
Objectives of the service
We will have additional 2 billion people on our planet by 2050 and to meet the growing demand for food, our agricultural production must increase by 75%. This is a major global challenge while the arable land is limited, and climate change is making its cultivation unpredictable. Fertilizer use is one of the essential factors that can ensure increasing agricultural production. Thus, global demand for fertilizer is expected to reach more than 200 million metric tons per year, representing a ten-fold increase since 1950. This will accelerate the negative impacts on the environment and affect long-term health of agricultural lands. Therefore, fertilizer usage must become increasingly efficient, and our farmers and crop advisors need smart technology to be able to make better and faster fertilization decisions.
To address agricultural productivity under the frame of an environmentally friendly farming concept and considering the existing fertilization regulations, SIITAg provides an intelligent system called ANA (Agricultural Nutrient Assistant) that helps users to make better and faster fertilization decision. ANA combines satellite data and ground truth observations coming from smartphone cameras to provide plant need-based fertilization map, which shows the current nutrient uptake and the nutrient demand, expressed it in kg/ha. This is easy to understand and much more actionable in comparison to vegetation index values like NDVI.
By using ANA, the farmers and crop advisors are making better and faster agricultural decisions, which enable farmers adopting sustainable agricultural practices, with the minimum hurdle possible. Naturally it reduces the agricultural greenhouse gas emission and nutrient leaching into our ground water. We have run pilot with 60 farmers and advisors in 2020. The finding of 2020 pilot was that farmers were able to gain additional 28 Euro profit per hectare.
At Spacenus, we develop our services together with farmers and crop advisors to create the best product fit and ensure usability on the field. To reach the world and scale up our impact, we market our services as a worldwide available API to agricultural input producers, ag retailer, agronomic advisories, farm management software providers etc. For those customers who do not have their own software system to consume the API output, our web app ANA provides a portal with all they need to serve their farmers.
Users and their needs
SIITAg identifies the end user as farmers with their specific needs.
- Farmers
- Strict regulations on fertilizer application and the need for cost-effective production create pressure for farmers to reduce their fertilizer usage and at the same time optimize yield.
- Farmers require user-friendly, easy to use and without having to purchase complex and costly system to address their requirements.
Additionally, two groups of intermediary customers have their own specific needs that are met by SIITAg.
- Agricultural consultants
Consulting farmers on their fertilization demands requires increasingly specific, individually tailored advice. This requires efficient technology that can identify field management zones on a large scale, using accurate Plan Nutrient Deficiency information.
- Agribusinesses (e.g. agrochemical and machinery companies)
Strong customer relationships are essential for a scaling business. To provide their customers with valuable additional services and stand out from the competition, companies require state-of-the-art technology and knowledge coupled with easy-to-use interfaces.
Depending on markets and demand, these specific target groups will be monitored and adjusted if necessary.
SIITAg service i.e. ANA is designed to be available globally. Internally the service has been piloted in Germany in 2019-20. Later, the service will be available for the EU countries, Asia, North America and South America consecutively.
Service/ system concept
Using the SIITAg service, farmers can visualize their fertilizer needs using fertilization recommendation maps and adapt these recommendation maps according to their knowledge of the spatial variability of their fields. The web portal allows farmers to get clear insights about their recent field’s nutrient demand and enhance their agricultural decision-making processes significantly.
SIITAg system i.e. ANA is operating as a mobile-app as well as a web-app for end users. The back-end system service designed with machine learning algorithms by combining satellite data with data collected through the app to generate the recommendations. The system is designed to make the process as simple as possible and as user-friendly as possible.
Ideally farmers can take pictures of few crop canopies in the field using the ANA mobile-app and the system analyses the status of the plant nutrient content for all 5 nutrients i.e. N, P, K, S, and Mg that is essential for the growth. The SIITAg system ANA then retrieves a satellite image with relative field nutrient uptake and calibrates the relative values with those in-situ data, generating absolute nutrient demand values for the entire field as a variable rate fertilization recommendation. Based on the crop type and crop condition, SIITAg system i.e. ANA is generating a variable rate fertilization map with the variable amounts of nutrients for each zone needed to attain optimum nutrient concentration, which the farmer has the option to tweak if desired. The application map can be uploaded directly to the fertilizer spreader through ISOBUS technology (if available in the tractor), or a ‘Driving Mode’ can be used to assist in manually varying fertilizer application rates during fertilization. The functioning of the whole system is outlined in the following figure
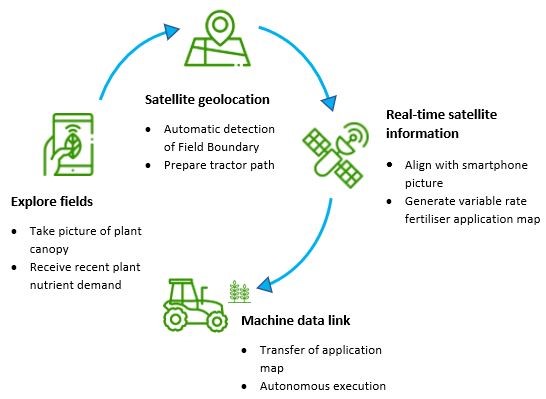
Space Added Value
Spacenus makes use of EO data of Sentinel-2 images, additionally GNSS information from Galileo mission for computational applications. Based on Sentinel-2 images, our system enables the generation of Field Boundaries, relative nutrient deficiency maps and field productivities. Combined, the above-mentioned components provide field zone management recommendations for farmers.
Because satellite images only deliver relative values, Spacenus counteracts this with our AI driven PND system. SIITAg calibrates satellite images for each field with in-situ sample pictures of crop canopies. When taking a photo with our tool, the phone also connects with the GNSS to provide the geolocation of the picture within the field. GNSS is also used to generate the variable fertilization map, a machine-readable map for the fertilizer spreader tractor enabling the distribution of designated amounts of fertilizer at specific geolocated field management zones.
Current methods, such as a mobile application catalogue or field nutrition sensors either require canvassing entire fields, analyse just certain nutrients in that case nitrogen and taking samples every few metres to achieve the same result. Working with satellite imagery enables SIITAg to cover entire fields at once and the 5 essential nutrients for growth of a plant, which are important factors in terms of time- and cost-efficiency, and thus in scalability.
Current Status
The SiiTag demonstration project and subsequent CCN has been completed successfully in October 2021.
Spacenus completed the Final Review of the SIITAg demonstration project in December 2020 and
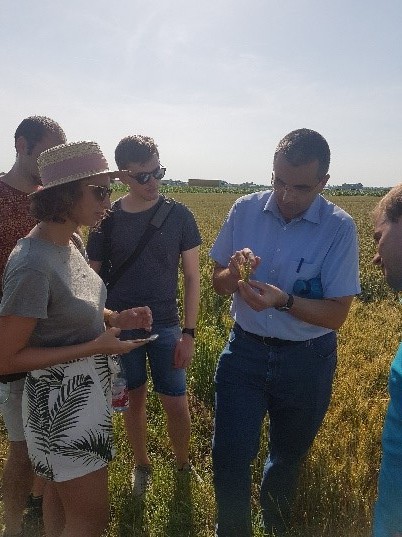
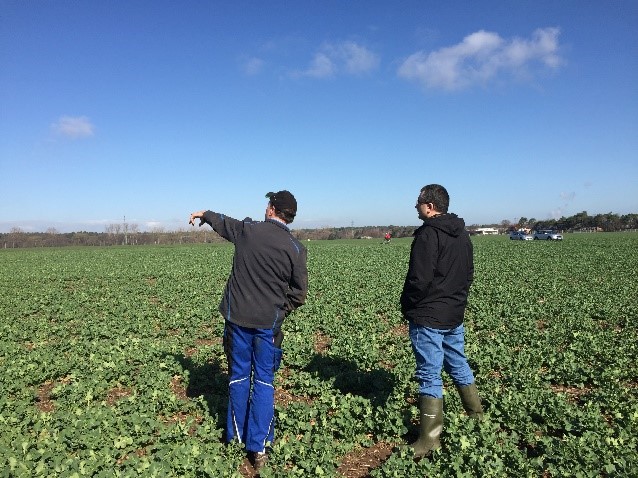


Figure 2: Spacenus visited different crop fields to investigate real world scenarios and the goal was to get to know pilot farmers and gather real experience from them.
Image credit: Spacenus GmbH
moved forward with the field validation for a commercial role out of the SIITAg service i.e. ANA. A CCN addressed further service features starting in 2021. Spacenus has already ensured four customers from four different market segments e.g. Input Manufacturers, Agricultural Retailers, Crop Advisor and FMIS Companies. and is now moving forward with the commercialization and global roll out of SIITAg service ANA.



