
Objectives of the service
The TeleAssist solution demonstrated its novelty and advantages in addressing critical healthcare challenges in underserved, remote, and emergency settings by leveraging augmented reality (AR) and telepresence technologies. Key user problems addressed were limited access to specialized medical expertise, delays in emergency response, and logistical inefficiencies in medical training. Traditional telemedicine tools, often reliant on handheld devices, can be cumbersome and obstruct hands-free operation.
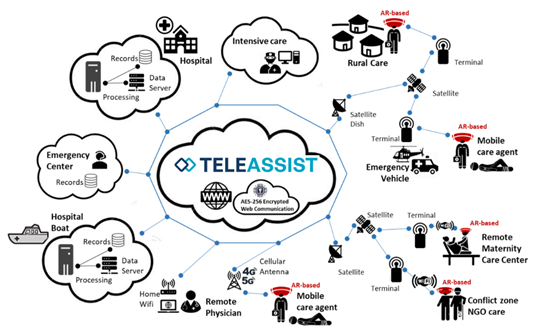
TeleAssist provides a hands-free, real-time AR system enabling bi-directional communication between local care providers and remote medical experts. Using lightweight AR glasses, a secure online platform, and hybrid connectivity (via cellular networks or satellite systems), it ensures reliable support in challenging environments. Features include video streaming, live annotations, and procedural guidance directly in the user's field of view.
The objectives included:
-
Improving patient outcomes by bridging expertise gaps in remote areas.
-
Enhancing emergency medical services with rapid, remote guidance.
-
Offering scalable training tools for medical professionals.
-
Ensuring seamless global connectivity through adaptive network solutions.
-
Supporting cost-effective and secure adoption by NGOs, EMS providers, and healthcare institutions.
TeleAssist aims to revolutionize healthcare delivery by integrating cutting-edge AR technology, addressing disparities, and improving medical accessibility worldwide.
Users and their needs
During pilot demonstration, TeleAssist was tested across the globe in 9 countries as Rwanda, Colombia, or the Czech Republic. It enabled the remote support of healthcare professionals in rural areas and in areas lacking WI-FI or cellular network connectivity. The primary user groups included:
-
Non-Medical Healthcare Professionals (e.g., paramedics, nurses, midwives): Require real-time guidance to perform medical procedures in emergencies and low-resource settings.
-
Medical Students: Need interactive and immersive training to enhance their skills and confidence during supervised procedures.
-
Physicians: Require tools for remote consultations and procedural support to extend their expertise to inaccessible areas.
-
Medical Experts: Need a platform for efficient global knowledge-sharing and guidance.
Key User Needs
-
Reliable connectivity in areas lacking cellular or internet infrastructure.
-
Hands-free, intuitive operation to focus on patient care.
-
Clear and real-time bi-directional visual and annotatable communication for accurate guidance.
-
Scalable and secure systems to protect sensitive patient data.
Challenges
-
Ensuring system usability and adoption across diverse technical skill levels.
-
Adapting solutions for different medical scenarios.
-
Tackling differences in regulatory requirements across the globe.
These user groups drive the development of TeleAssist, ensuring it meets real-world needs while addressing logistical and technological barriers.
Service/ system concept
TeleAssist kit is adapted for two main use cases: the stationary (Teleassist OR) and mobile (Teleassist Mobile), designed for respectively operation rooms (OR) and the ambulances.
The main components of the ecosystem are:
-
AR headset
-
Server station
-
Online Web platform
-
Pocket Unit
-
OR camera
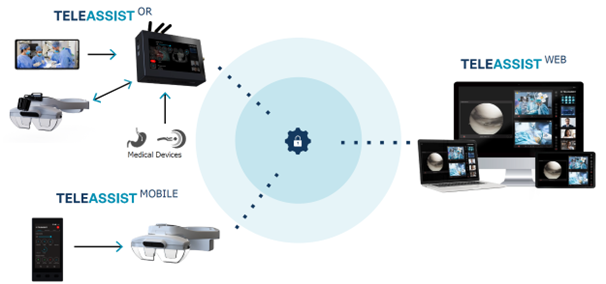
Key Features and Functionalities:
-
Live video and audio communication with remote experts.
-
Ability to share documents, medical imaging, chat messages and annotated visuals to remote experts or audience, and in the direct sight of medical professional wearing the AR headset.
-
Connectivity through cellular or satellite networks
-
Scalable support for multiple users in one session, ideal for team-based emergencies or training.
How It Works
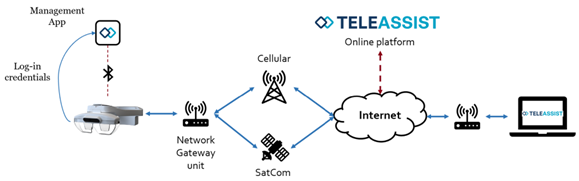
Space Added Value
Satellite communication (SatCom) ensures reliable connectivity in regions lacking cellular networks or terrestrial infrastructure and enables real-time data transfer essential for the system's live video and two-way interaction.
Added Value of Satellite Communication:
-
Global Coverage: SatCom provides connectivity in remote or underserved areas, including rural regions where cellular networks are unavailable or unreliable.
-
Resilience: Satellite networks are less prone to disruptions caused by natural disasters, infrastructure damage, cross-border provider changes, or network congestion.
-
Flexibility: By combining SatCom with cellular networks, TeleAssist dynamically adapts to the best available connectivity, ensuring seamless operation across diverse environments.
Advantages Over Current Methods:
While cellular networks suffice in urban areas, their limited reach in rural areas restrict medical telepresence applications. Traditional cellular-based systems often face latency, signal loss, and network congestion. By integrating SatCom, TeleAssist ensures uninterrupted communication, supporting real-time decision-making and improving medical outcomes in critical scenarios. This hybrid approach bridges the gap between urban and remote healthcare services, expanding the reach and reliability of telemedicine.
Current Status
TeleAssist project has successfully completed its pilot phase with positive outcomes in all its objectives, demonstrating high usability (SUS score: 70) and robust connectivity across diverse locations, including Rwanda, Colombia, and the Czech Republic. Notable achievements include 15 completed teleconsultation sessions in stationary and 7 in mobile use cases, improved patient outcomes (e.g., reduced treatment delays in Colombia), and knowledge sharing that enhanced surgical and diagnostic practices. Cost savings were documented at the certain testing sites, primarily by avoiding unnecessary patient transfers.
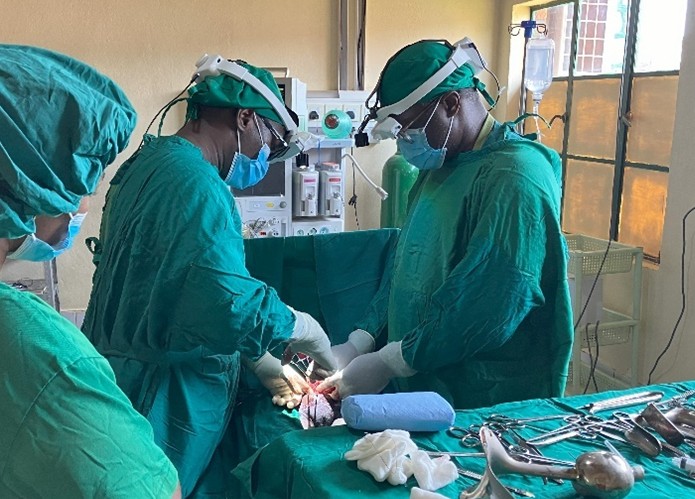
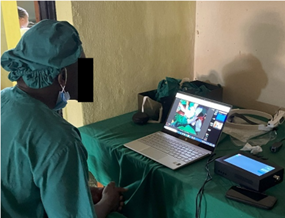
Surgeons using Teleassist in Rwanda:
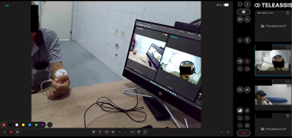
Physicians using Teleassist in Colombia:
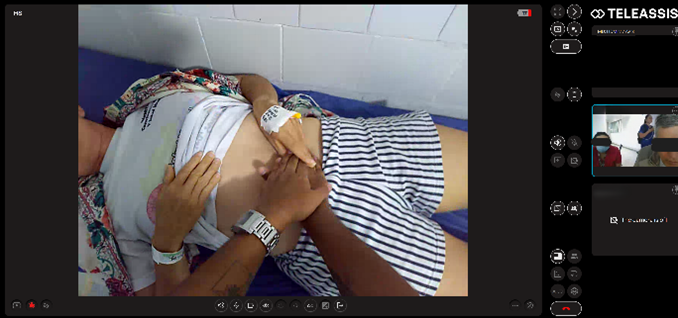
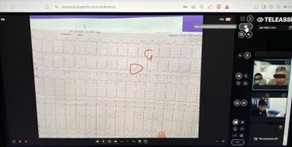
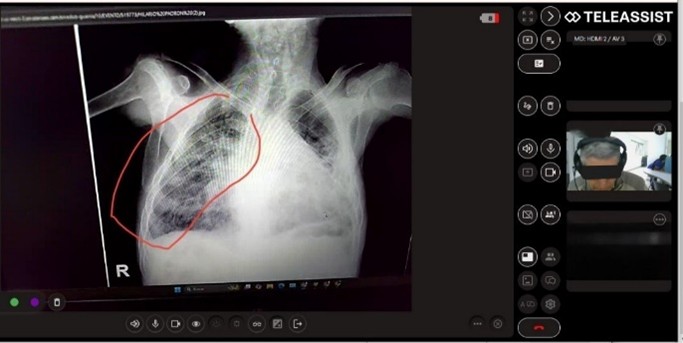
Paramedics testing Teleassist in the Czech Republic:
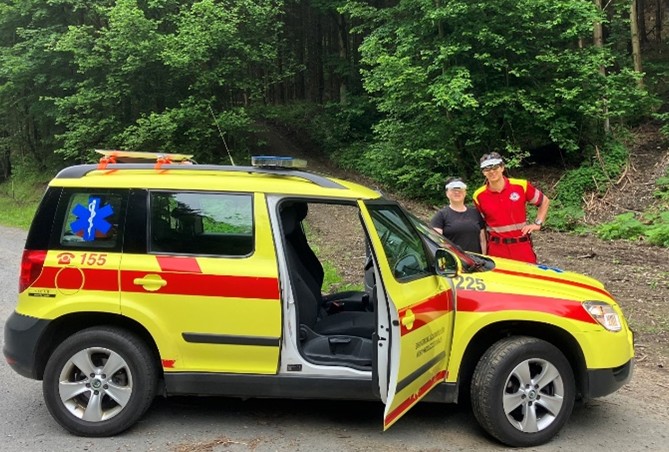
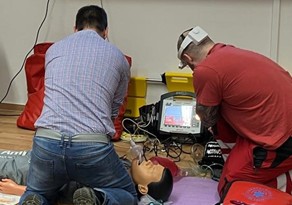


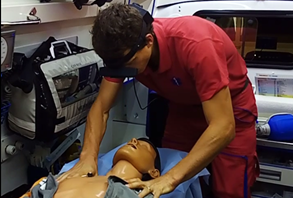
The TeleAssist project has concluded though the demonstrations and integrations are continuing, with current efforts focused on enhancing the mobile application, geographical availability, and widening the scope of use cases. Next steps for example include scaling the system to new regions (Africa, Latin America, Asia) and preparing the broader commercial roll-out.


