
Objectives of the service
PARK solution is a GNSS accuracy positioning service, responding to the “urban cluttering problem” and fully integrated in the operator’s App. PARK solution avoids costly infrastructure and with zero-impacts for users. It provides users a parking compliance notification by using GNSS Raw Measurements, which enables a voucher or prevents a penalty.
Users and their needs
Micro-mobility operators are the Customers identified for the PARK service. Complaints about improper parking of micro-mobility vehicles are a common issue, which can lead to clutter, obstructed sidewalks, and inconvenience for pedestrians. To address these concerns, micro-mobility operators and city authorities are looking for solutions. The need originators are Municipalities. The Paris case is emblematic: citizen chose to ban shared electric scooters citywide in a referendum, for the consequent urban cluttering.
Micro-mobility urban cluttering is thus the most challenge faced by micro-mobility operators, what they call: the “problem”. A solution to prevent it is to implement an accurate geofencing check, fully integrated in the operator’s App and thus avoiding costly infrastructure and with zero-impacts for users.
Customer needs is to have a park compliance notification to be sent directly to users via App and by using Raw measurement positioning.
Service/ system concept
A preliminary overall system architecture is presented hereafter
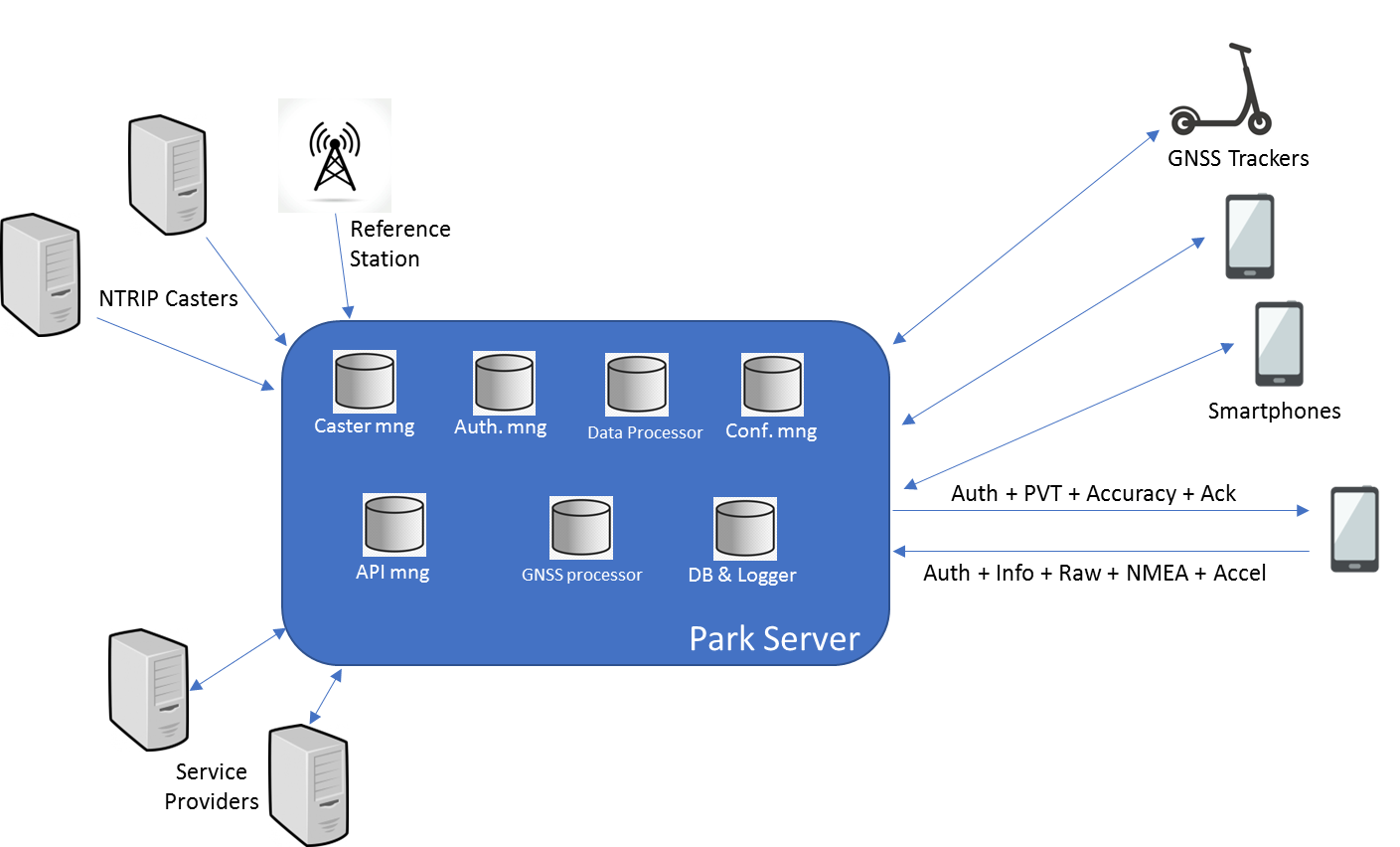
The constituent subsystems are the following:
-
The PARK Server
-
The Service Providers
-
The source of differential correction
-
The source of GNSS data
The PARK Server is constituted by the following elements:
-
Caster Manager. It manages the different sources of differential corrections and choose the best considering the estimated position of the final user.
-
Authorization Manager. It manages the access to the service to authorized users only.
-
Data Processor. It processes the PVT data from the different sources and estimated accuracy, for deciding about the compliance parking and protection level.
-
Configuration Manager. It chooses the best configuration of the GNSS processor and Data Processor taking into consideration previous database, the model of GNSS, PVT and accelerometric data.
-
API Manager. It manages all the interfaces versus the service providers.
-
GNSS processor. It uses the GNSS raw data, the configuration given by the configuration manager and the differential correction to provide PVT and estimated accuracy.
-
Database and logger. It is the database of the tracing and parking of the devices and also the data logger for the events generated by the other elements.
Space Added Value
PARK is based on the use of GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite Systems) raw measurement data for improving the positioning accuracy of micromobility vehicles. GNSS raw measurements can be extracted by dedicated trackers to be installed on the vehicles, or by Android based smartphones. All new smartphones that feature Android 7.0 (and higher) give application developers direct access to raw GNSS measurements. This unique feature allows users to get not only pseudoranges, Doppler and carrier phase measurements, and opens the possibility of using alternative strategies for position, velocity and time (PVT) computation, that is the fundamental of PARK.
-
In most cases, the raw data processing (RTK – Real Time Kinematics) achieves better position accuracy than the internal calculated positioning (NMEA data).
-
The choice of proper algorithms, parameters and filtering for GNSS raw data processing are still an open theme , as the quality of mobile phone raw measurements is considerable worse than traditional GNSS receivers. Processing must be adapted to the environment, to the device and to the parking slot size and shape. The role of the configuration manager is crucial for delivering high accurate positioning data.
Current Status
Customer confirmed its interest in the PARK solutions, asking for more tests in realistic context and a demo phase. Economic feasibility is proceeding positively: PARK service prices are considered competitive. Real World testing is very important as many variables affect the positioning accuracy, such as the device chipset, body attenuation, multipath, shadowing etc. A statistical and probabilistic approaches (eventually aided by ML or AI), rather than deterministic algorithms based on classic geofencing, seems to be the best to solve the problem of determining the compliant/non-compliant parking. An interesting viable alternative to mobile phone is to use a tracker able to generate GNSS raw data, to be installed on the e-scooter. This option will be tested during the demo phase.



