
Objectives of the service
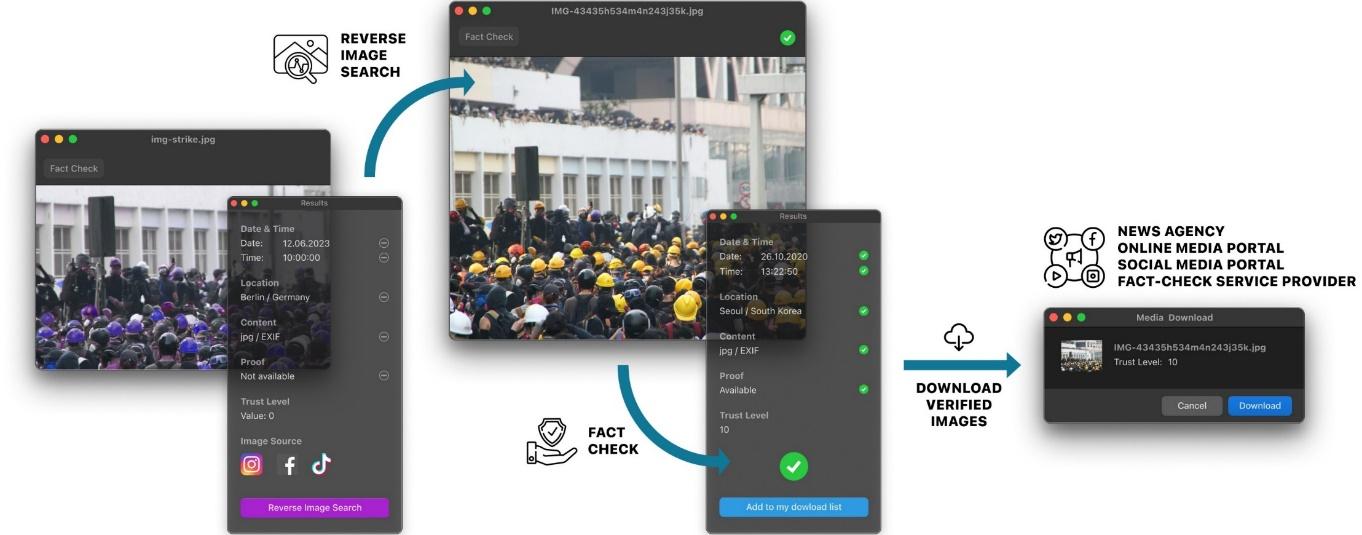
Is this post true or fake? Shall I believe that if there is also a photo or video attached? But when and where was that photo or video taken? Is this even real or just a generative AI content? How can I check? How fact-check service providers, news agencies, online media portals, social media portals can check?
These are common questions nowadays and shows how hard is to find the truth behind a post if it does not come from a trusted source (e.g. contracted photojournalist) but it comes from an untrusted source (e.g. social media).
There are many security attributes that can be used in making such decisions but location and date/time attributes (embedded into photos or videos) are probably the most important ones. And that is exactly the point where GALILEO (EU) has an important advantage related to other Global Navigation Satellite Systems.
The goal of the service is to embed authentic location and date/time attributes into photos and videos and store them as reference sources. These reference sources can be used by news agencies or at fact-checking of social media posts.
Users and their needs
Proving the authenticity of a photo or video gets more important in the era of generative AI. If such authentic information is embedded, it saves time for fact-checking and the content of the content provider (e.g. photojournalist, influencer) can be easier approved. These contents can be used by online media portals with higher confidentiality. And also, readers of these online media portals can be sure that they get authentic news. So, the beneficiaries of such service can be all the:
-
content providers (photojournalists, influencers, anyone who creates photos or videos),
-
content verifiers (fact-check service providers, news agencies, online media portals, social media portals),
-
content consumers (readers, citizens).
Recognizing disinformation is always important but three topics are highlighted by experts where spreading disinformation is intensively used in order to influence readers:
-
elections (in campaign period),
-
war (to support or not a crisis),
-
pandemic (COVID vaccination).
Service/ system concept
The service has four modules:
-
user management: to register&verify user (perform a KYC of the content provider based on EU-compliant eIDAS ecosystem);
-
protected metadata processing: to create&store content (embed all security attributes at the creation of the photo, using a special camera application) and to find&verify content (perform signature verification on GALILEO/OSNMA raw data and on overall protection layer);
-
reverse image search: to find&verify content (based on perceptual hash and steganography technologies);
-
correlation analysis: to analyse context (based on natural language processing, large language model, retrieval augmented generation, computer vision technologies).
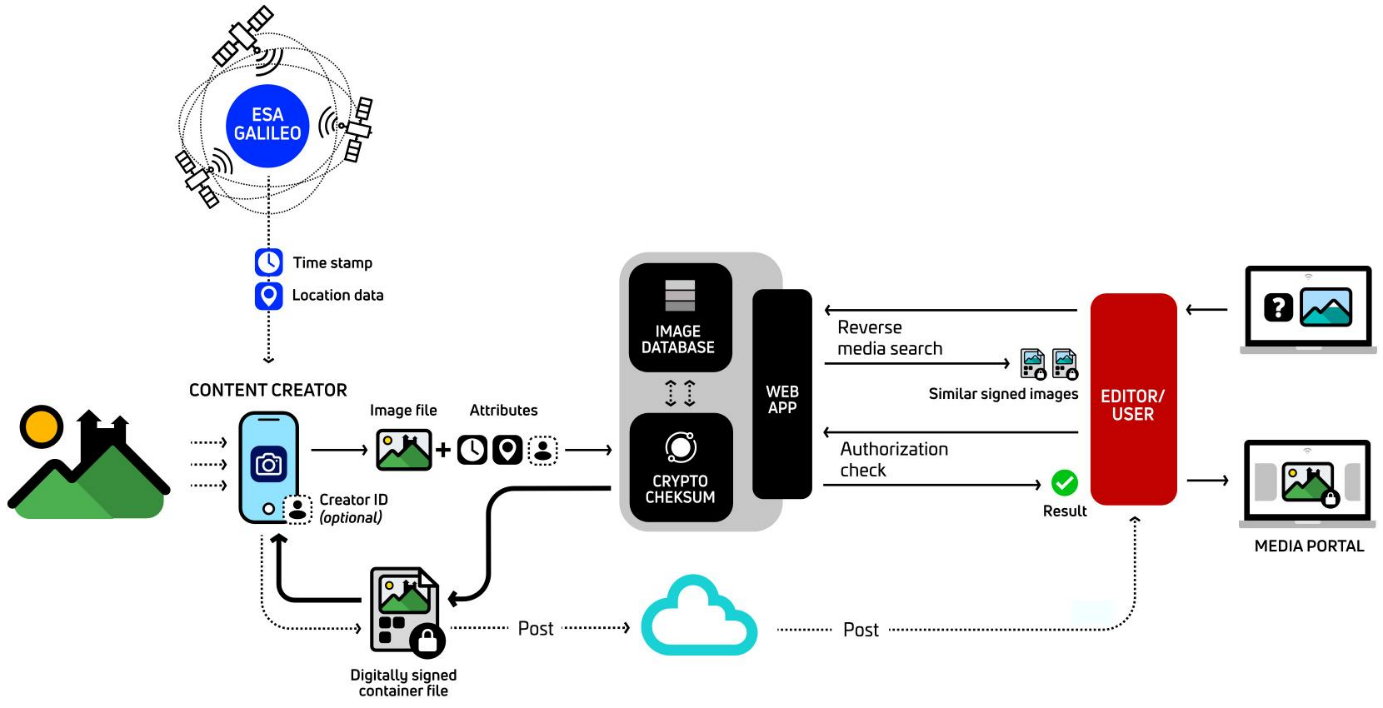
These modules can support various scenarios based on the verification request type:
-
the protected photo is uploaded and just security attributes (location and date/time) shall be verified;
-
the modified photo is uploaded and first the reference photo shall be identified in order to get security attributes (location and date/time);
-
the textual content is also uploaded together with the photo in order to verify security attributes of the photo (location and date/time) and their occurrence in the text.
As it can be seen, the prerequisite of every scenario is the existence of security attributes (location and date/time), embedded as raw data of GALILEO/OSNMA layer.
Space Added Value
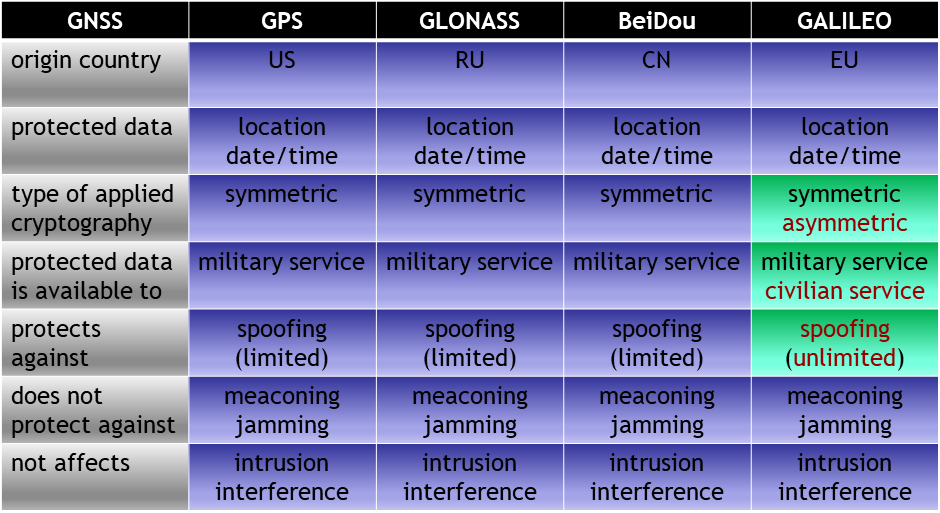
The broadcasted raw data of GALILEO/OSNMA is signed by the system. This signature is based on asymmetric key cryptography which means that anybody can verify the authenticity of the protected data. In this case, not just military services but also civilian services can verify location and date/time security attributes. This a real advantage compared to other GNSS services such as GPS, GLONASS or BeiDou.
The verifiability of such security attributes is a key factor for gaining protection against spoofing attacks, either they are performed by externally (HackRF SDR device) or internally (FakeGPS Free Android application).
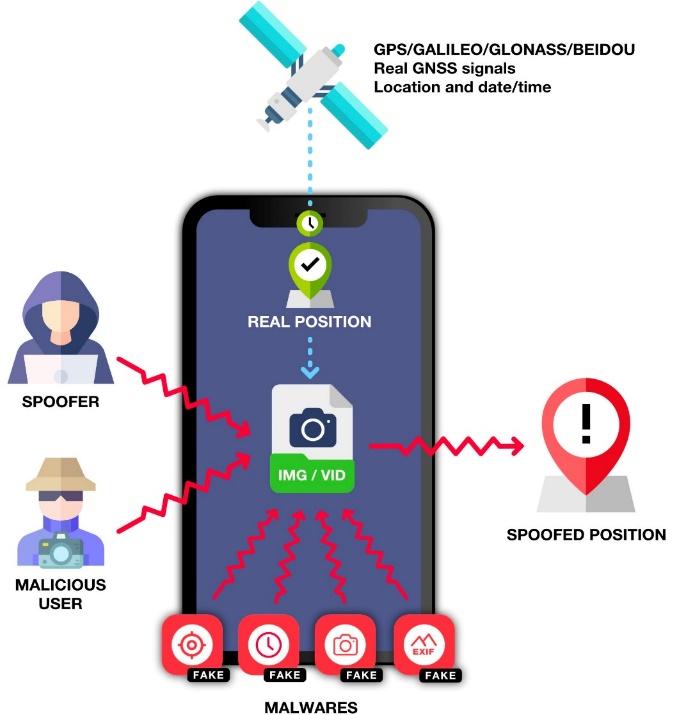
If all the broadcasted data chunks of GALILEO/OSNMA (and signal receiving timestamps) are gathered and embedded into EXIF tag (MakerNote and UserComment) of a photo, anyone else could verify where and when the photo was taken.
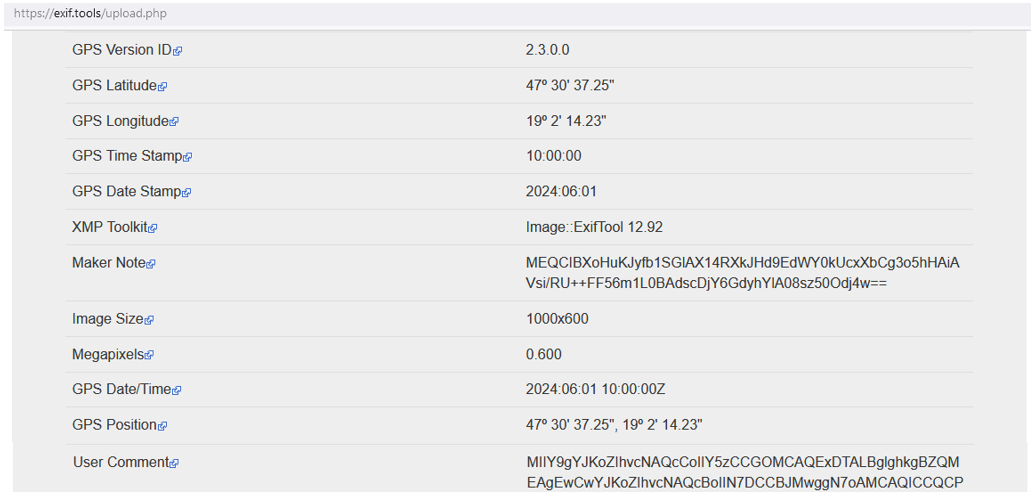
Based on this key feature, the designed, complex fact-checking service (with reverse image search and correlation analysis) can be implemented.
Current Status
Currently, processing GALILEO/OSNMA data is supported (protected metadata processing) and some base operation of reverse image search is in testing phase (ResNet, DenseNet, GoogLeNet convolutional neural networks have been set and Koch, Bruyndonckx, Dugad steganography algorithms are applied). For the user management function, the eIDAS-compliant EUDIWallet of E-Group is available in production environment since April, 2024.



