ESA is seeking promising business ideas for new service concepts that are empowered by Moonlight's lunar communication and navigation services and that address the needs of final customers in the lunar environment or down on Earth – as well as related short-term business opportunities.
Returning to the Moon
Teams of space agencies and private organisations across the globe plan to return to the Moon. Many of the proposed lunar missions will require reliable navigation and telecommunication capabilities. Building these capabilities independently would be inefficient and costly due to complex, recurrent developments.
ESA is elaborating how best to facilitate this exploration. As part of Moonlight, the Agency is encouraging European space companies to develop lunar telecommunications and navigation services. Having infrastructure dedicated to lunar telecommunications and navigation could reduce design complexity, liberating missions to concentrate on their core activities and make each individual mission more cost-efficient while increasing the return on investment.
Moonlight Lunar Communications and Navigation Services
Moonlight aims to establish a suite of both communication and navigation services on the Moon.
To develop and operate the corresponding infrastructure, ESA invited space firms to create such lunar services.
Moonlight will offer a range of lunar communication and navigation capabilities for integration into innovative businesses models with applications on the lunar surface and on Earth. The following capabilities could unlock business opportunities for entrepreneurs of the lunar economy:

Lunar Communication Services
Capabilities of future lunar communication services may include:
- Data Transfer: bulk data transfer between two user assets located anywhere within the defined lunar service coverage or on Earth; not intended for real time needs.
- Data Streaming: real-time audio and video bi-directional streaming between two user assets located anywhere within the defined lunar service coverage or on Earth; could satisfy time-sensitive user needs.
- Tele-operations: real-time streaming service, specifically intended for the real time operation of lunar assets (e.g., rover operations, deployment of structures, experiments requiring asset manipulation); encompasses telemetry/telecommand real-time channel and streaming channel for visual and audio.
Lunar Navigation Services
Capabilities of future lunar navigation services may include:
- Absolute Position: obtaining the absolute position in real-time (e.g., for georeferencing, navigation applications)
- Absolute Velocity: determining the absolute velocity in real-time (e.g., for mobility or monitoring applications)
- Universal Time: real-time determination of accurate time; for example, synchronised with Earth Coordinated Universal Time.
- Post-Processing Position, Navigation, Timing Service: included capabilities to provide much more accurate enhanced post-processing-time position, navigation, and timing services.
- Lunar Surface Augmentation Services: local lunar surface augmentation services (for example, via surface beacon stations) could provide very accurate enhanced position, navigation, and timing for the local service area.
Application Areas supporting a sustainable Lunar Presence
Towards the development of a sustainable lunar economy, a plethora of business opportunities is enabled by lunar communication and navigation services. These are expected to initially focus on the establishment of a presence on the Moon’s surface before commercialising lunar data and exploiting in-situ resources.
Electricity
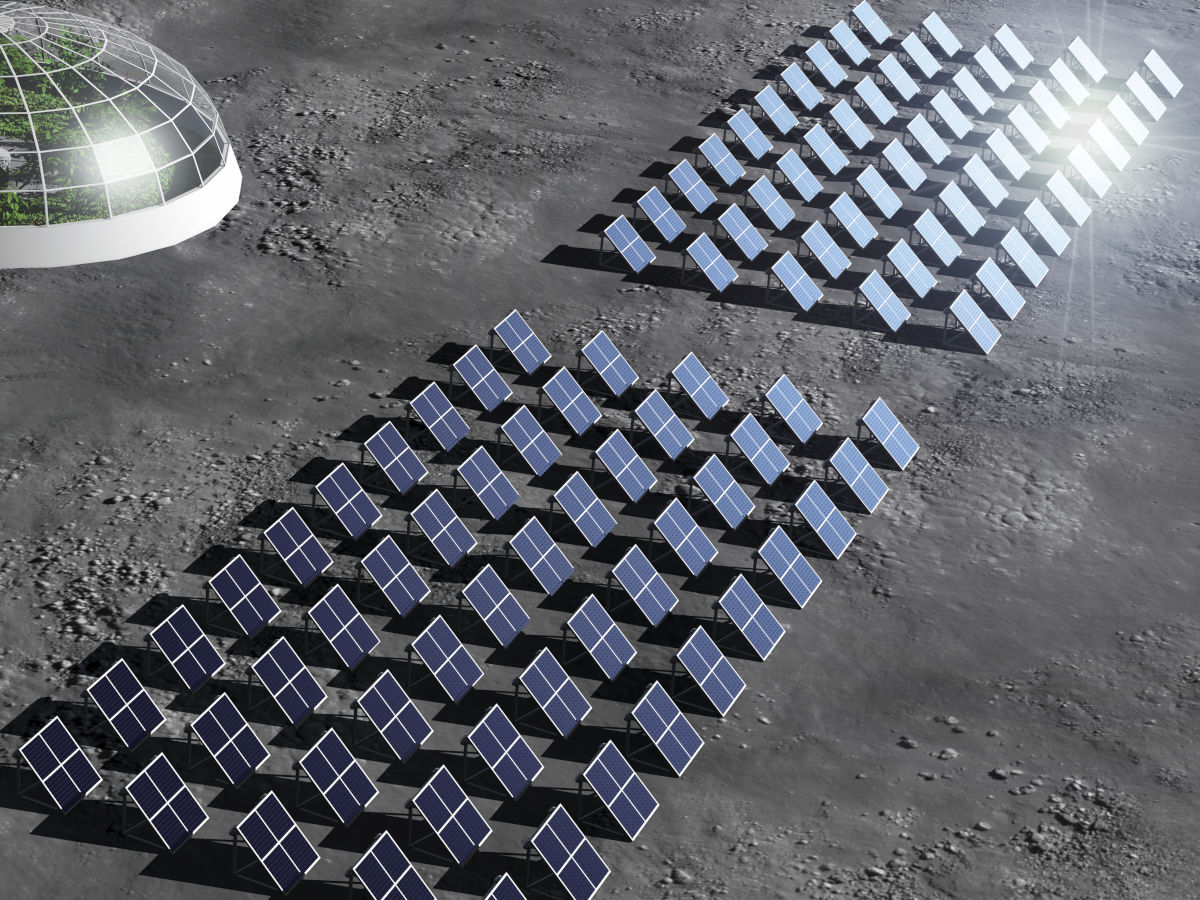
Generation of electricity, for example, via solar cells. Its storage in fixed or mobile batteries. And its distribution towards energy users, for example, via power grids, energy supply vehicles and fuel stations, interconnected in a smart Internet of Things like lunar network.
Water, Hydrogen, Oxygen
Water enables a variety of industrial processes and supports a sustainable human presence on the Moon. The prospecting, extraction, storage, and distribution of water will be important tasks. Water can be transformed into oxygen and hydrogen for life support and fuel.
Construction & Manufacturing
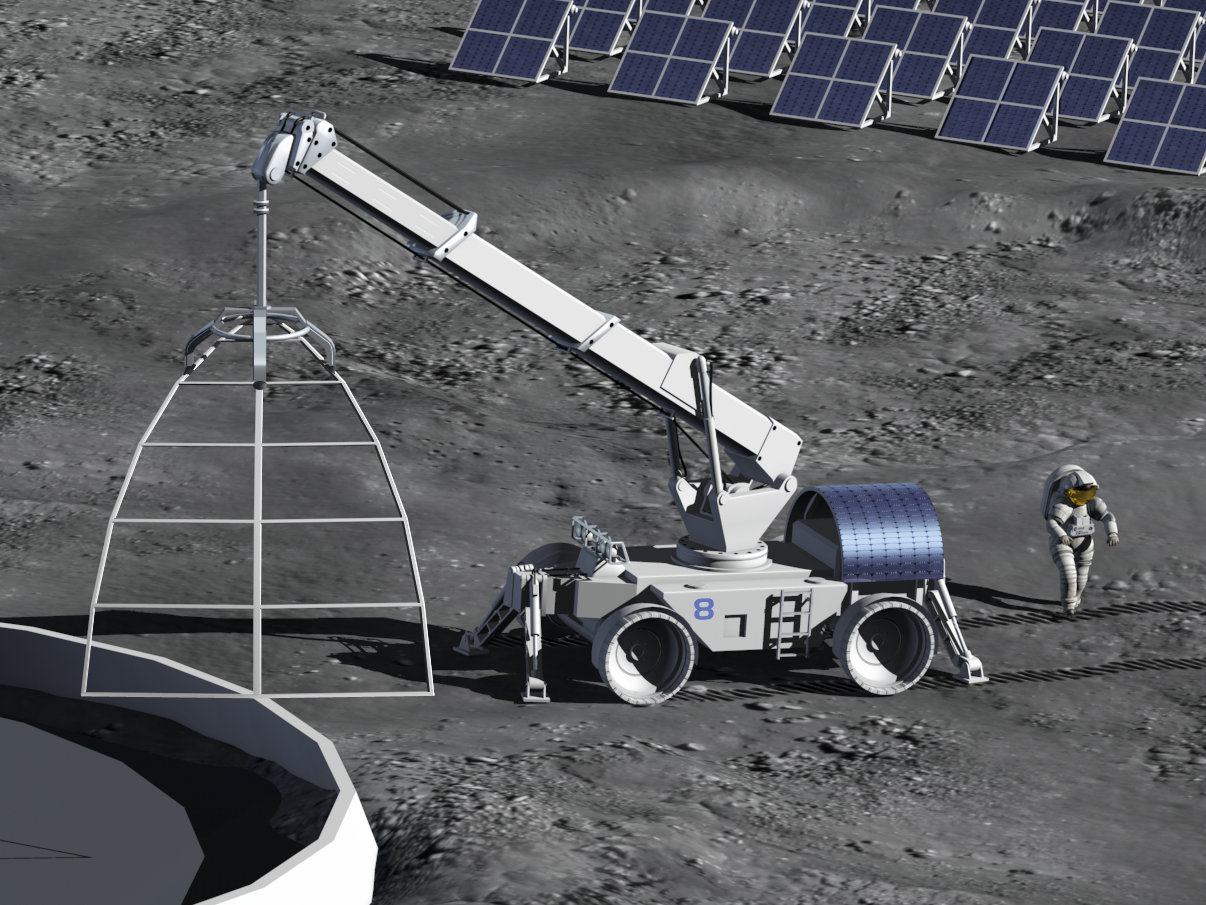

Roads, habitats, machinery parts, and other building blocks will likely be required for a permanent lunar presence. Lunar soil, regolith, is one of the lunar resources that might be used as a material for construction or for extracting elements such as metals.
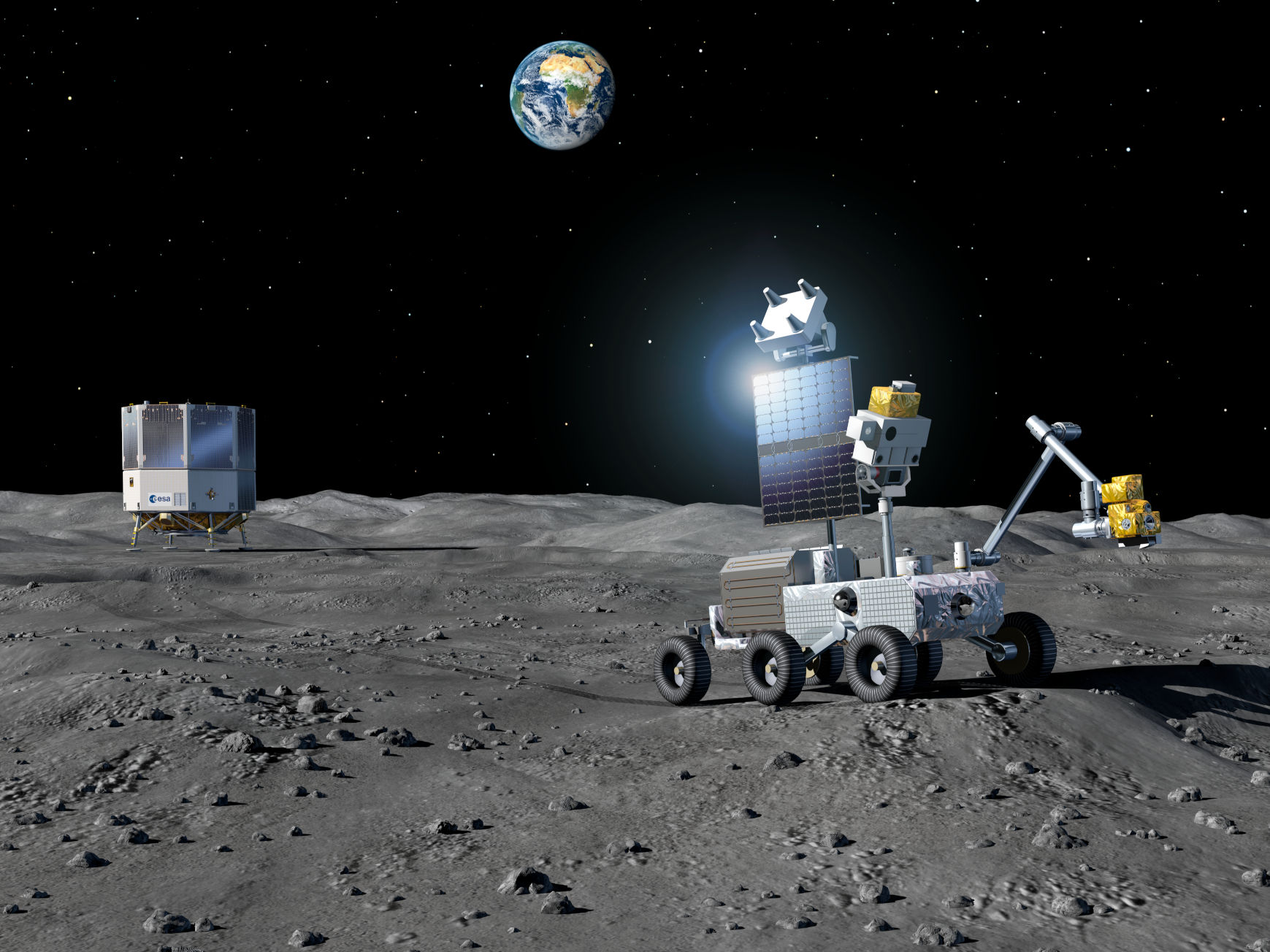
Transport & Logistics
Transport and logistics services connecting different actors on the lunar surface that may require the storage, exchange, and transport of resources, goods as well as mobility services for humans.
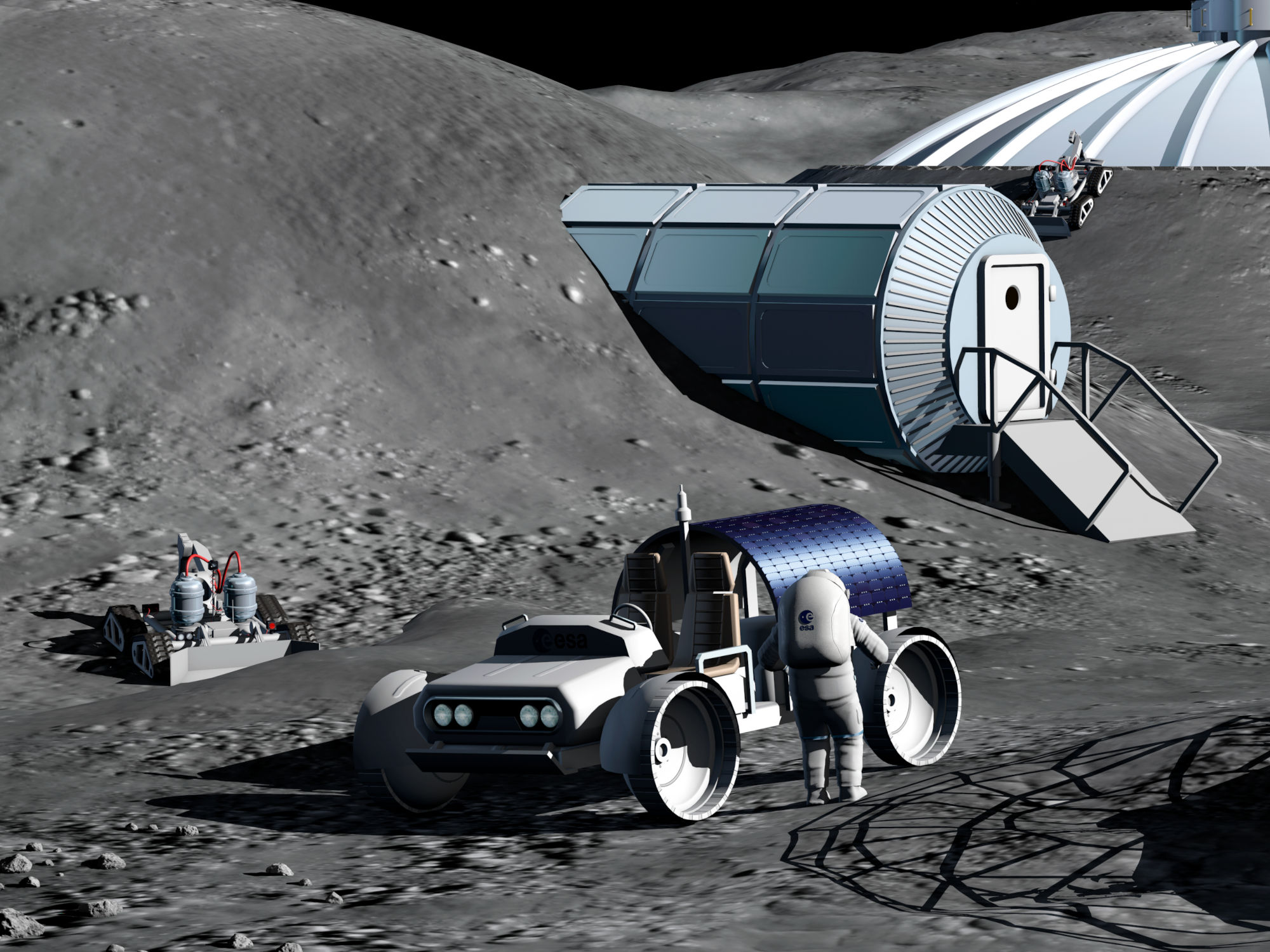
Habitation
Habitation protecting humans from the harsh conditions in space, such as large temperature differences, lack of oxygen, impacts, radiation, or dust, to support the long term presence of humans on the Moon.
Food & Waste Management
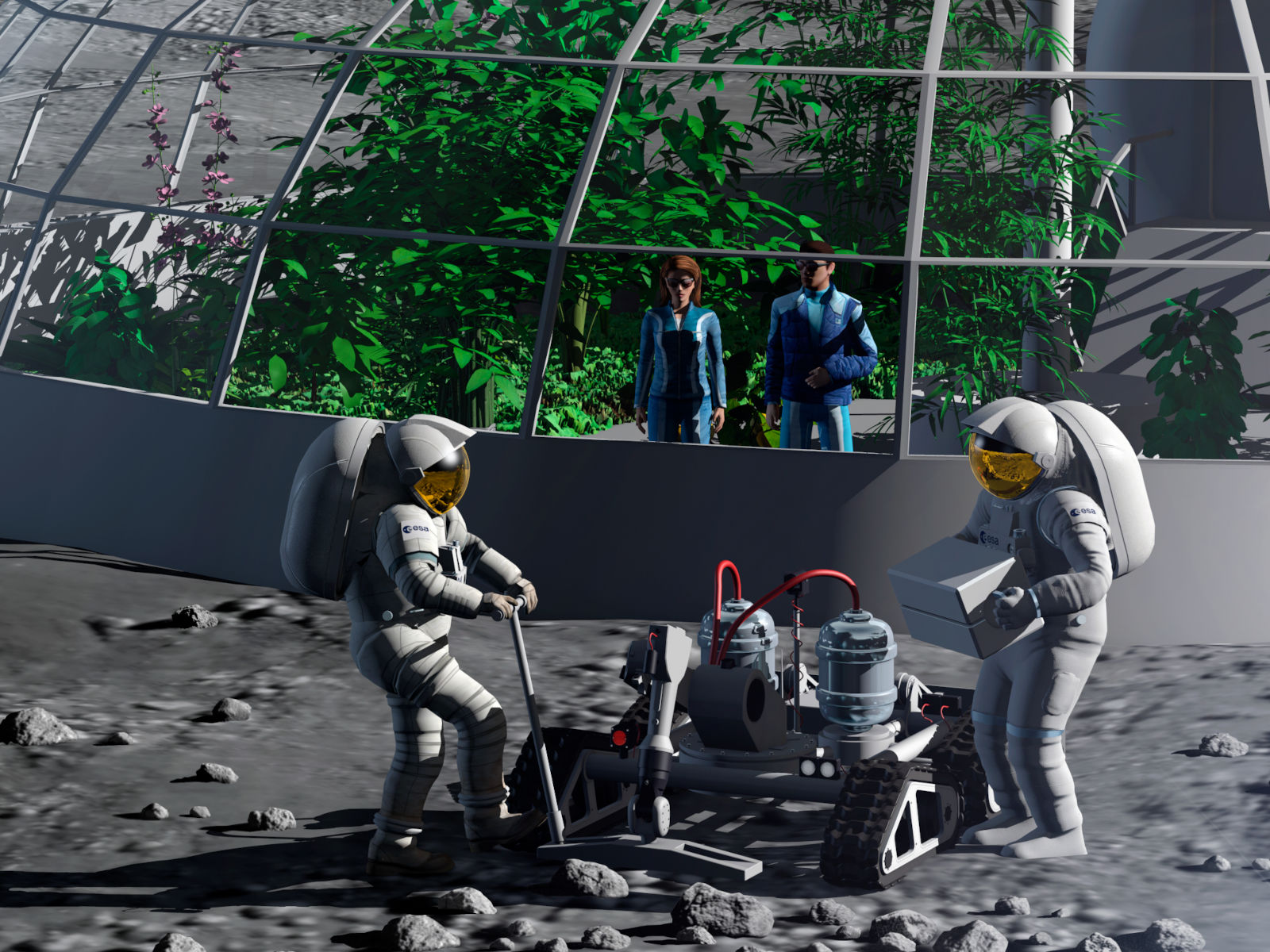

Food production and the effective management of scarce resources contribute to enabling a human presence on the Moon and support life.
Health
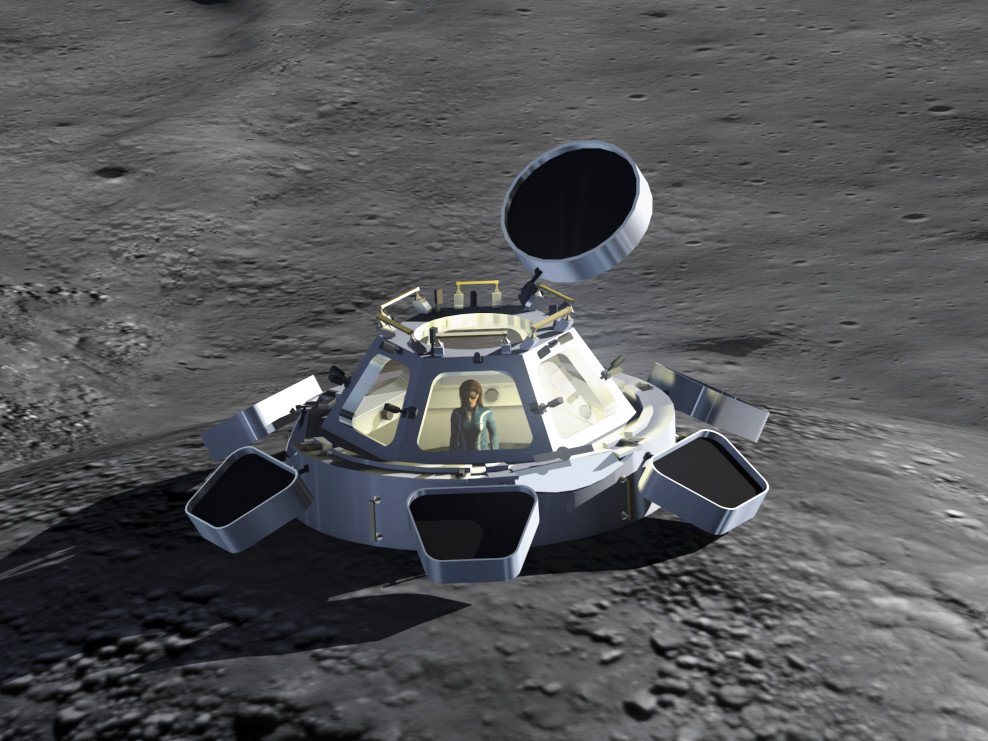

Monitoring and preserving the health of lunar inhabitants with the help of lunar or terrestrial medical teams. Assisted or robotic tele-surgery. Search and rescue operations.
Entertainment & Education
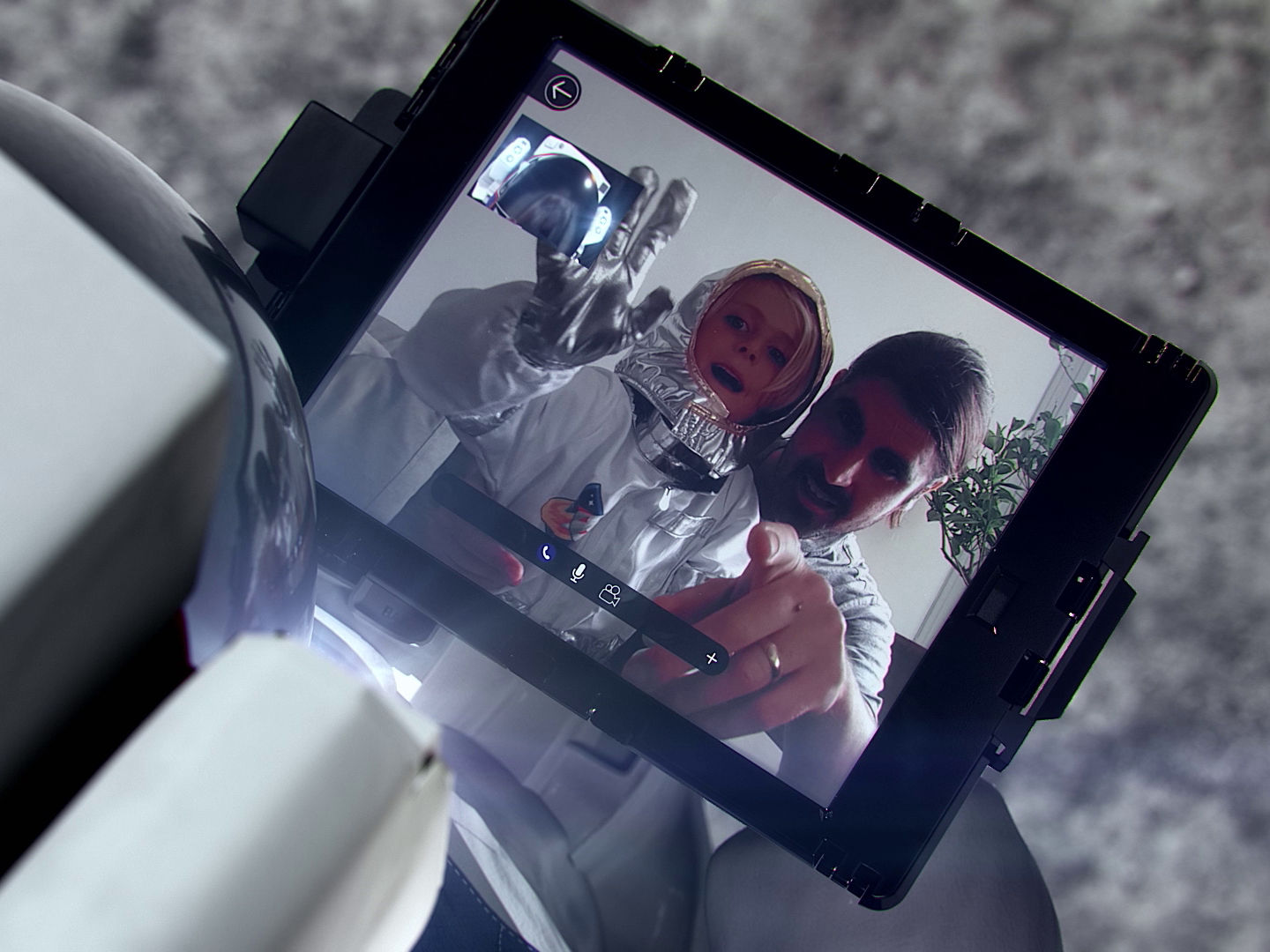

Entertainment and education services to empower both lunar inhabitants and audiences on Earth and to connect astronauts on the Moon with families, friends, and colleagues on Earth. From virtual and augmented reality services to luxury tourism.
Smart Infrastructure
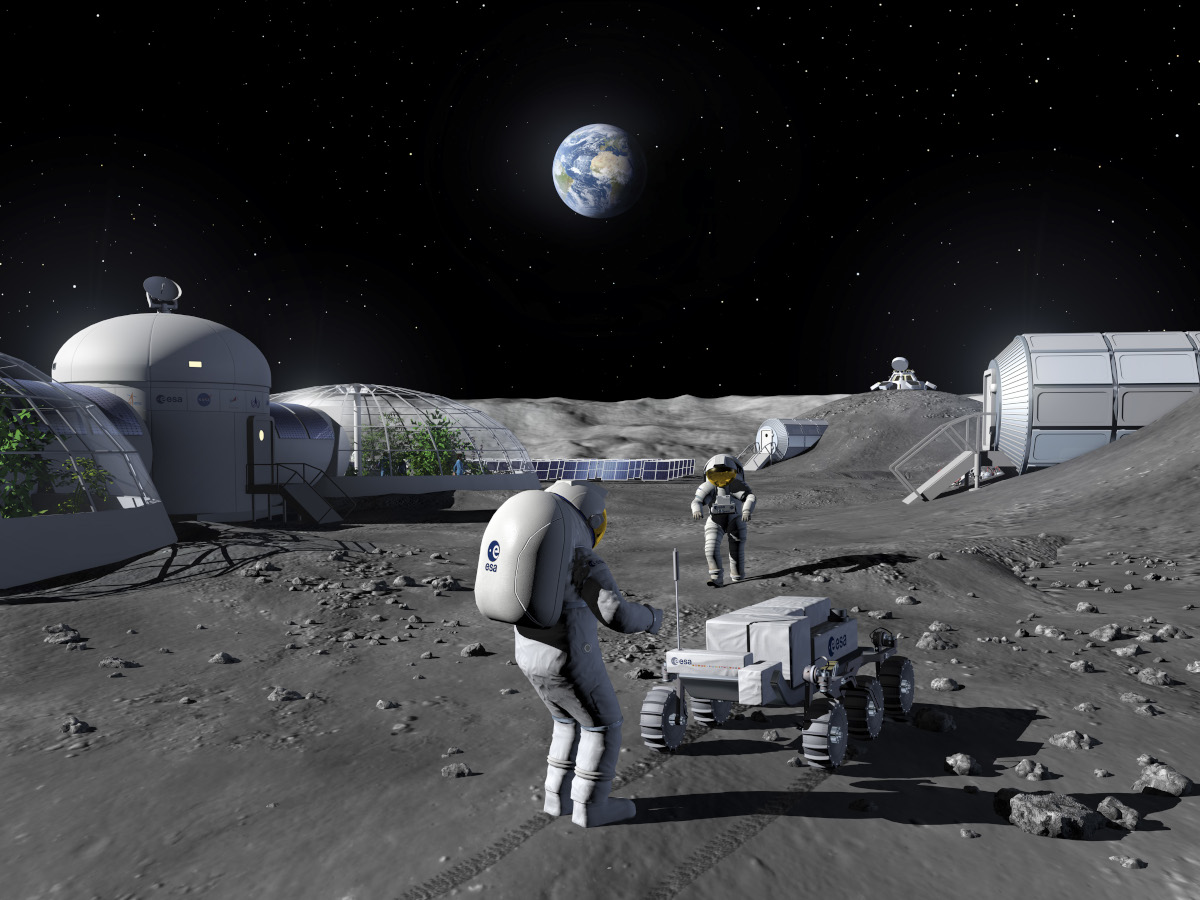

Connecting, automating, and remotely maintaining lunar infrastructure to reduce time, human exposure, and associated risks.
Legal & Regulations, Safety & Security
Support services, such as insurance services, to help reduce risks and resolve incidents.
Other Areas
These application areas are merely an initial subset to inspire conversations about the many needs that might benefit from lunar communication and navigation services and potential business opportunities.
Business Opportunities
More than 400 missions are forecast to launch to the Moon between 2022 and 2032, including scientific, robotic, and human crewed missions (source: NSR). The capabilities enabled by the Moonlight communication and navigation services as well as the diverse application areas that could be addressed exploiting these services open up opportunities for innovative business models. Initial ideas for use cases of lunar communication and navigation were pitched at ESA Space for Inspiration 2022 and the Agency is looking for further business ideas to help develop the lunar economy.
What We Offer*
For selected business ideas, we intend to offer Enabling Studies for the development and assessment of new end-to-end business concepts and lunar economy applications that benefit from Moonlight's communication or navigation services and that address the needs of potential paying customers.
- Zero-equity funding of up to 200,000 Euro per study
- Personal ESA consultant
- Technical & commercial guidance
- Access to our network of partners
- Credibility of the ESA brand
* Subject to internal approvals, terms and conditions.
The envisaged scope of each study will include, but is not limited to, the
- development and maturation of business cases including operational end-to-end service concepts enabled by lunar communication and navigation services
- assessment of the desirability by potential customers, of the technical feasibility, and of the commercial viability of these business cases
- proof of concepts on ground to test critical assumptions regarding desirability by customers, feasibility, and viability of the proposed service
- preparation of a roadmap for the implementation and commercial rollout of the operational service
What We Look For
ESA is looking for entrepreneurs with promising business ideas that would benefit from Moonlight's lunar communications and navigation services and which address relevant needs of downstream customers/users on the lunar surface and down on Earth. This includes:
- Attractive market opportunities and customer/user engagement
- Commercially viable service concepts
- Technically feasible solutions
- Added value of Moonlight's lunar communications or navigation services
- Motivated teams with business and domain expertise
- Terrestrial business model profitable in the short term until the lunar business materialises
Relevant customer/user communities include lunar users that benefit from Moonlight-enabled services, terrestrial service providers, and terrestrial end-customers/users.

How to Apply
To be eligible for funding, your team must be based in one of the participating ESA member states, as indicated in the official tender package. To date, these are 🇦🇹 Austria, 🇧🇪 Belgium, 🇨🇿 Czech Republic, 🇩🇰 Denmark, 🇪🇪 Estonia, 🇫🇮 Finland, 🇫🇷 France, 🇩🇪 Germany, 🇭🇺 Hungary, 🇮🇪 Ireland, 🇮🇹 Italy, 🇱🇹 Lithuania, 🇱🇺 Luxembourg, 🇳🇴 Norway, 🇵🇱 Poland, 🇵🇹 Portugal, 🇷🇴 Romania, 🇸🇮 Slovenia, 🇸🇪 Sweden, 🇨🇭 Switzerland, and the 🇬🇧 United Kingdom. Authorisation of Funding letters from the corresponding National Delegations are required as part of the application. Teams can involve entities outside participating member states, but their contribution to the activity cannot be funded by ESA.
- Register your team on esa-star Registration today. If your team is made up of more than one organisation, each entity will need to register.
- Download the official tender documents from esa-star Publication (Tender Action Number 1-11607). This includes a letter of invitation, statement of work, proposal template, and additional information about this opportunity.
- Prepare your proposal using the official tender documents and reach out to your National Delegation to obtain a Letter of Authorisation.
- Submit your proposal via esa-star Tendering by the deadline.



