Portable 3D imaging technology reaches key milestones
 ESA-backed innovation announces FDA clearance and live clinical trials in the UK.
ESA-backed innovation announces FDA clearance and live clinical trials in the UK.
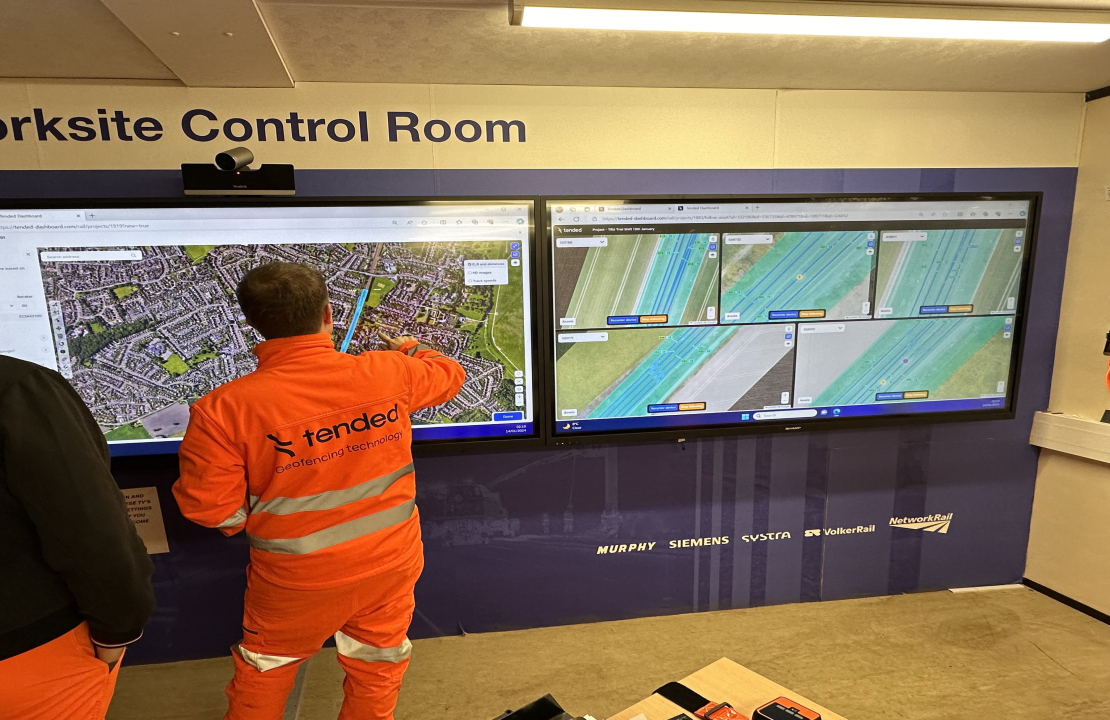
UK-based company Adaptix, who developed a pioneering portable 3D X-ray imaging system with support from ESA’s Business Applications and Space Solutions (BASS) programme and the UK Space Agency, has announced two major milestones: FDA 510(k) clearance for its Adaptix Ortho350 Imaging System and the start of live clinical trials on patients at the Royal Devon University Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust in Exeter.
The Adaptix Ortho350 system delivers high-quality, low-dose 3D imaging for orthopaedic applications. It enables clinicians to obtain a stack of detailed diagnostic slices through the patient with a far higher level of accuracy than 2D X-rays. Unlike CT scanners it is a portable solution which is particularly beneficial in remote or resource-limited settings, reducing delays and improving access to care.
The recent FDA clearance marks a critical step towards commercial deployment in the United States, validating the system’s safety and effectiveness. Meanwhile, clinical trials in Exeter are assessing its real-world performance, focusing on workflow efficiency and patient outcomes.
“This achievement demonstrates how space-derived technologies can deliver tangible benefits on Earth,” said Arnaud Runge, Technical Officer for ESA on the project. “We are very pleased to have supported this project from the early days and to see it achieve commercial and technical success across multiple markets. The low radiation dose and compactness of the system also mean we could even see Adaptix Ortho350 used in space in the future.”
Dr Paul Bate, CEO of the UK Space Agency said: “This progress shows the impact of collaboration between space and healthcare in driving innovation. By applying techniques originally developed for space, Adaptix is helping clinicians access faster, safer and more accurate diagnostics, directly benefiting patients and improving recovery pathways. We’re proud to have supported this journey through our partnership with ESA and look forward to seeing this technology improve patient outcomes across the UK and beyond.”
Sarah Small, CEO at Adaptix, said: “Securing this FDA 510(k) clearance represents a significant milestone for Adaptix in our mission to transform radiology. We already have a great deal of interest from healthcare providers and clinicians and are looking forward to delivering “3D-First” enhanced orthopaedic DT imaging across Primary Care, Intensive Care and Emergency Departments throughout the US and beyond.”
Adaptix’s imaging technology grew out of methods originally developed for space applications, ensuring compliance with stringent healthcare standards while maintaining portability and cost-effectiveness. It is already in use across the veterinary and non-destructive testing sectors and has also delivered positive results in human cadaver trials. The trial in Exeter is focusing on patients with inflammatory arthritis and will evaluate the performance of the Adaptix 3D imaging technology when compared to traditional 2D X-rays, focusing on three main areas: diagnostic potential, effective measurement of joint space and evaluation of bone density.
“Up to 30% of people with early rheumatoid arthritis are missed when diagnosed using 2D X-rays, but more-detailed 3D imaging – such as MRI and CT scans – is expensive and waiting lists can be long,” said Dr. Siân Phillips, Chief Medical Officer at Adaptix. “The compact design and lower radiation and power requirements of the Adaptix Ortho350 make 3D imaging much more accessible for clinicians and patients alike. These new trials mark an exciting new stage of our journey, not only delivering a clinical assessment of its effectiveness when compared to traditional 2D X-ray modalities, but also proves our range of clinical use cases from diagnostics to assessing disease progression.”
With regulatory approval secured and clinical trials underway, Adaptix is now preparing for commercial rollout in the US, paving the way for a new era of accessible diagnostic imaging worldwide. Looking ahead, CE marking for the system is also in progress, opening the door for commercialisation across Europe in 2026.









 Workplace transport is typically fragmented, inefficient and costly. UK company
Workplace transport is typically fragmented, inefficient and costly. UK company  The pilot activity demonstrated that this service can provide more than 75% of patient transport for the participating departments, equating to over 900 rides a month. In addition, their two dedicated electric vehicles saved 24 tonnes of CO₂ across the year, contributing to NHS targets to reduce emissions by 80% by 2032.
The pilot activity demonstrated that this service can provide more than 75% of patient transport for the participating departments, equating to over 900 rides a month. In addition, their two dedicated electric vehicles saved 24 tonnes of CO₂ across the year, contributing to NHS targets to reduce emissions by 80% by 2032. “What has space got to do with agriculture?” – a commonly-asked question, according to Rita Rinaldo, Head of Applications Projects and Studies Division at ESA, speaking in London this week as part of the
“What has space got to do with agriculture?” – a commonly-asked question, according to Rita Rinaldo, Head of Applications Projects and Studies Division at ESA, speaking in London this week as part of the 
 Climate change is leading to an unprecedented increase in extreme rainfall events and flooding. Between 2014 and 2023, flood losses across the Nordic regions have increased by 22% and 54% of these losses have been caused by extreme rainfall, causing a challenging situation for insurance companies and policyholders. Norwegian company
Climate change is leading to an unprecedented increase in extreme rainfall events and flooding. Between 2014 and 2023, flood losses across the Nordic regions have increased by 22% and 54% of these losses have been caused by extreme rainfall, causing a challenging situation for insurance companies and policyholders. Norwegian company 


