Putting Galileo in the driving seat for autonomous vehicles
Accurate positioning is vital for autonomous vehicles. Now, a new sensor using Galileo’s GNSS signals will provide exactly that, thanks to an international collaboration between Deimos Engenharia and Accurision, fostered by ESA Space Solutions network.
Automated and autonomous driving depend heavily on different sensor technologies incorporated into the vehicle's sensor fusion engine. For positioning, it’s important to have a range of different technologies for redundancy reasons, including Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS), which provides absolute positioning based on radio signals to complement visual sensors like cameras.
A partnership between Portuguese space specialist company Deimos Engenharia and Austrian start-up Accurision has created a highly accurate positioning sensor using Europe’s Galileo GNSS system. Galileo provides world-class navigation, offering a natural solution for terrestrial applications, such as sensors for autonomous driving but moving from an initial idea to a practical solution is a complex process.
Spotting potential and spreading the news

In 2013, Instituto Pedro Nunes (IPN), ESA Space Solutions Centre in Portugal identified Deimos Engenharia’s GNSS receiver as having exciting potential applications on Earth. Developed specifically for the Galileo GNSS system, it relies on radio signals to better determine a user’s position and time. As a result, the technology was shared across the ESA Technology Broker Network in 16 countries.
Deimos Engenharia had been studying potential applications of this technology, including in unmanned aerial vehicles, for some time. “We wanted to make the most of the unique features of the Galileo system, which is why we decided to develop our own receiver. We needed to master the receiver technology and have full control at its deepest level to develop the product and integrate it in advanced navigation solutions,” remarks Deimos Engenharia Director Nuno Ávila.
Around the same time, Brimatech, an ESA Technology Broker in Austrian, met an entrepreneur searching for high precision satellite-based positioning sensors for autonomous driving.
“Within three weeks of meeting Accurision’s CEO Gunnar Fleisch at a conference, we had eight technology suggestions for him, pre-checked by our ESA network partners. That was impressive!” remembers Brimatech’s Andrea Kurz.

From the proposed space technologies offered, it was the Portuguese GNSS receiver from Deimos Engenharia that best suited the application. "Accurision's product approach is to be 'as robust as possible, as accurate as required'," mentions Gunnar Fleisch, Co-founder and CEO of Accurision.
Accurision is now using the Deimos solution to develop the GUIDANCE™ GNSS Sensor ASIC for autonomous driving. This takes advantage of one of the world’s most advanced civil GNSS signal, Galileo E5 AltBOC, to provide unparalleled robustness while achieving the required precision in dynamic rural and urban environments necessary for autonomous driving. It also features an integrated ionospheric delay estimation engine (IDEE), integrated interference detection and a mitigation engine (IDME) to further improve overall performance.
Accurision’s key aims with the new sensor are robustness, integrity, accuracy and precision. GUIDANCE will be ready to support the upcoming Galileo E6 High Accuracy Service, which will be available free of charge from late this year.
The complexity of brokering technology transfers
Making this international cooperation happen involved considerable effort. IPN and Brimatech brokered the first meeting between the two parties and supported them to agree and sign a technology transfer agreement, enabling future downstream technical developments.

“Technology transfer is an elaborate activity,” explains Carlos Cerqueira, IPN’s Innovation Director. “Its cornerstone is the fit between technology and market requirements, but in the end what it takes is an excellent relationship with all parties, the ability to spot a need, find a matching offer and get the timing right. With Deimos, it was no different. It took time, but substantial economic impact is just about to happen.”
The partnership between Deimos Engenharia and Accurision teams is a clear example of the power of ESA’s ‘behind the scenes’ network and how a united European approach to space is fundamental to fostering the economies and societies through space technology. In future there will be autonomous vehicles relying on Galileo’s GNSS via the GUIDANCE™ GNSS Sensor ASIC, based on a patent jointly owned by the two companies for their Galileo Code Sensor – all thanks to the far-sightedness and hard work of ESA Space Solutions partners network. To further foster this technology transfer, Accurision received the support of the ESA Business Incubation Centre (ESA BIC) in Austria, where it was incubated. “It is our mission to support ground-breaking business ideas, building on existing European high-quality space capacity,” says Martin Mössler, Managing Director of Science Park Graz, General Manager of ESA BIC Austria.
ABOUT ESA SPACE SOLUTIONS
ESA Space Solutions is the go-to-place for great business ideas involving space in all areas of society and economy. Our mission is to support entrepreneurs in Europe in the development of business using satellite applications and space technology to improve everyday life. Our programme is designed to provide multiple entry points such as ESA Business Incubation Centres (ESA BICs), ESA Technology Broker Network, and ESA Business Applications programme. Funding typically ranges from 50KEuro to 2MEuro and supports everything from space technology transfer, early stage incubation programs, Feasibility Studies to large-scale Demonstration Projects.
FATMAP – new features for leading outdoor platform

Getting out in the fresh air is more ‘in’ than ever this year, and with FATMAP’s adventure platform, activities in the Great Outdoors have never been easier to plan. With the support of ESA Space Solutions, FATMAP have now added some crucial ‘live data’ enhanced features, which take the application to new heights.
“Better, safer adventures”, FATMAP have boasted since they launched the world's most advanced 3D outdoor map. This adventure platform for web and mobile means hikers, skiers, mountain bikers and trail runners can plan the perfect route, equip themselves like a professional, and then record and share their adventures with the community.
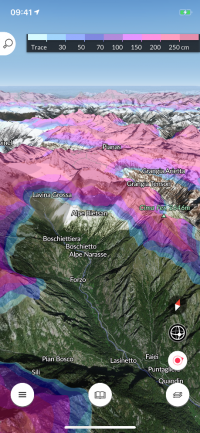
“Whilst explorers of old needed extreme amounts of preparation or often simply strode blindly into the wilderness - at FATMAP we have brought together cutting-edge technologies and local experts to make adventures simpler and safer,” says Marcel Düe, Chief of Staff at FATMAP.
Now with the support of ESA Space Solutions, detailed and contextual live information has been added to the app.
Live Lift and Piste status, Snow Coverage and WebCam
“Having up-to-date data in the palm of your hand even if you don’t have Internet connectivity can make a critical difference in enjoying an exhilarating but safe adventure,” says Francesco Feliciani, Head of the Companies-Led Projects Section at ESA. “The team have made use of a range of satellite data to create new features including game-changing real-time snow conditions such as snow depth, fresh snow and snow forecasts as well as live resort status updates including which lifts and pistes are open or closed.
“I myself am a ski enthusiast and use FATMAP, which has literally saved me a number of times from being stranded at the end of the day in some remote corner of a ski resort I was exploring with my friends.”
The app makes use of data from Earth observation satellites (such as radar-based and high-resolution imagery) to provide the rich digital terrain and surface models producing 3D images as well as the computational mapping overlays including gradient, aspect, flat zones and distance mapping.
“Knowing in advance the type of terrain and conditions helps beginners as well as experienced individuals to plan – making adventures accessible to those who are not experts in reading traditional maps or in the local geography,” says Düe. “Webcams are an easy way to get a rough idea of current conditions”.
The mobile platform allows users to preload the heaviest data chunks. This ensures that an adventurer who is already outdoors only has to download a small percentage of the overall dataset in order to have access to the most up-to-date information, displayed in a rich 3D context.
Challenges and data engineering
Adding these live features was not without hurdles as the team had to obtain access to local data and then harmonise different data sets in coverage in order to update both the cycle and display. “Ultimately the aim was to be able to offer a consistent user experience based on inconsistent and sparse data. Thanks to ESA’s support we have achieved this,” says Düe.
Future plans for the global FATMAP platform include the incorporation of more data sets with easier ways for users to contribute; to be rolled out in 2021.
ESA and SBIC Noordwijk celebrate new 6-year incubation contract
The European Space Agency (ESA) and the Netherlands Space Office have announced a 6-year extension to the contract for SBIC Noordwijk to manage the ESA Noordwijk Business Incubation Centre (ESA BIC). The incubation programme for space-based businesses in the Netherlands will continue to be run by SBIC Noordwijk until at least 2026.
ESA BIC Noordwijk was ESA’s first Business Incubation Centre. Established in 2003, the ESA BIC programme has helped over 120 start-ups in the Netherlands, and over 800 across Europe, to integrate the use of space technology into their businesses. The programme in the Netherlands has been managed by SBIC Noordwijk since 2011.

Fostering innovation in the space industry
Matthew Edwards, Business Incubation Officer, ESA Space Solutions, said: “We are very pleased to extend our activities with ESA BIC Noordwijk. By 2026, over 150 space-related start-ups in the Netherlands will have received support through ESA BIC Noordwijk and its partners. This is a fantastic number for a relatively small country and demonstrates the value added to the local and national economy by such programmes.”
The extension of the contract will see SBIC Noordwijk managing the programme in the Netherlands for a minimum of 15 years in total.
“We are delighted with the trust and support we get from both the Netherlands Space Office and ESA to continue the all-round support for space-based businesses in the Netherlands,” declared Martijn Leinweber, COO of SBIC Noordwijk.
“With their help, we can maintain our reputation as the go-to place for start-ups and innovative companies, and be their guide in both the Dutch and international space communities.”
“With that in mind, our next steps will be to show the greater impact of space business in general, to inspire those seeking a career as an entrepreneur in the world of space, and to create an even stronger Dutch space start-up community.”
Create impact on Earth
The ESA BIC programme is one of the many ways ESA and local space organisations (in this case, the Netherlands Space Office) have an impact on Earth. By creating businesses through technology transfer, by using an ESA patent, or working with any space-based technologies, such as Earth observation data or satellite navigation, numerous jobs – and an international network of innovative start-ups – have been, and continue to be created.
There are currently 21 ESA BICs in Europe, each managed by a country-specific third party to ensure local needs are met and local skills and experience are identified and fostered. For the Netherlands, SBIC Noordwijk offers businesses support for every stage of their entrepreneurial journey through business programmes, workshops and relevant events. Businesses incubated at ESA BIC Noordwijk benefit from its location on the Space Campus Noordwijk alongside ESA’s ESTEC R&D centre and many other key players from the space industry.

Niels Eldering, Section Head at ESA Space Solutions, said: “The ESA BIC programme has, through the years, successfully enabled many technology transfers. With the continuation of the programme in Noordwijk, we can once again demonstrate what’s possible when you combine the worlds of space and entrepreneurship. A lot of innovative power on Earth is space based, and we need the world to see that.”
"There's a massive potential in developing a wide array of new businesses with space technology and satellite data. The development of smallsats for IoT or Earth observation services for monitoring urban green areas are great recent examples of this. We have a lot of creative bright minds in our country who are able to develop new revenue models with this approach", says director of the Netherlands Space Office, Harm van de Wetering. "That's why we want to give start-ups with good ideas the opportunity to further develop their business plan."
ABOUT ESA SPACE SOLUTIONS
ESA Space Solutions is the go-to-place for great business ideas involving space in all areas of society and economy. Our mission is to support entrepreneurs in Europe in the development of business using satellite applications and space technology to improve everyday life. Our programme is designed to provide multiple entry points such as ESA Business Incubation Centres (ESA BICs), ESA Technology Broker Network, and ESA Business Applications programme. Funding typically ranges from 50KEuro to 2MEuro and supports everything from space technology transfer, early stage incubation programs, Feasibility Studies to large-scale Demonstration Projects.
ukowapi UG (haftungsbeschränkt)
Robert-Bosch-Straße 7
64293 Darmstadt
Germany
The Convex Lens
Media Cube, IADT Dun Laoghaire, Kill Avenue.
Dun Laoghaire
Ireland
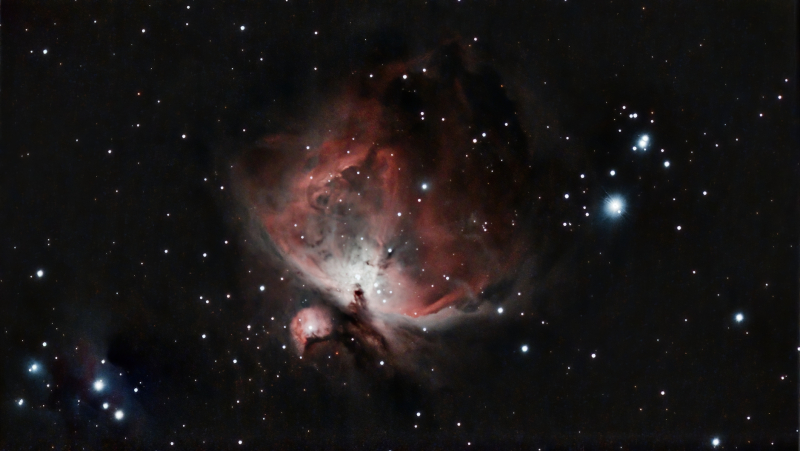
Vaonis raises $2.5 million for affordable smart telescope
A graduate of ESA’s Business Incubation Centre (ESA BIC) in South France, Vaonis has raised over $2.5 million for its newly-announced hybrid between a smart telescope and a camera. Designed to be the world’s most compact consumer smart telescope and positioned at an entry-level price, Vespera is the start-up’s second commercial product and sees it bidding for a prominent position in the world of amateur astronomy.

During the current health crisis, sales of astronomical instruments have surged due to a combination of people spending more time at home, limitations on travel and a desire for a return to nature. Vaonis, a start-up that specialises in the production of astronomical instruments, has seen orders of its flagship telescope Stellina (Italian for ‘little star’) more than double since the beginning of the first national lockdowns early in 2020, along with similar growth in the number of photos shared by Stellina owners.
The company’s ambition is to revolutionise the world of amateur astronomy by making it accessible to all. Now it has announced its second product, Vespera, which is a miniaturised version of Stellina aimed at a wider audience. “The team at ESA BIC Sud France helped me to turn my idea, a smart consumer telescope/camera hybrid, into a real product that is now used all over the world by hundreds of space lovers. They helped us to finance its initial development and contributed to the geolocation technology that the smart telescope requires to operate properly”, says Cyril Dupuy, founder of Vaonis.

Small, smart and social
Weighing less than 5 kg and measuring 40x20x9 cm, Stellina's little brother Vespera combines high precision optics, electronics and mechanics, plus a patented autonomous image processing algorithm. It is designed to cater for newcomers to stargazing, thanks to its ease of use and mobile app. Once the telescope is set up, users can observe the night sky’s hidden gems, including galaxies and nebulae, on their smartphone screens and then share their photos on social media.
In addition to being the smallest smart telescope in the world, Vespera is the only such instrument to offer a shared and interactive stargazing experience, with a multi-user mode that supports up to five users.

Fundraising for future finance
Today, Vaonis has 15 staff and expects a turnover of €1.5 million in 2020 – double that of 2019. Its famous fans include American astronauts Scott Kelly and Terry Virts.Vaonis was founded by Cyril Dupuy in 2016 and hosted at ESA Business Incubation Centre (ESA BIC) South France for two years. Its initial product was Stellina, which was the first observation station to allow anyone to photograph celestial objects at the touch of a button. This won several awards, including a CES Innovation Award in 2018 and a Red Dot Design Award in 2019. In 2018, Stellina was selected for inclusion in New York’s Museum of Modern Art’s MOMA Design Store. In order to finance the production chain of its new creation, Vaonis opted to use the Kickstarter crowdfunding platform. This raised $2 559 952 from 2163 backers in October 2020, far exceeding its target of $1 million. Deliveries are expected during the Christmas holidays in late 2021.
ABOUT ESA SPACE SOLUTIONS
ESA Space Solutions is the go-to-place for great business ideas involving space in all areas of society and economy. Our mission is to support entrepreneurs in Europe in the development of business using satellite applications and space technology to improve everyday life. Our programme is designed to provide multiple entry points such as ESA Business Incubation Centres (ESA BICs), ESA Technology Broker Network, and ESA Business Applications programme. Funding typically ranges from 50KEuro to 2MEuro and supports everything from space technology transfer, early stage incubation programs, Feasibility Studies to large-scale Demonstration Projects.




