
Objectives of the service
DeFROST is a near real-time snow monitoring service for energy companies willing to improve water availability forecasting from snow melt. The service has the ability of providing digital snow maps and data daily at 20m resolution, easily integrable in current hydrology distributed and semi-distributed models.
Energy companies have lots of uncertainty when trying to forecast water availability in Spring when snow melts, because of the difficulty in getting accurate and precise snow data. With DeFROST being plugged to their water forecasting models, they will reduce this uncertainty having actual data on the amount snow in their catchment areas, bringing efficiency to their energy production processes and reducing their operational costs.
Based on the combination of satellite, weather and ground data, DeFROST provides daily, observable, homogenous snow cover and snow depth data of catchment areas, to support Energy companies in making hydropower energy more cost effective and remove dependencies with field work or hardware, used for snow data recall.
Users and their needs
This solution is addressed mainly to Energy companies providing actual snow data on their region of interest (catchment areas) to help in operational management of their reservoirs and dams.
The users require:
- Fast and easy access to near-real-time data on snow metrics such as snow cover and snow depth.
- Daily snow data with a spatial resolution of 20 meters.
- An ability to integrate this data in their water forecasting models.
- Historical snow data to train their hydrology models.
The targeted users’ main countries are Switzerland, France, Spain and Canada.
Service/ system concept
DeFROST automatically delivers daily updated information with global coverage on:
- Daily snow cover (20 meters spatial resolution), by combining and processing near real-time satellite data and weather nowcasts
- Snow depth based on ground stations and meteorological models.
- Validation system based in Switzerland, with high resolution cameras to understand the precision on the delivered data.
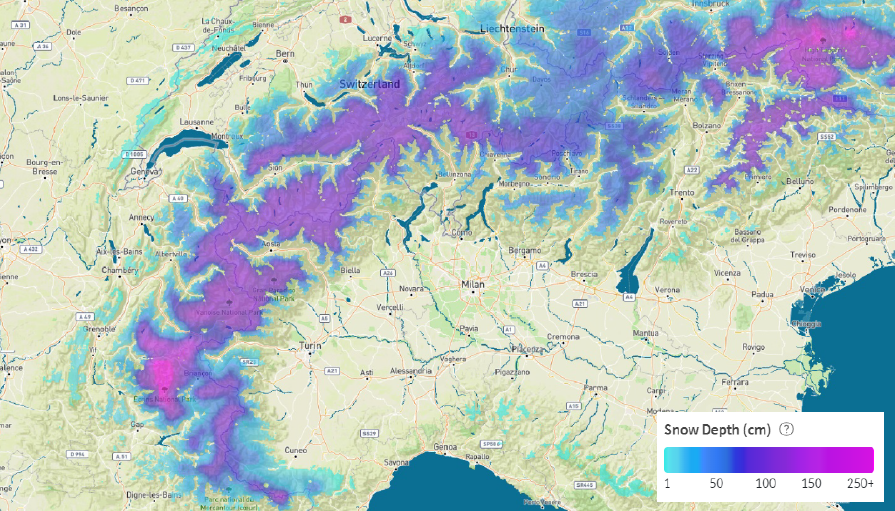
Users benefit from:
- Accurate and integrable snow data to directly plug in their water inflow forecasting models.
- Historical snow data to help train their models
- Finally helping them increase the precision in their water inflow forecasting capabilities from 80% to 95%.
The technology powering this use case is explained in more detail on the schema below:

Space Added Value
The space assets used for the snow cover products include Earth observation data from the European Sentinel family, including all automatically available Sentinel-2 and Sentinel-1 data. Furthermore, NASA’s operating VIIRS as well as both MODIS Aqua and Terra sensors are included. To account for areas with persistent cloud cover over prolonged periods, we exploit probabilistic logic and weather nowcasts (ICON, GFS) to predict the likelihood of snow cover beneath and account for the snow depth metric. With persistent cloud cover together with the probabilistic logic and weather nowcast the system includes Sentinel-1 SAR data to overcome the cloud mask problem.
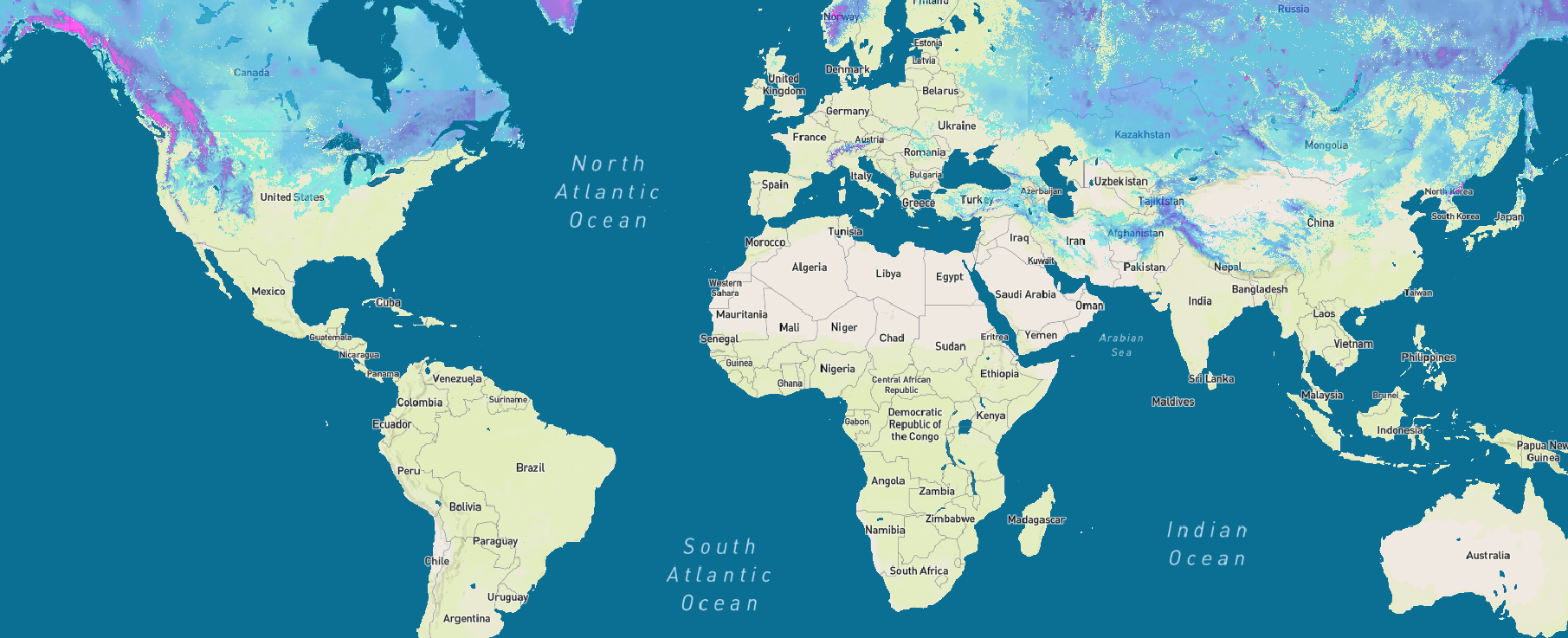
This procedure, generating daily global maps on snow cover and depth, outranks currently available methods used in the Energy Industry in terms of scale, reliability and complexity. It is the combined ability of harnessing satellite data in a high spatial, temporal and spectral resolution on a global scale during variable weather conditions, which makes this space asset indispensable – while its smart combination with geo-positioned ground data and weather nowcasts completes any potential data gap.
Current Status
The “DeFROST for Hydropower” project is a continuation of the Demonstration Project “DeFROST”, which started in March 2019 and finished in March 2020.
“DeFROST for Hydropower” started on 1July 2020. The pilot phase with two hydropower energy providers and the related hydrology organisations started on the 26 September 2020 and finished during January 2021.
The WeGaw team passed successfully the Final Review in January 2021 and is currently servicing the customers that took part in this project, helping them to reduce water inflow forecasting errors and to optimize clean energy trading and generation.
In terms of additional functionalities, WeGaw will continue investing in the product development of DeFROST to achieve remote sensing based operational Snow Water Equivalent (SWE) for hydropower.



