On this page
SPACE FOR LAND MOBILITY
Mobilising space technology for sustainable terrestrial transportation solutions
Road transportation and logistics play an integral role in our society, with both passenger and freight volumes on the rise around the world.
Transport is responsible for about 25% of the EU’s total CO2 emissions, with road transport representing the greatest share of this (72.3% in 2022) .
As the sector looks towards more sustainable alternatives, especially around emissions reduction, electric and autonomous vehicles, innovative traffic control measures, just-in-time supply chains and better public transport systems, space technology has an important role to play.
Vision
ESA is committed to using space to protect our planet and combat the effects of climate change. ESA supports solutions that help to increase the adoption and accessibility of electric vehicles (EVs) and alternative fuels, improve infrastructure and services, and facilitate greener logistics management both in urban and rural areas.
Focus Areas
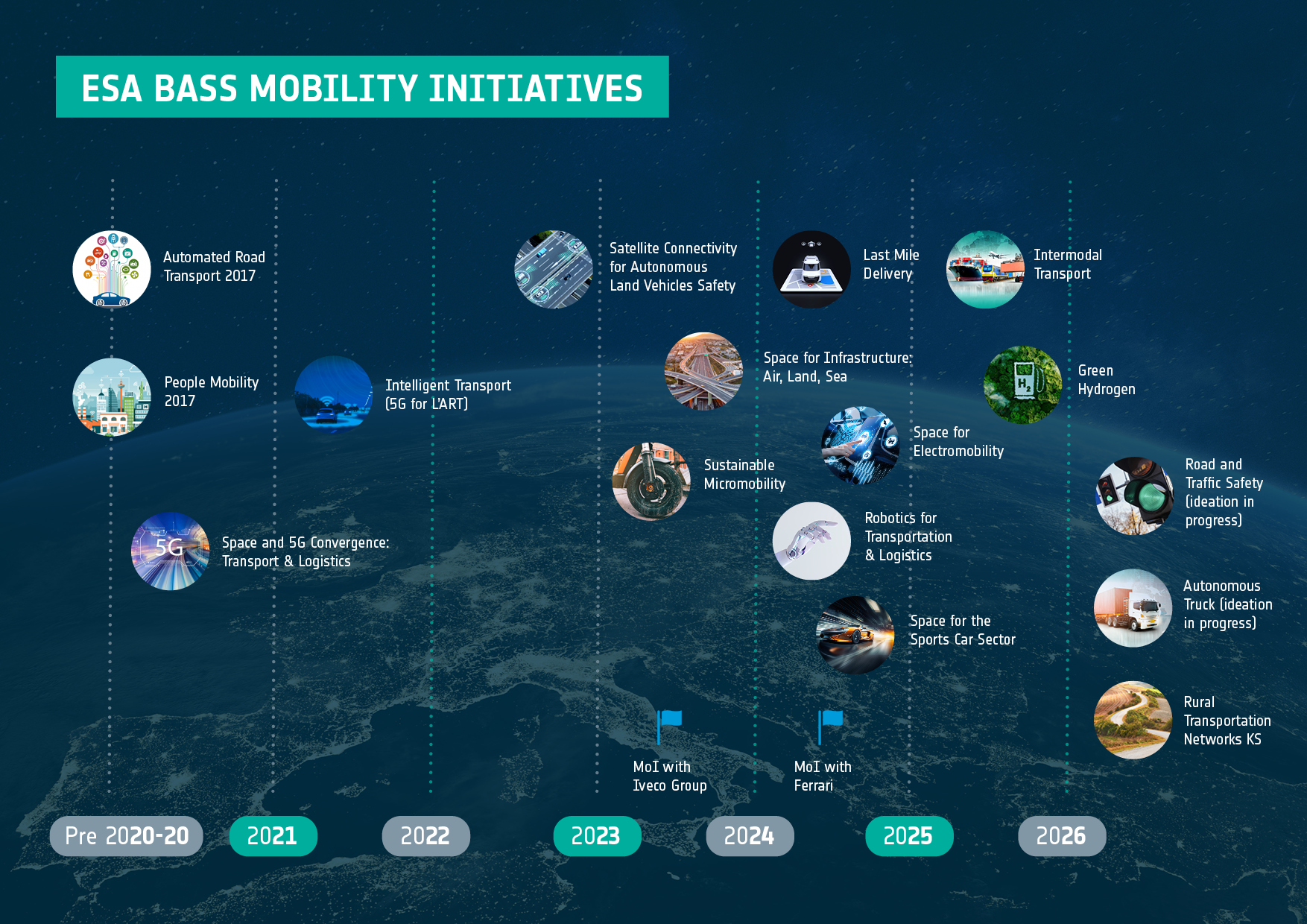
With the sector facing multiple challenges, there is an urgent need to find innovative and sustainable solutions across the road mobility landscape.
ESA's Business Applications and Space Solutions programme (BASS) has identified several key focus areas for the road mobility sector.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Value of Space
|
|
Satellite Communications (Satcom)Satcom plays a crucial role in the management and capabilities of all types of transport enterprises, from urban drones and traffic management to long-haul trucking. Communication is always key for effective and secure management of goods, vehicles, and other logistics. Improving and ensuring connectivity in environments that have inadequate, unreliable, compromised, or absent mobile cellular connectivity are needed to guarantee reliable use for a variety of logistic and mobility services. For example, this could be significant for services involving autonomous long-haul transportation. New developments in satellite communications, such as Low-Earth Orbit (LEO) Broadband satellite constellations, can enable certain services where reliable and secure connectivity is currently lacking. Satellite connectivity can also play a crucial role in the signalling of critical situations for passenger vehicles, such as SOS alerts, breakdowns, accidents, break-ins, or car theft in remote or low connectivity areas. |
|
|
Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS)Technologies such as GNSS can enable innovative applications for the tracking and tracing of vehicles and goods through precise positioning, navigation, and timing. For road mobility, satellite positioning can assist with:
Augmentation of GNSS can offer higher positioning accuracies via systems such as Galileo HAS (High Accuracy Service), RTK (Real-Time Kinematic) and others, with the selection dependent on the service requirements. |
|
|
Satellite Earth Observation (SatEO)SatEO data can be used to monitor and assess environmental conditions. Through land monitoring, SatEO can assess variables such as emissions, land use, topography, weather, accessibility and environmental data. By combining insights from space-based sources such as satellite imagery and remote sensing with data collected from in-situ sensors, organisations can assess emissions with enhanced precision and reliability. Data can also be used to monitor compliance of supplier operations with environmental standards and policies. Earth observation can achieve these, for example, by:
|
Socio-economic impact
Developing more sustainable transport solutions can provide us with safer and more efficient ways of moving people and goods. ESA BASS has supported many projects which have contributed to the transition to sustainable transportation whilst fostering commercial success.
Mobility Initiatives