
Objectives of the service
The service proposed for e-Mobility is asoftware/app for the management ofcharging stations aggregation in urban or metropolitan areas, with the aim of providing a service of flexibility to the distribution network. Therefore, for the DSO that must manage the distribution network avoiding congestion and/or peaks. The targeted customer is more likely to be an aggregator or a virtual power plant service provider (e.g. UVAM in Italy). Target Customer: Aggregator/Balancing Service Provider.
In the SENECA system three services, corresponding to three potential final-users, were envisaged:
- Smart charging: the software can communicate with third party device to acquire data for the Machine Learning System runtime as well as to communicate the dispatching strategy to the charging station fleet.
- V2G (Vehicle To Grid): for the E-Mobility Service Provider (EMSP), using smart-contracts coding embedded in the blockchain, the energy flow can be optimized to avoid grid disturbances from solar and wind power sudden increase/decrease using the e-vehicle as a buffer-battery, rewarding the e-driver for having his/her vehicle used as temporary storage system to alleviate grid-congestions.
- Ticketing services: alarm notification system or additional systems to be easily integrated into proprietary systems
The goal of the services derived from this kick-start, is to allow in the future the users to perform energy-transactions in a secure and agile blockchain environment, where smart contracts will enable the utilization of e-vehicles battery in relationship with renewable energy availability, facilitate e-vehicles fleet management needs, and finally support the electrical grid necessities.
Users and their needs
The main players involved in the service are:
- The Charging Point Operators (CPOs) manage a network of interconnected charging stations (which the operator may or not own) operating through an application platform.
- The Electric Mobility Service Providers (EMSPs) offer electric charging services to the end customer, managing the payment and customer care, and offering value-added services (booking charging sessions, displaying available stations on a special map, etc.).
- The Distribution System Operators (DSOs) manage the distribution network.
- The Aggregator or Virtual power Plant service provider is an intermediate player between the DSO, the CPOs, the EMSPs, and the electric driver. In some cases, it can correspond to the EMSPs.
The services proposed introduces/requires several changes in the value chain. Three levels will be needed to deliver the services proposed (see table below):
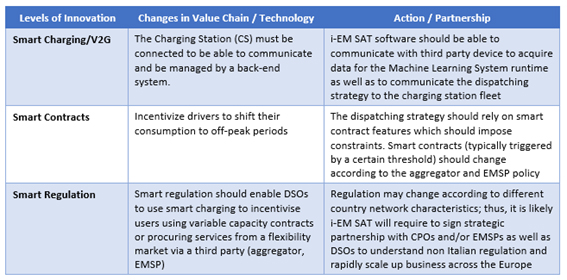
Service/ system concept
New value-added services related to the following topics:
- Manage local grid congestions by reducing peak loads
- Manage charging processes, highly dependent on immediate communication, seamless exchange of user data as well as digital transfer of value
- Tackle voltage problems possibly due to the injection of PV-produced electricity
- Monitoring of energy flow, assessing, and qualifying energy provenance
- Reduce frequency and duration of outages by supplying backup power during grid maintenance or by shedding loads in emergency situations
- Business opportunities with secure, distributed, and decentralized structure reducing intermediaries, improving performances, and saving costs.
The usage of the blockchain technology will reduce the risk of frauds during the payment process, reduce costs allocated to the maintenance and data protection, increase the opportunities of having new commercial partners without passing through mediators.
The architecture of the system is proposed in the following figure:
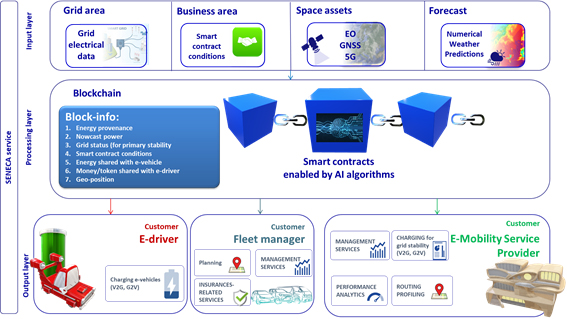
This infrastructure will provide all the services needed for the described system:
- A front-end layer with App services able to provide the service to all types of customers
- A Processing and registry layer used to implement the blockchain architecture
- An IoT tier to communicate with on-field systems, such as charging stations and vehicles
Monitoring tools and APIs to enhance the service with cross-application features
Space Added Value
The space assets that can contribute to the ADVISER service and their added value with respect to competing non-space technologies that could be used for the same function are:
Satellite Navigation – Global Navigation Satellite Systems are essential for the system, they are useful to locate final users to correctly screen AR elements on 3D and holographic viewers but at the same time they are used for positioning of robots and to geographically locate their collected data.
Satellite communication - For the whole ecosystem it is crucial to have a large bandwidth and low latency communication link with wide coverage. Another important aspect is that a widespread coverage will allow the user to potentially be free to move on all areas, especially the ones affected by digital divide or poor terrestrial mobile network coverage. Here 5G space assets come into play allowing to extend operation ranges and assuring definitive robustness to the service itself.
Satellite Earth Observation – EOassets can be used for visible maps to select the service area and to construct basic VR environments, but their very important contribution resides in providing near real-time, historical and forecast data to enable statistic processing for Big Data Analytics, like solar irradiation, temperature, wind, etc.
Current Status
In the following, the main blocks of the system are analysed in terms of level of maturity, needed development activities, how the blocks will be realized, some specifics risks and mitigation actions correlated.
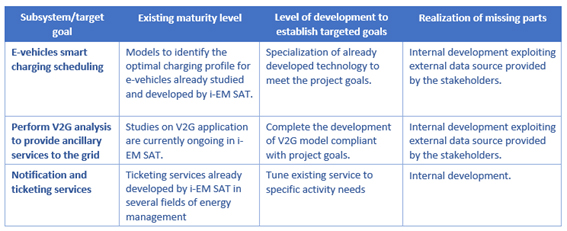
The e-Mobility service meets the need of monitoring and optimizing smart grid behaviour exploiting the e-Mobility elements (i.e. e-vehicles and charging stations) to preserve the grid energy supply balancing in case of failures or imbalances of the other grid elements (fossil-fuel based elements, renewable energy power plants, etc…). i-EM SAT developed a prototype of the envisaged service.
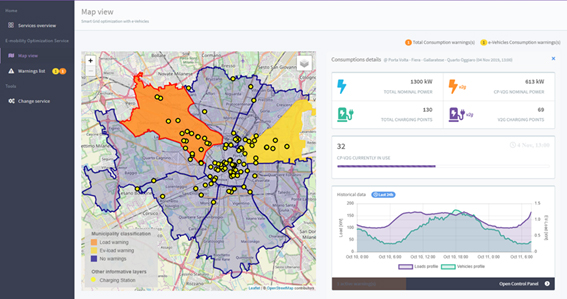
Customers:
- Distribution System Operators
- Charging Point Operators
- e-Mobility Service Providers
- Aggregator/Balancing Service Provider
Main features:
- Grid un-balancing prediction from e-vehicle consumption forecasting
Outputs:
- Warnings of forecasted grid unbalancing
- Ticketing service to support operator’s decision
Value proposition:
- Integrated management system (ADMS) or sub-packages integrated into customer ADMS
Weather nowcasting/forecasting



