
Objectives of the service
There is no source of truth for methane emissions globally. Existing methane estimates under-represent energy asset emissions by up to 70% The world needs decision-making clarity for reducing, reporting and managing methane emissions on oil and gas assets at global scales. Current techniques for monitoring methane emissions use ground-based detection methods e.g. laser scanning. These methods are effective for detecting leaks, however they do not enable large-scale and global quantification due to a lack of consistent data across 11.5 millions of oil and gas assets.
Orbio Earth (OE) is powering the global energy transition with methane intelligence. Orbio’s vision is to advance methane intelligence, using satellites to track and quantify methane emissions from the oil and gas industry. The Orbio Earth service platform fuses satellite and ground data to provide decision-useful methane emissions data, and uses machine learning to drive quantification and ultimately methane reduction. The technology developed by Orbio Earth has the capability to significantly enhance and replace costly ground monitoring techniques and make data available to many stakeholders on needed global scales.
In order to fully develop and validate a service ready to be commercialised, Orbio Earth have undertaken a 12-month demonstration project to refine the solution through technical developments and integrations, in order to advance the early-stage prototype into a market-ready solution and to assess the capabilities of the OE platform and satellite analytics in an operational environment via two pilot trials.
Users and their needs
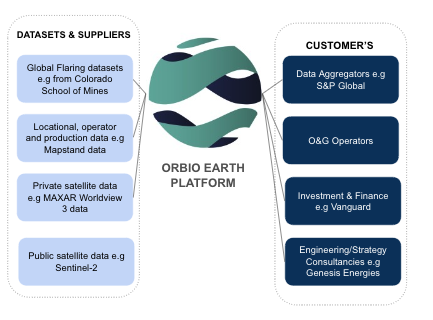
The key customers/customer segments targeted by the Orbio Earth service are stakeholders in methane-emitting businesses (B2B) that are under pressure from methane regulators/policy (e.g. Global Methane Pledge) to accurately report on and reduce their emissions. Target users include:
-
Data aggregators that provide data to the energy industry for due diligence and benchmarking e.g. production, energy consumption, emissions, ESG scores, ownership etc. Data Aggregators need to provide cutting-edge data to global methane-emitting businesses to stay at the top of their market and outperform competitor data quality.
-
Investment and finance firms use data to determine good investment opportunities/identifying risk for buy-side investors. The output of their work is a research report that sets out financial estimates for stocks. OE can provide global, uniform and transparent methane emissions data that facilitates more accurate comparisons of portfolios, companies and assets.
-
Engineering/Strategy consultancies who work with clients (e.g. oil and gas operators) to design and implement short-mid term projects to improve site infrastructure, increase overall asset performance and improve emission footprints, as well as investment parameters (e.g. ESG scores).
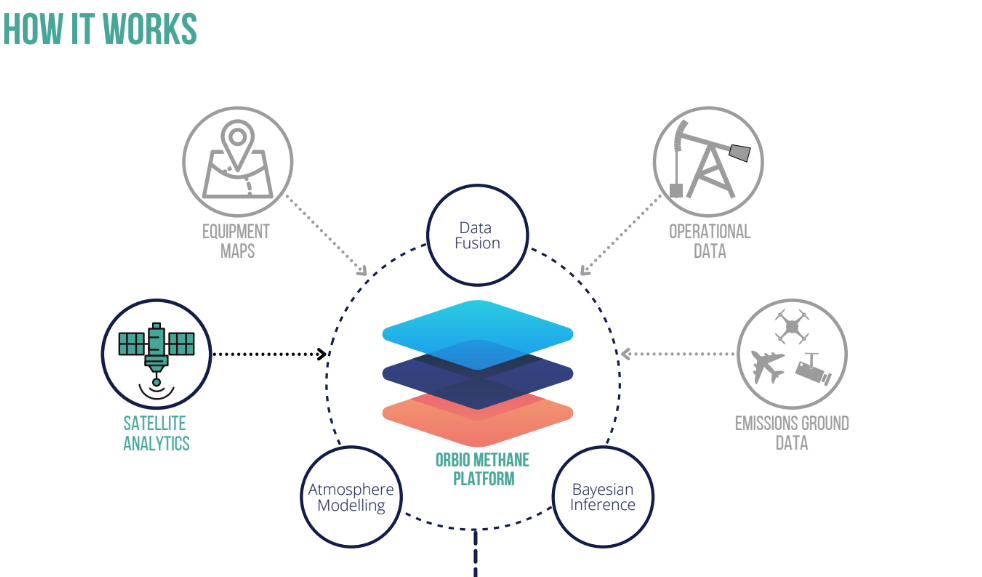
Service/ system concept
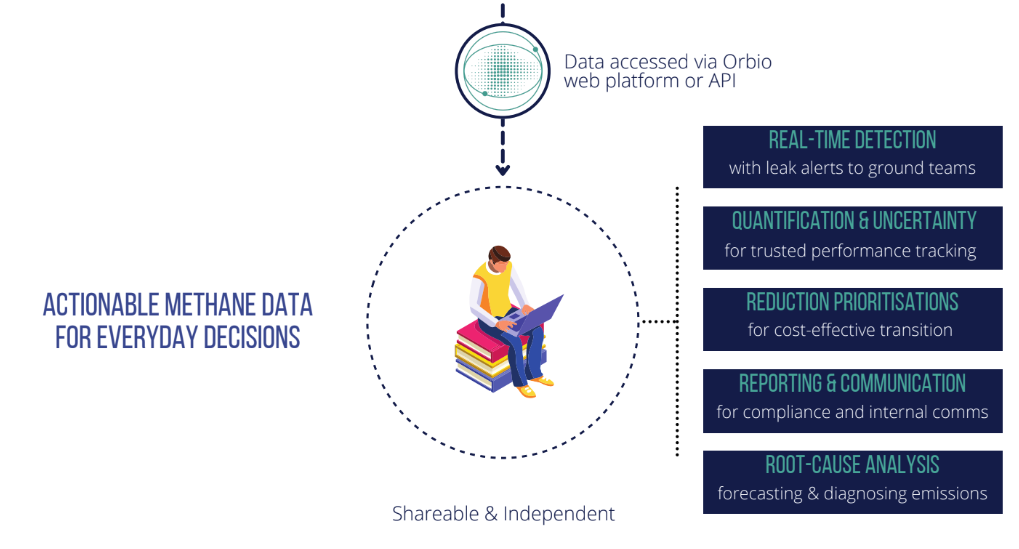
The OE platform enables these businesses to monitor, quantify and critically make data-informed decisions to reduce emissions. OE platform is designed to be accessible via a web-based browser and an integrated Data Application Programming Interface (API), providing users with:
-
Reliable methane emissions detections via satellite imagery with a 5-day revisit rate for any operational site globally.
-
Accurate quantifications of asset-level methane plumes and interactive emission visualisations.
-
Emissions trend analysis for current and historical emissions to understand root-cause relationships.
-
Reliable uncertainty estimations based on Bayesian inference testing and machine learning.
-
Reportable and standardised emission reports for compliance with regulatory and investors
Space Added Value
The OE platform incorporates a wide range of space datasets for its automated detection and quantification algorithms including:
-
Copernicus Sentinel-2: Temporal and spectral deviation algorithms are used to analyse Band 11 and 12 from S-2 to detect changes in spectral response that could be induced by unusually high methane concentration in the atmosphere. Visual bands are used for land cover classifications.
-
Copernicus Sentinel-5P: For global, daily CO2, CH4 values in the 5kmx5km grid to feed those values as background signals into the radiative transfer models that simulate the atmosphere between a Sentinel-2 measurement and the Area of Interest.
-
NASA GEOS-FP: Global wind data are used in quantifications of emissions relating to plumes of methane detected.
-
MAXAR World-View 3/ASI PRISMA/NOAA NPP VIIRS/ NASA EMIT: Global SWIR data induced similarly to Sentinel-2 data into the processing algorithms for spectral and temporal deviation analysis.
-
NASA EOSDIS: Atmospheric pressure, Water Vapour and Cloud Cover Data for data filtering, error corrections, and insight improvement (e.g. atmospheric pressure to give indication if methane emissions might be created by a drop in atmospheric pressure on site).
-
Satellite datasets can be added in the future (and when available): MethaneSAT, Landsat-8, Carbon Mapper.
Current Status
The Final Review of this demonstration project took place on 7 November 2024 and the activity is now closed.
During the project, Orbio Earth have tested and validated their solution in an operational environment via the delivery of two pilot cases:
-
Data aggregator use case: this validated the data as an API proposition and models ability to deliver accurate and useful emissions data using satellite data. Shipped over ~12m data points on ~300.000 emission detections.
-
Finance and consultancy use case: this validated the data model's ability to detect the highest emitters in Middle East and North Africa regions using satellite data and to benchmark target operators against peers. Shipped over ~100.000 data points on ~2.000 emission detections.
The platform and satellite analytics tool have been validated with two key user groups. The pilots were deemed successful and generated significant traction in the product and company. Orbio Earth has now commercialised the solution.



