
Objectives of the service

The Wind Sat service addresses critical challenges faced by wind energy producers and grid operators. These include inaccurate production forecasts, inefficient asset management, and difficulties in grid balancing due to wind power's intermittent nature. Wind Sat solution provides high-frequency wind energy production forecasts, ranging from 15 minutes to 8 hours ahead, with projections extending up to 7 days. By integrating satellite imagery, weather data, and on-site sensors, Wind Sat delivers more precise forecasts than traditional methods. The study is developing and validating AI-driven forecasting models, integrating diverse data sources including Satellite Earth Observation (SatEO), and creating a user-friendly platform for real-time forecasting and decision support.
Users and their needs
Wind Sat targets three primary user communities:
-
Wind energy producers
-
Energy management companies
-
Transmission System Operators (TSOs)
Team is actively collaborating with energy producers in Italy for initial testing and implementation. These users face challenges in optimizing wind farm performance, reducing operational costs, and maximizing revenue in volatile energy markets.
Key user needs include:
-
More accurate short-term wind power forecasts (15 minutes to 8 hours ahead)
-
Improved asset management and maintenance scheduling
-
Better integration of wind power into the grid
The main challenge is developing a system that integrates diverse data sources (satellite imagery, weather data, on-site sensors) to provide forecasts that significantly outperform current methods. Initially, the focus is on the Italian market, with plans to expand to other European countries participating in the Cross-Border Intraday (XBID) Market, including France, Germany, and Spain.
Service/ system concept
The Wind Sat service provides users with high-frequency wind energy production forecasts, ranging from 15 minutes to 8 hours ahead, with extended projections up to 7 days. These forecasts are delivered through a user-friendly dashboard that displays:
-
Real-time wind power generation predictions
-
Probability distributions for forecast accuracy
-
Asset performance metrics and optimization suggestions
The system works by integrating multiple data sources:
-
Satellite imagery for wide-area wind pattern analysis
-
Local weather station data for ground-level conditions
-
Historical wind farm production data
-
Real-time sensor data from wind turbines
Wind Sat AI algorithms process this diverse data to generate accurate forecasts. Users can access these insights via web interfaces, with customizable alerts and reporting features.
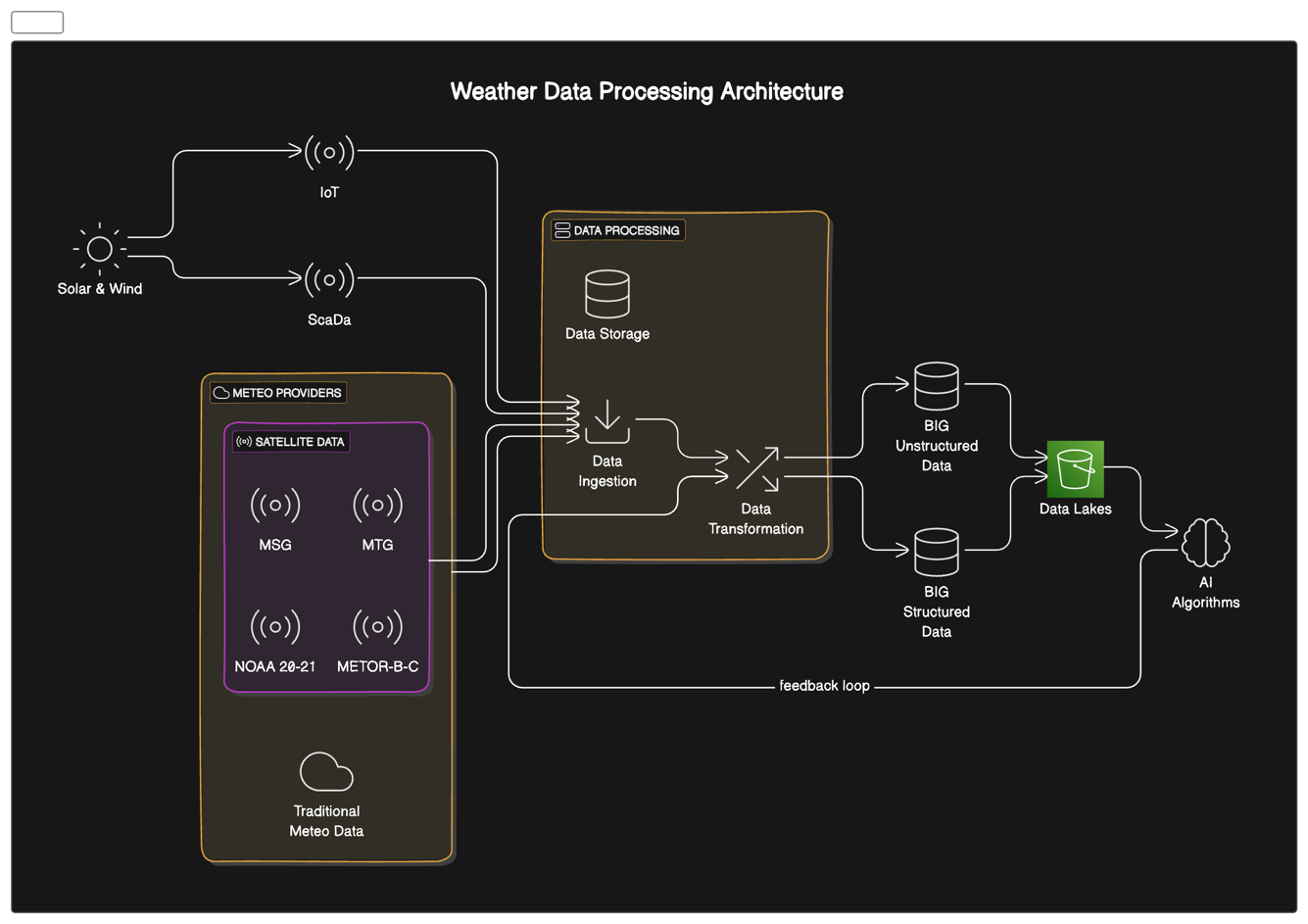
Space Added Value
Wind Sat leverages multiple space assets to enhance wind energy forecasting:
-
European Meteosat satellites (First, Second, and Third Generation):
-
MVIRI, SEVIRI, and FCI instruments for wide-area atmospheric monitoring
-
GERB and LI for additional atmospheric data
-
-
European METOP constellation:
-
IASI and AVHRR for detailed atmospheric profiling
-
-
American NOAA satellites (20 and 21):
-
CrIS and VIIRS for complementary atmospheric and surface observations
-
The key added value of using these space assets includes:
-
Wider geographical coverage, especially over oceans and remote areas
-
Higher temporal resolution (up to 15-minute intervals) for more frequent updates
-
Ability to observe multiple atmospheric layers simultaneously
-
Integration of diverse spectral data for more comprehensive analysis
By combining these space-based observations with ground sensors and weather models, Wind Sat achieves significantly higher accuracy in wind forecasting compared to competitors who rely primarily on ground-based data or limited satellite information.
Current Status
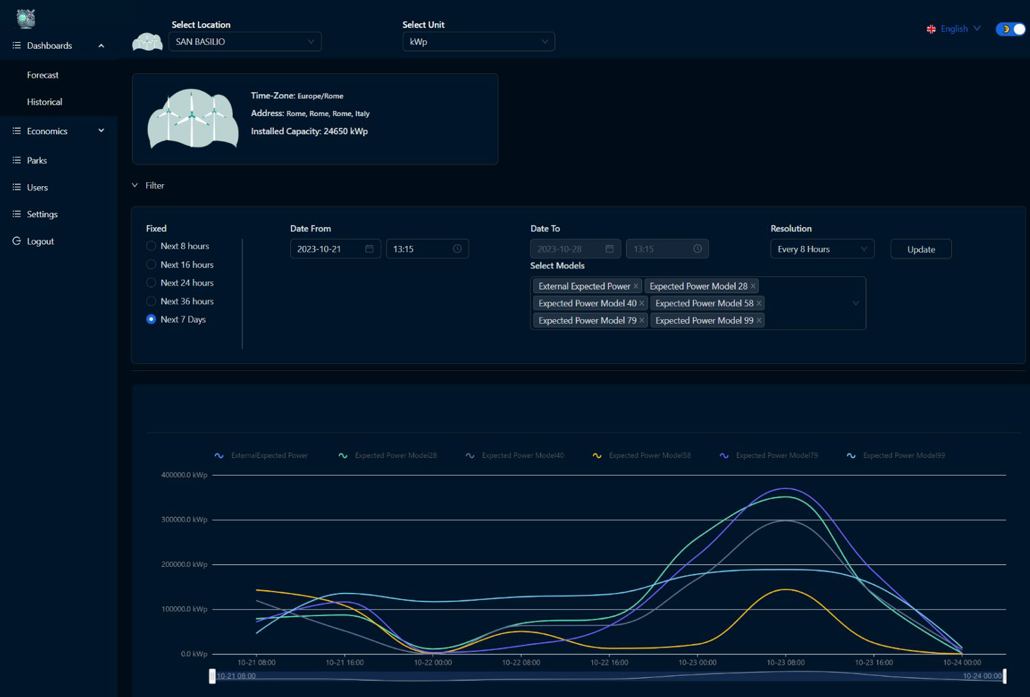
The Wind Sat project has made significant progress:
-
Completed a successful Proof of Concept (PoC) with big wind producer, using historical data from their 1967MW capacity wind farms.
-
Initiated a strategic partnership with important energy producer in Italy, finalizing a wind production forecasting service contract for 10 wind farms.
-
Developed an initial AI model achieving hourly granular wind production forecasts up to 8 days ahead, updated hourly.
-
Established data pipelines for ingesting satellite imagery from EUMETSAT and NOAA satellites.
-
Created a prototype dashboard for visualizing forecasts and asset performance metrics.
Currently, we are:
-
Refining our AI algorithms to incorporate Atmospheric Motion Vector (AMV) data from satellite observations.
-
Developing the integration layer for real-time sensor data from wind turbines.
Next steps include:
- Launching a beta version of the Wind Sat platform for real-world testing.



