
Objectives of the service
The project's main goal is to develop a method for efficiently and accurately valuing biodiversity indicators to support the financial sector in understanding how an investment (current or future) affects biodiversity. This will facilitate the transformation to more insightful financial decisions regarding nature.
By understanding what impact an investment has globally on nature and biodiversity, the service helps asset owners take responsibility for preventing harm to local communities that are living in an affected area. Moreover, increased data and insights on biodiversity can support community awareness and education campaigns and assist in developing and supporting both emerging and established businesses like eco-tourism and sustainable agriculture.
In order to comply with new sustainability standards, financial institutions need to be able to better regulate and guide their internal processes and decision-making through the project's increased knowledge of how to value nature and biodiversity.
Users and their needs
Space2CLIMB focuses on the financial service sector, including the investor community and the (re)insurance community, the largest actors concerned with the long-term impact of large corporate portfolios on biodiversity.
The project aims to provide finance industry reporting frameworks and intelligence for informed decisions, while also targeting corporates struggling to report about themselves and their supply chains.
The key customer segments targeted are:
-
Investment banking and investment funds: interested in understanding how a potential investment may both affect and be affected by nature.
-
Credit institutes (inc. commercial banking and export guarantees): interested in understanding nature-related risks in land areas where they are considering granting a loan.
-
(Re)Insurance companies: interested in understanding at what cost and to what risk a specific company can be insured, related to nature risk and natural disasters.
-
Consultancies: These could be generalist organisations assisting financial service clients with overall business risk and strategy.
-
Major transnational companies: they need to prove secure sourcing with as little negative impact on nature as possible and also turn towards becoming net positive.
-
Bio-credit providers: they have the need to measure biodiversity within a specific area to provide the different markets with KPIs that value nature and the state of nature.
Service/ system concept
The consortium aimed to create a tool that could provide users with a rapid and cost-effective assessment and valuation of biodiversity for targeted sites. This service also sought to permit an increased/enhanced compliance with existing and arriving legislation on biodiversity risk/impact from both the corporate and investor sides where there are few scalable solutions in the market.
Investors and insurance companies will have greater visibility of the risks that their portfolios represent and will be able to compare one target company (and its supply chains) with another in terms of biodiversity impact, therefore enabling better operational decisions.
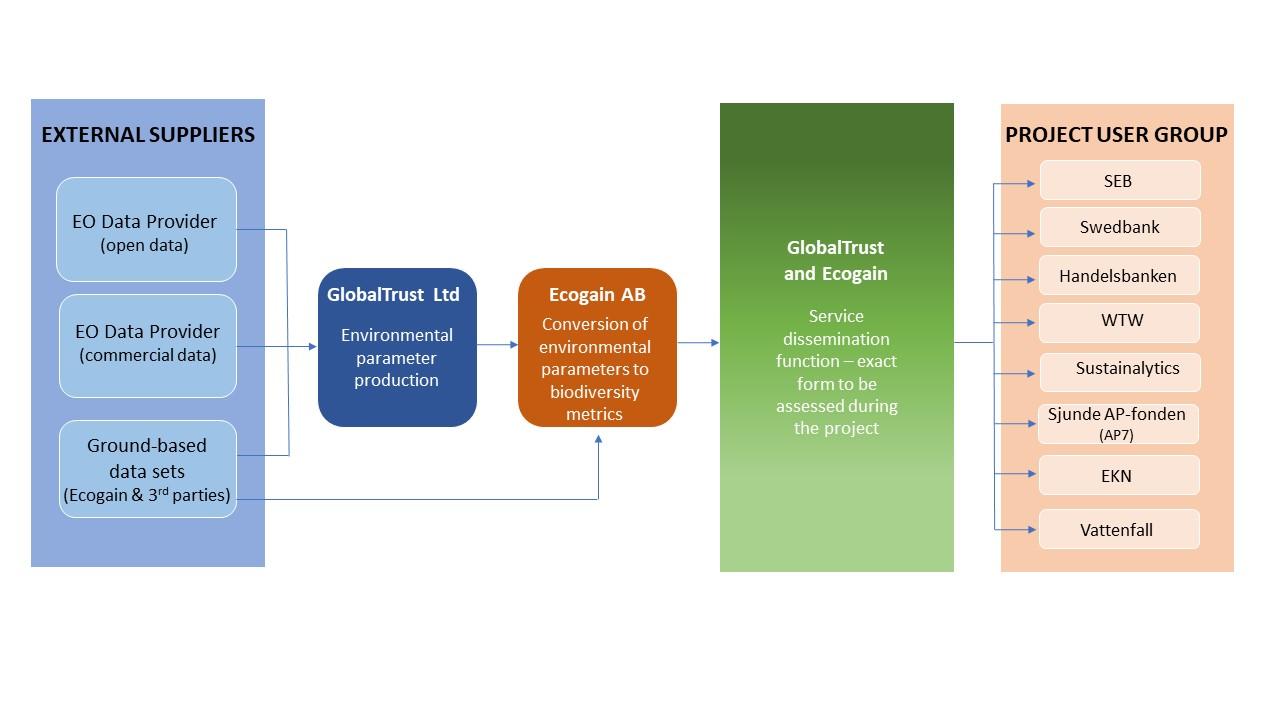
The work process involved the integration of Earth Observation data from external suppliers, both open and commercial, as well as ground-based data sets provided by Ecogain and third parties.
GlobalTrust was responsible for processing the environmental parameters derived from the Earth Observation and ground-based data. Meanwhile, Ecogain took these environmental parameters and helped to convert them into biodiversity metrics.
Once the data has been processed and converted, GlobalTrust and Ecogain collaborated to create a service dissemination function. This function is designed to deliver the processed data and biodiversity metrics to the project user group, which consists of eight entities.
Space Added Value
Earth Observation is the primary space technology used in this project. In the comprehensive assessment of financial services sector targets, a combination of optical and radar sensors from various missions such as Worldview, Satellogic, alongside Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 data, will be utilised. Optical sensors provide high-resolution visual data for detailed analysis, especially beneficial for identifying surface features and land cover classifications. Meanwhile, radar sensors (Umbra) offers all-weather and day-night capabilities, enabling the detection of structural and sub-surface features, crucial for assessing various potential challenges and mitigating risks. Integrating data from these diverse sensor sources ensures a thorough understanding of target locations.
Satellite technology offers a cost-effective means for global data acquisition and continuous monitoring of target sites, enabling financial services to gather vital insights regardless of geographical boundaries and making the process economically feasible. Automation through satellite monitoring alleviates the impracticality of manual surveillance, especially when numerous targets require continuous assessment for multiple service customers. Satellite measurements ensure consistency, repeatability, and independence from ground biases, fostering trust in the accuracy and objectivity of the acquired information.
In contrast to conventional methods, the integration of space assets optimises efficiency, accessibility, and reliability.
Current Status
The Space2CLIMB project made significant progress since its kick-off meeting in December. It has gathered insights on biodiversity risk management, measurability, and future service design, and has organised the end user needs consistently with the project’s objectives.
From a technical perspective, the requirements have allowed the team to address critical technical challenges, including tests over multiple sites against ground-truth data. This illustrated both the potential for satellites to add value, as well as showing the likely limitation of such a service.
Overall, the feedback showed a continued interest in following this topic, as it does address a genuine industrial challenge. Further work is required to develop this service and reach full operations, however the activities can also be split into two primary service offerings. These should be pursued together, but could be addressed individually if circumstances require. 1) a high value, very detailed offering, and 2) lower granularity offering but at a much lower price point.
Prime Contractor(s)
Subcontractor(s)




