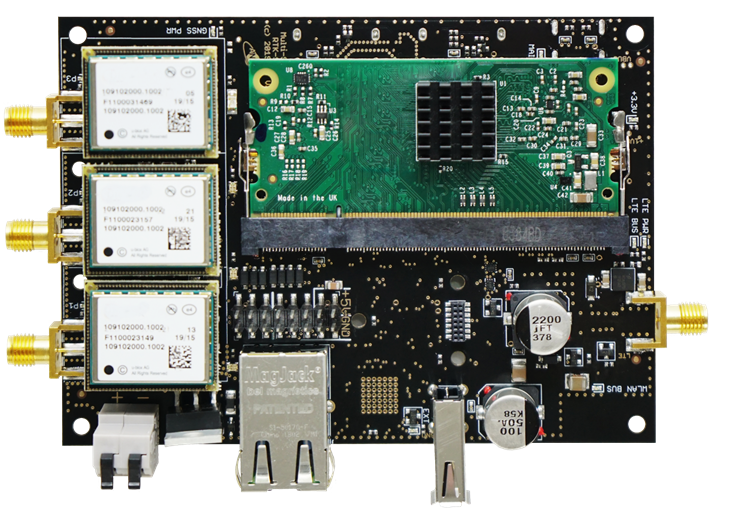
The ANavS Multi-Sensor RTK module (Fig. 4) includes 3 Multi-frequency, Multi-GNSS receivers, an IMU, a CAN interface for the wheel odometry and for outputting the solution, an LTE module for reception of the RTK corrections, and a processor for the sensor fusion. The ANavS Multi-Sensor RTK module also includes an Ethernet connector for the reception of camera/ Lidar based position information obtained from the computer vision board via the ISP interface board.
Fig. 2: Architecture of ANavS Integrated Sensor Platform (ISP)
Image credit: ANavS GmbH, Project: MUSE/ ISP
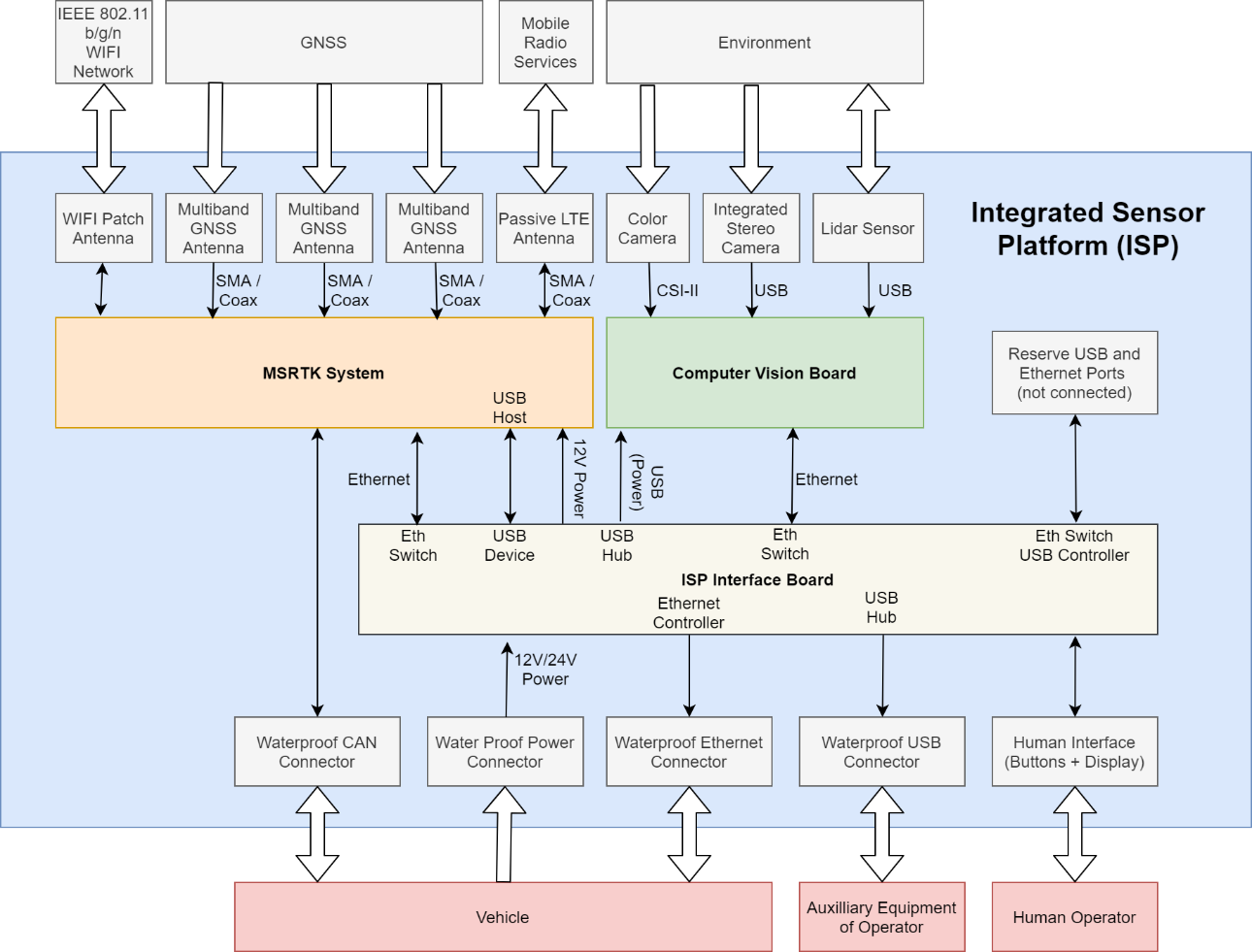
Fig. 3: The ANavS Multi-Sensor RTK module
Image credit: ANavS GmbH, Project: MUSE/ ISP
Space Added Value
There are two space assets used in the MUSE/ ISP project:
The first space asset is satellite navigation. Multi-frequency carrier phase, pseudorange, Doppler and signal strength measurements from all 4 GNSS (GPS, Galileo, Beidou, and Glonass) and RTK corrections are processed for maximum precision and minimum convergence times.
The second space asset is Earth observation. Maps based on Geo-referenced satellite images enable a visual positioning with cameras. This drift-free visual position information is fully integrated into the sensor fusion to outperform conventional GNSS/ INS RTK positioning systems.
Current Status
The development of the Integrated Sensor Platform (ISP) and of the Multi-Sensor RTK/ PPP module were completed successfully. Various customers from both industry and academia were already acquired. The Integrated Sensor Platform (ISP) has a very modular design, i.e. it is available in different configurations to best meet the customer requirements.
As next step, ANavS would like to develop a precise mapping system based on the ISP with a CCN.